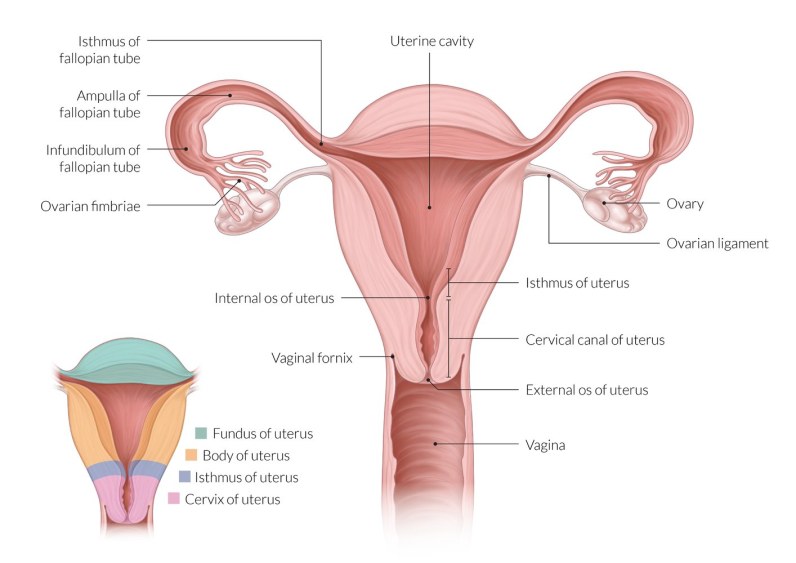
Uterus
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ, situated obliquely in the lesser pelvis between the urinary bladder below and in front and the rectum, sigmoid colon above and behind.
Subdivision
Divided into three parts from above downwards
| Fundus |
| Body- extends from the fundus to a constriction known as the isthmus which corresponds with the internal os of the cervical canal. |
| Cervix- lies below the isthmus and is subdivided by the vaginal wall into supravaginal and vaginal parts. |
Axes of Uterus - It prevents the prolapse of the uterus into the vagina.
| Anteversion - It is a forward angle between the axis of the cervix and that of the vagina measuring about 90°provided the urinary bladder and the rectum are empty. |
| Anteflexion - It is a forward angle between the body and the cervix at the isthmus measuring about 125°provided the urinary bladder and the rectum are empty. |
Ligaments of Uterus
| True ligaments- These are fibromuscular and 8 in number. |
| Round ligaments of uterus- 1 pair Mackenrodt's ligament- 1 pair Utero-sacral ligaments - 1 pair Pubo-cervical ligaments- 1 pair |
| False ligaments- They are peritoneal folds and 6 in number. |
| Utero-vesical fold (anterior false ligament) Recto-vaginal fold (posterior false ligament) A pair of recto-uterine folds A pair of broad ligaments. |
Histological Structure of Uterus:
Structure of Fundus and body - From within outwards the uterus presents.
| Endometrium- Consists of surface epithelium and lamina propria. Lining: Before puberty - Lined by Ciliated columnar epithelium After puberty - By simple columnar epithelium. Anatomically the endometrial layer can be subdivided into three zones-. Stratum compactum Stratum spongiosum Stratum basale During Menstruation, Stratum compactum and Stratum spongiosum undergoes shedding. Both layers are together known as Stratum functionalis. Functionally, the endometrium consists of Outer basal layer Inner functional layer |
| Myometrium - Consists of 3 ill-defined layers of smooth muscles Outer longitudinal Middle circular Inner reticular layer |
| Perimetrium - Typical serosa consisting of a single layer of mesothelial cells. |
| Lining of the cervix Supravaginal part- Lined by Simple columnar epithelium. Vaginal part- By stratified squamous epithelium |
Blood Supply of Uterus
| Arterial Supply Chiefly supplied by two uterine arteries Partly supplied by ovarian arteries |
| Venous drainage - The veins correspond to the arteries and drain into the internal iliac vein via the uterine and ovarian veins. |
Nerve Supply of Uterus
Sympathetic- From T12, L1 segments of spinal cord
Parasympathetic- From S2, S3, S4 segments of spinal cord.
DEVELOPMENT (Germ Layer - Mesoderm)
Fundus and body- developed by the fusion of the intermediate horizontal parts of two paramesonephric ducts.
Cervix - Developed from the upper part of the uterovaginal canal.
Ectopic Pregnancy:
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy most often occurs in a fallopian tube, which carries eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. This type of ectopic pregnancy is called a tubal pregnancy.
SITES OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
- Fallopian tube,
- ovary
- abdominal cavity (most frequently in POUCH OF DOUGLAS),
- Internal os of uterus.
| Implantation - the attachment of the fertilized egg or blastocyst to the wall of the uterus at the start of pregnancy. |
| Fertilization -the action or process of fertilizing an egg or a female involving the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote. |
| Ovulation -The release of the ripe egg (ovum) from the ovary. ... Ovulation occurs around 14 or 15 days from the first day of the woman's last menstrual cycle. |
| Menstruation - the process in a woman of discharging blood and other material from the lining of the uterus at intervals of about one lunar month from puberty until menopause, except during pregnancy. |
3 phases of the menstrual cycle
- Proliferative phase- (5th to 14 days)
- Secretory phase- (15th to 28th days)
- Menstrual phase- (1st to 4th days)
Uterus bicornis: A bicornuate uterus, commonly referred to as a "heart-shaped" uterus, is a type of uterine malformation where two horns form at the upper part of the uterus.
Also read: Anatomy Question Collection
Also read: Anatomy Questions & Answers
Also read: Anatomy notes

Comments (0)