Watchman Procedure
What is the watchman procedure?
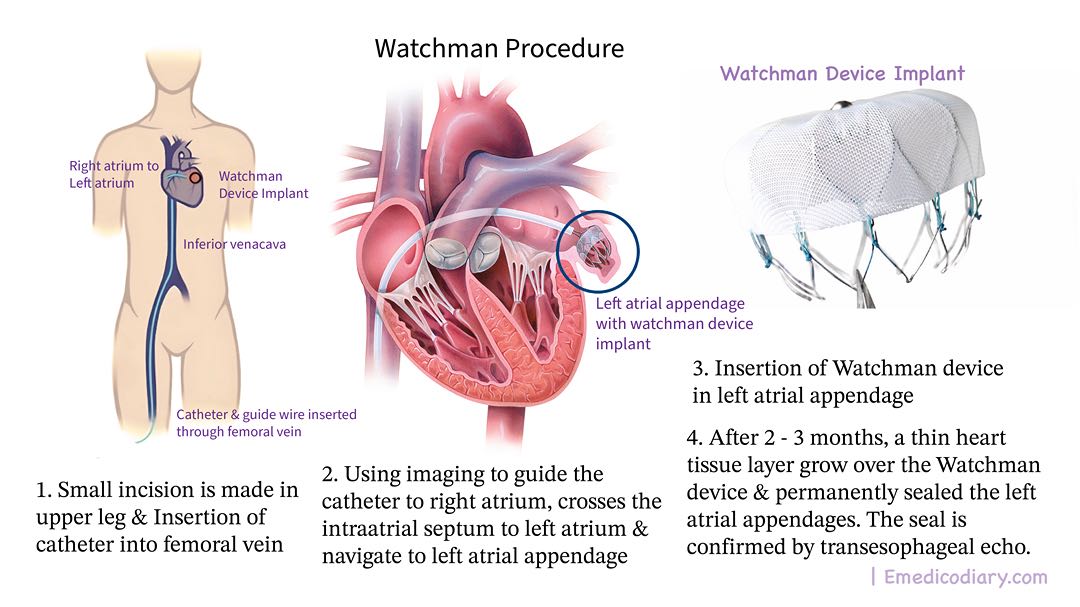
The watchman procedure is a one-time, minimally invasive procedure that lasts for life long and protects against the stroke risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. It is the best FDA-approved procedure alternative to oral anticoagulant therapy. It is performed by the cardiologist in which a small incision is made in the upper leg and guided wire is inserted through the femoral vein to the heart and a watchman device is placed in the left atrial appendages.
In patients who have atrial fibrillation, stroke is one of the dreaded complications due to the high chance of thromboembolism. In most patients, blood thinner (anti-coagulants i.e. dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, etc) is sufficient to reduce the risk of stroke. However, some patients cannot take blood thinner because it causes them to bleed or there is a high risk of bleeding such as patients who fall repeatedly in those patient watchman devices is the only FDA-approved alternative to this medical therapy.
Why does atrial fibrillation increase the risk of stroke?
Atrial fibrillation always comes from the atria which are the top portion of a person's heart. Atria instead of beating and contracting adequately, it is just quivering. It is going so fast and so erratic, it's not pumping blood very well, and blood tends to become stagnant when people had atrial fibrillation which can eventually lead to clots and an increase in the risk of stroke/cerebrovascular accident (CVA). But the main risk of stroke actually comes from very specific areas of the heart. In an area of the heart, and specifically in the left upper chamber of the heart there is a little pocket in the left side of the heart called an appendage where blood tends to become very stagnant leading to clot formation.
What is a Watchman device?
A watchman device is a filter that is placed in the left atrial appendage the area of the heart where strokes most commonly form due to the formation of blood clots.
How does the watchman procedure work?
In patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation over 90% of stroke-causing clots that come from the heart originate in the left atrial appendage. A watchman is designed to permanently close the left atrial appendage preventing those blood clots from escaping.
How will you perform the watchman procedure?
The watchman procedure is performed under general anesthesia and in a catheterization lab using fluoroscopy and transesophageal echo. Using a standard percutaneous technique, the implanting physician inserts a guide wire and vessel dilator into the patient's femoral vein. Then wire ascends upward to the inferior venacava to the right atrium. Then using a standard transseptal access system the physician crosses the interatrial septum to the left atrium. The physician advances the access sheath over the guide wire into the left atrium and navigates into the distal portion of the left atrial appendage over the pigtail catheter. The physician then deploys and releases the watchman device in the left atrial appendage. The watchman device gradually endothelialized completely by the heart's inner layer to permanently seal off the patient left atrial appendage. Typically Watchman procedure takes an hour and the patient hospital stays for 1 day.
Medication after the watchman procedure:
Following the watchman procedure, the patient takes blood thinner (anti-coagulant) for 45 days, and Aspirin plus clopidogrel for the next 6 months. Then only Aspirin can be continued in the ongoing process until the left atrial appendage is adequately sealed/closed off. The seal is confirmed by transoesophageal echo after discontinuing the blood thinner.
How many time does a patient have to come for a follow-up after the watchman procedure?
Follow-up following the watchman procedure should be done at six weeks first, then at six months then yearly.
What are the benefits of the watchman procedure?
The benefits of the watchman procedure are it is a one-time, minimally invasive procedure that lasts for life long and protects against the stroke risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. The watchman device is the best alternative for those who have a high risk of bleeding manifestation associated with long-term use of oral anticoagulants (blood thinner) and offers stroke risk reduction comparable to oral anticoagulants.
Indications of Watchman Procedure
The watchman device is indicated to reduce the risk of thromboembolism from the left atrial appendage in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. The risk assessment of stroke and systemic embolism in atrial fibrillation can be done based on CHA2DS2-VASc scores and is recommended for anticoagulation therapy (blood thinner medication).
Direct-acting oral anticoagulants (eg. dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, etc) have been found to be effective & safer than warfarin for the prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. You can find out more about the Novel Approaches to Preventing Clots in Atrial Fibrillation. Those who have a high risk of stroke and at the same time contraindicated to blood thinner medication (anti-coagulant) should take non-pharmacologic alternatives to anticoagulants for prevention of stroke i.e. Watchman device is the best alternative.
Indication of Watchman Device Implant over Oral Anticoagulants therapy
Watchman device implant is indicated for those who have a high risk of thromboembolism i.e. stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Watchman device implant would be the best alternative over lifelong oral anticoagulant medication for those who possess a high risk of:
- Previous history of major bleeding or any bleeding disorder.
- Future high risk of bleeding or a high risk of falls/accidents.
- Lifestyle or occupation that possesses bleeding risk.
What are the contraindications of the Watchman device/Watchman Procedure?
Watchman device is contraindicated if the intracardiac thrombus is visualized by echocardiographic imaging, an atrial septal defect repair or closure device or a patent foramen ovale repair or closure device is present, the left atrial appendage anatomy will not accommodate a device, or there are contraindications to use of warfarin, aspirin or clopidogrel.
What are the complications of the watchman procedure?
A watchman procedure is an invasive procedure something mechanical in your heart, that you have done in 1% vicinity that includes perforation of the heart, bleeding, dislodging of device, or stroke. The major complications of the watchman procedure are
- Accidental perforation of the heart
- Bleeding
- Dislodge of Watchman device
- Air embolism
- Cardiac tamponade
- Allergic reaction
What is the reason for the watchman procedure?
The watchman procedure is the best alternative procedure for those who have the risk of stroke and are contraindicated to oral anticoagulants in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. It prevents the risk of long-term use of oral anticoagulants (Blood thinners).
Who is a candidate for the Watchman procedure?
Watchman procedure is indicated in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation who have a high risk of stroke. Watchman device is a non-pharmacologic alternative to oral anticoagulants.
Where is the watchman device implanted?
The watchman device is implanted in the left atrial appendage (LAA), a small blind pouch extension of the left atrium of the heart to prevent blood clot formation to reduce the risk of stroke.
Who Cannot take blood thinners (Oral anticoagulants)?
Oral anticoagulants are contraindicated in
- Recent major surgery
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Major trauma
- Previous history of major bleeding
- Bleeding disorders (such as hemophilia)
- Thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet count)
- Stomach ulcers or other issues that up your risk for internal bleeding.

Comments (0)