Cerebellum
5 years ago 6649
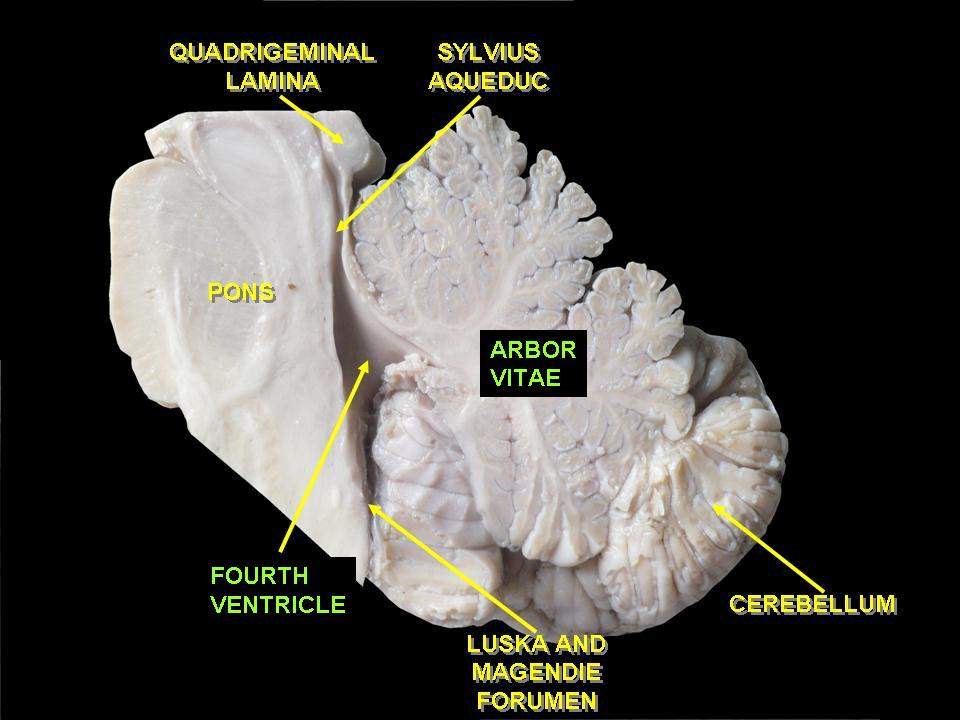
|
Anteriorly:
Fourth ventricle, pons & medulla |
| Posterioinferiorly: Squamous part of occipital bone |
|
Superiorly:
Tentorium cerebelli |
| A horizontal fissure cut the middle lobe into the superior half & inferior half separating the superior surface & inferior surface. |
| Parts of vermis | Subdivision of the cerebellar hemisphere |
| Lingula | ---- |
| Central lobule | Ala |
| Culmen | Quadrangular lobule |
| Declive | Simple lobule |
| Folium | Superior semilunar lobule |
| Parts of vermis | Subdivision of the cerebellar hemisphere |
| Tuber | Inferior semilunar lobule |
| Pyramid | Biventral lobule |
| Uvula | Tonsil |
| Nodule | Flocculus |
| Archicerebellum Made up of flocculonodular lobe & lingula It has a vestibular connection |
| Function: Maintenance of equilibrium, muscle tone & posture |
| Neocerebellum: Made up of the middle lobe except for the pyramid & uvula of the inferior vermis. |
| Function: Regulation of Fine movements of the body |
| Paleocerebellum Made up of the anterior lobe (except lingula) and pyramid & uvula of the inferior vermis. |
| Function: Regulate the crude movements |
| Outer cortex - made of grey matter |
| Inner central core - made of white matter |
|
And within the whiter matter-embedded intracerebellar nuclei.
|
| The cerebellum is made up of outer grey matter, the cerebellar cortex, and a central core of white matter. |
| Embedded within the central core of white matter are the masses of grey matter called intracerebellar nuclei. |
| Climbing fiber arises from an inferior olivary nucleus and synapses with the dendrites of the Purkinje cell. |
| Mossy fibers synapse with the granule cell. |
| Basket cell synapse with the cell body of the Purkinje cell. |
|
Intrinsic fiber
Make connections within the cerebellum. |
| Afferent fibers (sensory) or Input * Mossy fibers * Climbing fibers |
| Efferent fibers or output Axons of Purkinje cell |
Input from climbing fibers
|
Directly synapse with dendrites of Purkinje cell
Maximum input from the brainstem & higher brain via mossy fibers to the cerebellum
|
Synapse with granule cell
|
The axon of granule cell form parallel fibers
|
Parallel fibers connect with dendrites of Purkinje cell
Note:
All Four types of neurons of the cerebellum are inhibitory.
| Superior cerebellar artery, a branch of the basilar artery |
| Anterior inferior cerebellar artery, a branch of the basilar artery |
|
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery, a branch of the vertebral artery
|
| The basilar artery is formed by the union of the 4th part of the vertebral artery after coursing through the foramen magnum. |
| Basilar artery lodges in the basilar sulcus present in the anterior of the pons. |
|
The vertebral artery is a branch of the 1st part of the subclavian artery.
|
| Muscular hypotonia (low muscle tone) - less resistance |
| Intention tremors (tremors only during movements) |
|
Dysdiadochokinesia:
Inability to perform rapid & regular movements like pronation & supination
|
|
Gait ataxia -
Unsteady gait/ unable to walk on a straight path like an alcoholic person.
|
|
Nystagmus-
Involuntary jerky movement of eyeball
|
|
* Muscle tone is the partial state of contraction of muscle fibers.
* To maintain posture ie. sitting, and standing, some muscles are continuously working.
|
|
Different types of tremors:
* Parkinson’s disease (involuntary tremor- resting tremor) * Cerebellar lesion (intention tremor - tremor during performing voluntary movement) * Thyrotoxicosis (Fine tremor) |
| Three - 3 pattern: |
| Three parts: Archicerebellum Paleocerebellum Neocerebellum |
| Three lobes: Anterior lobe The middle or posterior lobe Flocculonodular lobe |
| Three fissures: Fissura prima (primary fissure) Horizontal fissure Posterolateral fissure |
| Three histological layers of grey matter: Molecular layer Purkinje cell layer Granular cell layer |
| Three peduncles: Superior cerebellar peduncle to the midbrain Middle cerebellar peduncle to Pons Inferior cerebellar peduncle to medulla oblongata |
| Three arteries for each hemisphere: Superior cerebellar Anterior inferior cerebellar Posterior inferior cerebellar |
| Three functions: Tone, posture & equilibrium by flocculonodular lobe Crude movements by the anterior lobe Smooth fine movement by the middle lobe |
Comments (2)