Typical Ribs & First Rib
Ribs
There are a total of 12 pairs of ribs.
Classification of ribs
1. According to features
- Typical ribs: 3rd -9th
- Atypical ribs: 1st, 2nd,10th,11th, and 12th
Note:
- Typical ribs have the same general features.
- Atypical ribs have special features.
2. According to relation with the sternum
- True ribs: 1st – 7th i.e upper 7 ribs
- False ribs: 8th -12th i.e lower 5 ribs
Note:
- True ribs =articulate with sternum anteriorly
- False ribs=Do not articulate with sternum anteriorly
3. According to articulation
- Vertebrosternal ribs= 1st -7th
- Vertebrochondral ribs: 8th -10th
- Floating ribs: 11th and 12th
Note:
- Vertebrosternal ribs: articulate posteriorly with vertebrae and anteriorly with sternum
- Vertebrochondral ribs: articulate posteriorly with vertebrae and anteriorly with costal cartilage of higher rib
- Floating ribs: articulate posteriorly with vertebrae and anteriorly free.
Typical ribs
Why it is called typical?
- It is curved
- It is angulated
- It is twisted
- A costal groove is present.
Anatomical point
- The posterior end consists of the head, neck, and tubercle which lies at the midline.
- Anterior end bears cup-shaped depression which lies anteriorly slightly below then the posterior end.
- Costal groove present in the lower margin of the inner surface.
Parts
- Anterior end
- Posterior end
- Shaft
1. Anterior end
- It bears a cup-shaped depression.
- It forms a costochondral joint which is the primary cartilaginous type of joint.
2. Posterior end
- It presents a head, neck, and tubercle.
Head
- It bears two articular facets,
- Lower facet is larger and articulates with the body of the corresponding vertebra.
- Upper facet is smaller and articulates with the body of the upper higher vertebra.
- Two facets are separated by a crest.
- Crest articulate with an intervertebral disc which is a fibrocartilage type of joint.
Tubercle
It has two-part
- The medial articular part articulates with the transverse process and forms a costotransverse joint which is the plane type of synovial joint.
- Lateral non-articular.
Shaft
- Two surface=outer surface and inner surface
- Two border=upper and lower border
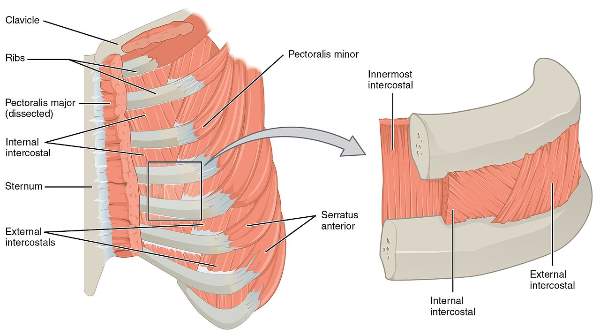
Attachment
- Internal intercostal muscle
- External intercostal muscle
- Intercostalis intimus
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Direction of fiber | Actions |
| External intercostal | Lower border of the rib above | Outer lip of upper border of rib below | Downward, forward, and medially | Elevates the rib during inspiration |
| Internal intercostal | Floor of the costal groove of the rib above | Inner lip of the upper border of the rib below | downward, backward, and laterally | Elevates the rib during expiration |
| Intercostalis Intimus | Inner surface of the rib above | Inner surface of the rib below | Downward, backward and laterally | Elevates the rib during expiration |
Costal groove
Contents
From above to downward
- Intercostal vein
- Intercostal artery
- Intercostal nerve
Note:
All together they are called neurovascular boundle.
Intercostal space
- It is the space between two adjacent ribs.
- Anterior intercostal space=9 in number
- Posterior intercostal space=11 in number
Contents
- Intercostal vain
- Intercostal artery
- Intercostal nerve
- Intercostal membrane
- Intercostal muscles
Movement of ribs
1. Palm handle movement
- It increases the anterior and posterior diameter
2. Bucket handle movement
- It increases the transverse diameter
Note:
When the diaphragm contracts, it increases the vertical diameter.
Ossification
- The process of formation of bone is called ossification.
- Intra cartilaginous ossification
Note
- All the flat bones except the vault and clavicle have Intra cartilaginous ossification.
- Whereas the vault and clavicle have intramembranous ossification.
- Morphologically it is a flat type of bone.
First rib
Side determination
- Its larger end is directed anteriorly and its smaller end is directed posteriorly.
- The surface of its shaft having two grooves separated by a ridge is directed superiorly
- Its concave border is directed inward and its convex border is directed outward.
The trick for side determination
- Put the ribs on the table.
- If both ends touch the table then be sure that the first ribs belong to that particular side.
Distinguishing Features
- Shortest, broadest, and most curved rib
- No costal groove
- It is not twisted.
- It has a single facet in the head.
Anatomical point
- This is the first rib of the left/right side.
- Posterior end bears a single facet.
- Anterior end bears a cup-shaped depression
- The superior surface is marked by two shallow grooves.
Features
End
1. Anterior end
- It articulates with the First costal cartilage.
- It forms a costochondral joint which is the primary cartilaginous joint.
2. Posterior end
- It articulates with the body of 1st vertebrae.
- It forms a costovertebral joint which is a plane type of synovial joint.
Surface
1. Superior surface
- It has two grooves which are separated by a slight ridge called a scalene tubercle.
- The Anterior groove lodges the subclavian vein.
- The posterior groove lodges the subclavian artery and lower trunk of brachial plexus.
- In front of the anterior groove it provides attachment to subclavius muscle and costoclavicular ligament.
- The area behind the posterior groove gives insertion to the scalenus medius.
- Serratus anterior inserted at the scalenus tubercle.
2. Inferior surface
- It is related to costal pleura.
Border
1. Outer border
- Serratus anterior originates from the 1st to 8th ribs.
- The serratus anterior is supplied by the long thoracic nerve.
- Injury of the long thoracic nerve leads to winging of the scapula.
2. Inner border
- The base of the supra pleural membrane is attached to the inner border of 1st rib.
- Whereas the apex of the supra pleural membrane is attached at the tip of the transverse process of C7
Anterior relation of neck
From medial to lateral
- Sympathetic chain
- First posterior intercostal vein
- Superior intercostal artery
- The ventral ramus of T1 spinal nerve

Comments (0)