AIDS
Definition of AIDS:
It is a condition where a person is infected by HIV. Here the infected person may not suffer from any symptoms associated with infection but in AIDS the person suffered from symptoms related to the infection.
OR,
AIDS the acquired immune deficiency syndrome is an end stage of human immune deficiency viral infections which breaks down the body’s immune system leaving the victim vulnerable to a host of life-threatening opportunistic infections, neurological disorders/ unusual malignancy.
Causative Organism of AIDS:
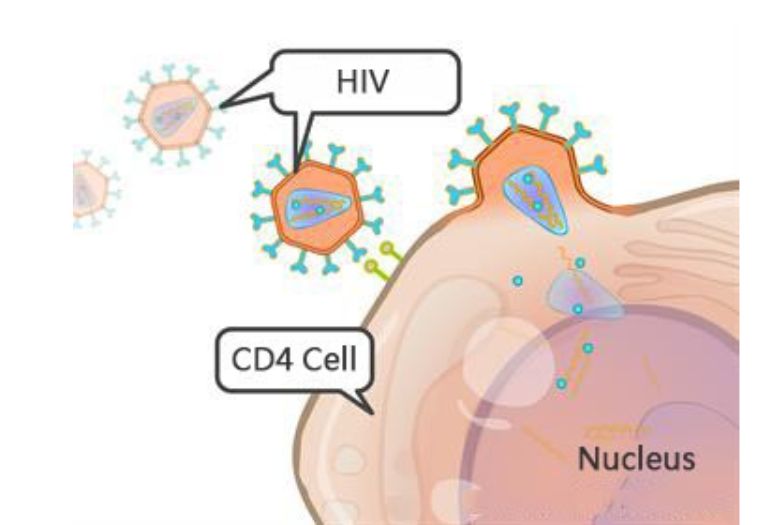
HIV= Human Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
Incubation period of AIDS: 6 months to 6 years or more.
Clinical features of AIDS:
1. Asymptomatic
2. Active infection syndrome is characterized by
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Rash
- Arthralgia
- Lymphadenopathy.
3. AIDS-related complex:
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea
- Skin rash
- Lymphadenopathy
- Herpes simplex
Stages of HIV Infection:
The clinical picture of HIV infection can be divided into three stages:
1. An early acute stage:
Fever, lethargy, sore throat, and generalized lymphadenopathy. Maculopapular rash on the trunk, arms, and legs, leucopenia, This stage resolves spontaneously in about 2 weeks.
2. A middle latent stage:
A long latent period, measured in years; usually ensures in untreated patients this stage lasts for 7-11 years. The patient is usually asymptomatic during this period.
3. A late immunodeficiency stage:
The late stage is acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is characterized by the marked reduction in the CD4 cells and the occurrence of opportunistic infections.
Target cells of AIDS:
- Helper T cells (specifically CD4 + T cells)
- Macrophage
- Dendritic cells.
Mode of Transmission:
1. Sexual transmission (75% - 85%):
- Homo sexual - more common
- Hetero sexual
2. Parental transmission:
- By blood and blood products
- By contaminated needles.
- By drug abusers.
3. Vertical transmission:
- Trans placental
- During birth
- Breastfeeding.
4. Probable other methods:
- Through donated organs and tissue such as organ transplantation and through denoted semen.
- Any skin piercing injection, ear piercing, or tattooing.
- By sharing sharp razors, toothbrushes (rarely)
Risk Factors:
- Male homosexual and bisexuals
- Prostitutes
- Intravenous drug users
- Transfusion recipients of blood products
- Hemophiliacs and clients of STD
Nursing Management of AIDS:
1. Health education-the healthcare workers must:
- Know the patient
- Avoid pear tactics
- Avoid judgmental & moralistic messages
- Be consistent & concise
- Use positive statement
- Give practical advice
2. Practice universal/standard precaution
- There is a need for thorough medical hand washing after every contact with a patient & after removing the gown & gloves, & before leaving the room of an AIDS suspect known AIDS patient.
- Use of universal barrier or personal protective equipment (PDE) eg-can, mask, gloves, face shield /goggles are very necessary.
3. Care should be taken to avoid accidental pricks from sharp instruments contaminated with potentially precious materials from AIDS patients
4. Gloves should be worn when handling blood specimens & other body secretions as well as surfaces, materials & objects exposed to them
5. Blood & other specimens should be labeled with special warnings AIDS precautions.
6. Blood spills should be cleaned immediately using common household disinfectants like chloral
7. Needles should not be bent after use but should be disposed into a puncture-resistant container
8. Personal articles like razors, and toothbrushes should not be shared with other members
9. Patients with active AIDS should be isolated
Prevention of AIDS:
- Health and sex education
- Prevention of blood-borne STDs transmission
- Control of prostitution
- Social welfare measures
- Ability by the law of religion
- Early diagnosis and treatment
- Post-exposure prophylaxis with zidovudine and lamivudine is advisable.
- Termination of pregnancy in HIV positive
- Avoiding breastfeeding
- Widespread voluntary counseling and testing (VCT)

Comments (0)