Pleura
Pleural cavity
A lung covered in the serous sac is called the pleural cavity
Pleura
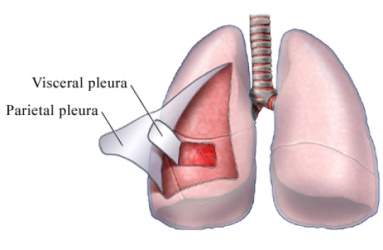
Covering of the lungs is called pleura
It is two types
- Visceral pleura = this is the inner layer
- Parietal pleura = this is the outer layer
Pleural cavity
- The space between the visceral pleura and parietal pleura is called the pleural cavity. This is the potential space between the two pleura.
1. Visceral pleura
- Except for the hilum and along with the attachment of pulmonary ligament, it covers all the surfaces of the lung.
- It cannot be separated as it is adherent to the lung surface.
2. Parietal pleura
- It is thicker than the visceral pleura
- It lines the wall of the pulmonary cavity.
Subdivision of parietal pleura
- Costal pleura
- Diaphragmatic pleura
- Mediastinal pleura
- Cervical pleura
1. Costal pleura
- It lies the inner surface of the thoracic wall
- It is loosely attached by a thin layer of loose areolar tissue called endothoracic fascia, which is easily sepratable from the thoracic wall in the case of living beings.
2. Diaphragmatic pleura
- It covers the upper surface of the diaphragm.
3. Mediastinal pleura
- It forms the lateral boundary of the corresponding surface of the mediastinum.
- By its reflection it covers the root of the lung and becomes continuous with visceral pleura.
4. Cervical pleura
- It covers the apex of the lung.
- It is covered by the supra pleural membrane.
- It is clinically important that’s why it should not penetrate while anesthetic needle.
Pulmonary ligament
- It is a pleural fold that surrounds the root of the lung and extends down as a fold called a pulmonary ligament.
- The function of the pulmonary ligament
- Pulmonary vein requires some space when it expands during the increased venous return at the time of exercise. At that moment it provides dead space.
- It allows the descent of the root of the lung with the descent of the diaphragm during inspiration.
The recess of the pleura
- The expended regions of the pleural cavity are called a pleural recess.
- It is essential for lung expansion during the deep inspiration.
it is of two types
- Costodiaphragmatic recess
- Costomediastinal recess
1. Costodiaphragmatic recess
- It is located inferiorly between the costal and diaphragmatic pleurae,
- They are the most dependent part of the pleural cavity, hence fluid of pleural effusion is first collected at these sites.
2. Costomediastinal recess
- It is located between the costal and mediastinal pleurae and lies between the sternum and costal cartilages.
- It is the place where changes in tone take place from resonant to dull. This is called the area of superficial cardiac dullness.
Nerve supply of the pleura
Parietal pleura
- It is developed from the somatopleuric layer of the lateral plate mesoderm that why it is supplied by the somatic nerve.
- It is sensitive to pain
- The costal and peripheral part of diaphragmatic pleura = supplied by intercostal nerve
- The mediastinal and central part of diaphragmatic pleura = supplied by phrenic nerve
Visceral pleura
- It is developed from the splanchnopleuric layer of lateral plate mesoderm that’s why it is supplied by autonomic nerve.
- Arises from T2- T5
- It is insensitive to pain.
Differentiate between the parietal and visceral pleura
| parietal pleura |
visceral pleura |
| lines the thoracic wall and mediastinum |
lines the surface of the lung |
| develops from the somatopleuric mesoderm |
develops from splanchnopleuric mesoderm |
| innervated by the somatic nerve |
inverted by autonomic nerves |
| sensitive to pain |
insensitive to pain |
Comments (0)