Second Stage of Labor
Definition of 2nd Stage of Labour:
The second stage of labor begins with full dilatation of the cervix irrespective of the presence or rupture of the beg of membranes and ends with the expulsion of the fetus.
Duration of the Second stage of Labor:
- Prinigravidae: 2 hours
- Multiparae : 30 minutes
Phases of the Second stage of Labor:
- Propulsive phase: It starts from full dilatation of the cervix up to the descent of the presenting part to the pelvic floor
- Expulsive Phase: It is distinguished by metered bearing down efforts & ends with the delivery of the baby.
Diagnosis of the Second stage of labor:
1. Change of pattern of pain:
- The intensity of pain increases
- The pains come at intervals of 2-3 minutes ( 3-4 ) contractions in every 10 minutes).
- Duration of pain increases ( > 40 seconds )
2. Bearing down efforts occurs
3. Membranes rupture with a gush of liquor p/v ( if membranes are previously unruptured)
4. Decent of the fetus as evident from abdominal & vaginal examinations.
5. Expulsion of the baby
6. Fetal signs: Brady cardia during contraction.
Crowning of the head:
After internal rotation of the head, further descent occurs until the sub-occiput lies underneath the pubic arch at this stage the maximum diameter of the head even after contraction is over; is called crowning of the head.
Clinical significance of crowning:
- One of the impartment signs 2nd the stage of labor
- Delivery of the head starts after crowning
- The patient is encouraged for bearing down after crowning which facilitates the descent of the head.
Common causes of delay in 2nd stage of labor:
A. Fault in power:
- Uterine inertia
- Inability to bean down
- Epidural analgesia
- Constriction
B. Fault in the passage:
- Pelvic abnormalities:
- Cephalo – Pelvic disproportion (CPD).
- Contracted pelvic
- Android Pelvic
- Undue resistance of the pelvic floor or perineum due to spasm or old scanning.
- Soft tissue pelvic tumor
C. Fault in passenger:
- Malpresentation: Transverse lie
- Malposition (Occipito- posterior position).
- Big baby
- Congenital malformation of the baby; e.g. hydrocele phalluses
Management of a Case of the Second stage of labor:
- The patient should be in the bed.
- Constant Supervision is mandatory & monitoring should be more frequent ( every 5-10 minutes)
- FHR record in 5 minutes interval
- Inhalation analgesics ( if available ): In the form of gaseous N2O &O2 to relieve pain during
- Per – vaginal examination: P/V/E is done at the beginning of the 2nd stage due to –
- Full Cervical dilatation: When there is no cervical lip is palpable or felt on per–vaginal digital examination is said to be full dilatation of the cervix.
- To detect any accidental cord prolapse.
- Review of position & station of the head.
- To ensure the progressive descent of the head
Preparation for delivery:
1. Position of the woman:
- A dorsal position with 15 left lateral tilt is commonly favored as it avoids aorta-caval compression & facilitates pushing effort.
- A woman may be in a lateral or partially Sitting position
2. The accoucheur Serubs up & puts on the sterile gown, mask & gloves, and stands on the right side of the table
3. Toileting of external genitalia & inner side of the thighs is done with a cotton swab soaked with chlorohexidine or 10% povidone.
4. Essential aseptic procedure: should be remembered as 3 ‘C’
- Clean hands.
- Clean Surface &
- Clean Cutting and ligaturing of the cord
5. Catherization
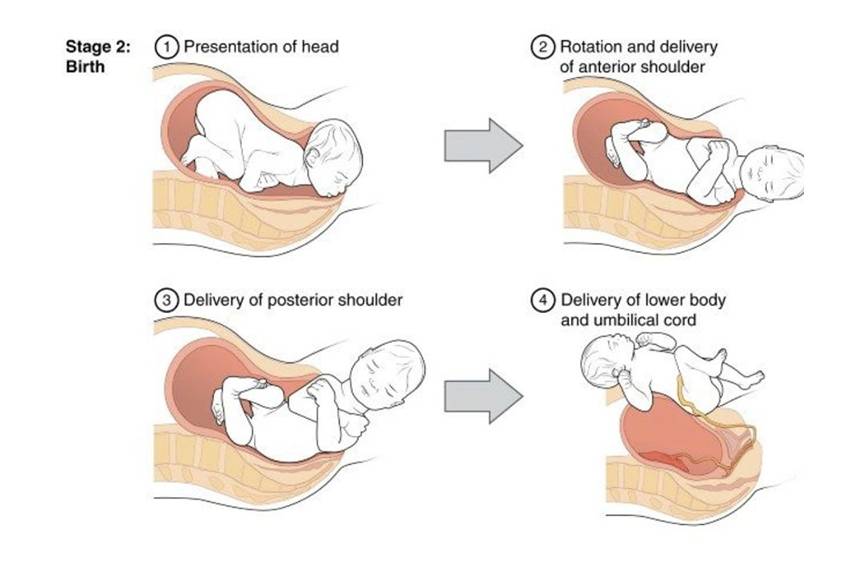
Conduction of delivery:
- Delivery of the head
- Delivery of the Shoulders &
- Delivery of the Trunk
Complications of 2nd stage of labor:
- Delayed 2nd due to malposition
- Fetal distress
- Cord prolapsed
- Intrapartum eclampsia.
- Perineal tear

Comments (0)