ACUTE APPENDICITIS
The vermiform appendix is a narrow thin tube that is joined to the large intestine. it sits in the right lower part of your abdomen. When your appendix is inflamed due to obstruction or others causes is called appendicitis.
Inflammation of the vermiform appendix is called appendicitis.
Definition:
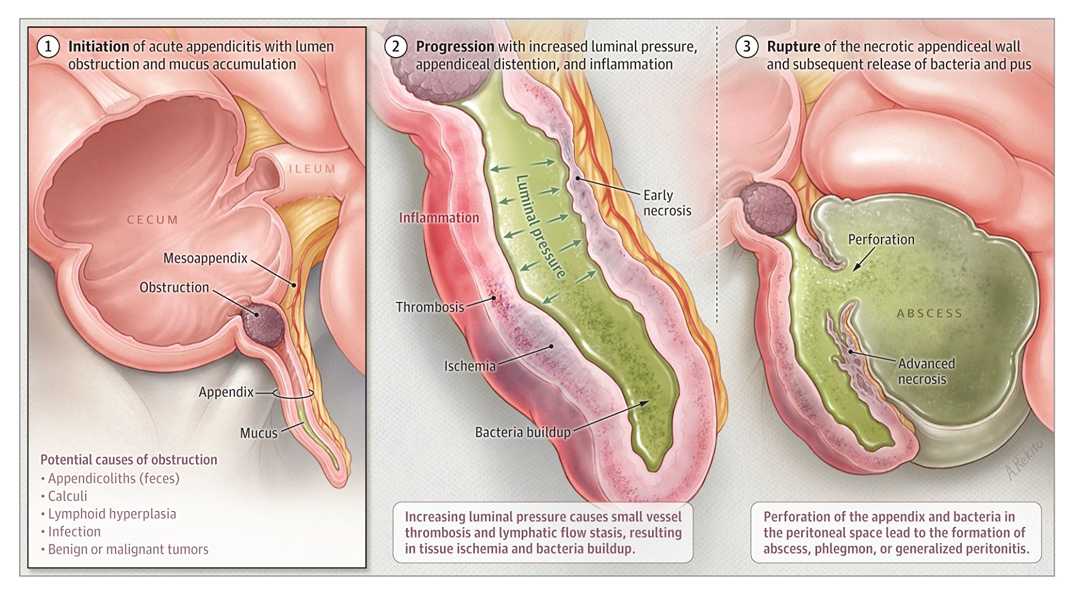
Acute appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the vermiform appendix, most likely due to obstruction of the lumen of the appendix by a fecalith, normal stool, or infective agent.
Classification of acute appendicitis:
A. According to the number of attacks:
- Acute appendicitis (commonest): First attack
- Recurrent appendicitis: More than one attack
B. According to luminal obstruction
- Obstructive appendicitis.
- Non-obstructive appendicitis.
Cause of appendicitis:
A. In the Lumen:
- Faecolith
- Pinworm
- Undigested Food
B. In the wall
- lymphoid hyperplasia
- Carcinoid Tumors
C. Outside the wall: Compression by band and adhesion.
D. Others
- Decrease dietary fiber.
- Increase consumption of refined carbohydrates( fast food)
- Bacteriology
Signs and symptoms of Acute appendicitis
- Severe pain around the umbilicus or epigastrium which shifts to the right iliac fossa
- Pain that becomes sharper over several hours
- The tenderness that occurs when you apply pressure to your lower right abdomen
- Sharp pain in your lower right abdomen that occurs when the area is pressed on and then the pressure is quickly released (rebound tenderness).
- Localized tenderness in the right iliac fossa
- Nausea, Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal swelling
- Constipation
- Diarrhea.
- Low-grade fever
Investigations for Acute appendicitis:
Still, in most cases, it is diagnosed clinically.
- CBC
ESR - Increased.
WBC - Count increased - USG of lower
- Urine R/M/E.
Medical Management of Acute appendicitis
1. Conservative management:
- Diet- Nothing by mouth
- Administer iv fluids 5% DNS OR DA.
- Administer analgesics, and antibiotics until surgery is performed.
- Administer antiemetic and antipyretic (if needed)
- Watch and record all vital signs routinely.
2. Surgical treatment:
Surgery (conventional or laparoscopic) is indicated if appendicitis is diagnosed and should be performed as soon as possible to decrease the risk of perforation.
Nursing management of Acute appendicitis:
A. Nursing assessment-
- Assess the level of pain
- Assess relevant laboratory findings
- Assess the patient's vital signs in preparation for surgery
B. Nursing diagnosis-
- Acute pain related to obstructed appendix
- Risk for deficient fluid volume
- Risk for infection related to a ruptured appendix
C. Planning and goal-
- Relieving pain
- Preventing fluid volume deficit
- Reduce anxiety
D. Nursing intervention-
- I/v infusion should be given to replace fluid loss
- Antibiotics should be given according to the doctor's order
- Positioning- after the surgery the nurses place the patient on a high fowler position to reduce the tension on the incision and Abdominal organ
E. Evaluation
- Relieve pain
- Prevent fluid volume
- Reduce anxiety
- Eliminate infection
- Attained optimal nutrition
Complications of Acute appendicitis:
- Appendicular lump
- Appendicular abscess
- Perforation of the appendix
- Gangrene of appendix
- Peritonitis – Generalized or Localized
- Recurrent appendicitis.
- Septicemia and systemic sepsis

Comments (0)