Abortion (Miscarriage)
Legally, abortion means the premature expulsion of the fetus from the mother’s womb at any time of pregnancy, before the full term of pregnancy is completed.
Unsafe abortion means, abortion not provided through approved facilities, and/or persons.
Medicolegal Classification of Abortion:
| 1. Natural: | 2. Artificial |
| I. Spontaneous II. Accidental |
I. Justifiable (therapeutic) II. Criminal |
Causes of natural abortion:
1. Defect in ova including chromosomal defect
2. Developmental defect of the fetus (common)
3. Low implantation of the zygote
4. Diseased condition of decidua or placenta
5. Rh incompatibility
6. Retroverted uterus
7. Malformed uterus
8. Uterine hypoplasia
9. Sub-Mucous uterine fibroid
10. Hypertension
11. DM
12. Hormonal deficiency
13. Sudden shock, emotional disturbance
14. Syphilis
15. Nephritis
16. As or Pb toxicity
17. Drug toxicity
Medico-legal importance of abortion: (Ref. Nandy)
1. Abortion may be induced without proper indication or in contravention to the provision of medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) act, when it amounts to a crime.
2. When a doctor violates the provisions of the MTP act, he is liable to be punished.
3. A pregnant or even a non-pregnant woman may malinger abortion due to assault to bring a false charge against an enemy.
4. Abortion may be feigned to bring a false charge of rape or intercourse by a man for blackmailing the man.
5. Abortion may be feigned to claim compensation by a working woman linking.
Criminal abortion
It is the induced destruction and expulsion of the fetus from the mother's womb unlawfully i.e. when there is no therapeutic indication for the operation.
It is resorted to mostly by widows and unmarried women. It is usually carried out before the third month. A case of criminal abortion is investigated only when the woman dies, and rarely when someone gives the information to the police.
Methods of procuring Criminal abortion:
The methods commonly used for terminating an unwanted pregnancy can be roughly divided into three periods:
(1) Up to the end of the first month, the woman may take violent exercises, hot baths, and purgatives. Extreme violence may lead to internal injury.
(2) Up to the end of the second month, when suspicion becomes certainty, abortifacient drugs are used.
(3) About the third or fourth month, after failing to procure an abortion by the above methods, mechanical interference is done either by the woman herself or by some other person.
A. Administration of drugs (Abortifacient Drugs):
They either produce a congestion of the uterine mucosa and then uterine bleeding, followed by contraction of the uterine muscle and expulsion of the fetus, or they cause the uterine contraction by stimulating the myometrium directly.
|
Drugs acting directly on the uterus 1. Ecbolic (increase contraction) 2. Emmenagogues (initiate or increase menstrual flow) |
|
Drugs acting indirectly on uterus 1. Drugs that irritate the genitourinary tract, produce reflex uterine contraction 2. Drugs which irritate GIT, Any substance which causes irritation of the colon may produce hyperemia and contractions of the uterus 3. Drugs having a poisonous effect on the body, Inorganic irritants, e.g. lead, copper, iron, or mercury. Organic irritants, e.g. Cantharides, juice of Calotropis, seeds of custard apple and carrots, and unripe fruit of papaya or pineapple, methi, saffron. |
B. Application of violence:
1. General
2. Local
|
General It acts directly on the uterus or indirectly by producing congestion of pelvic organs or hemorrhages between the uterus and membranes. Examples: 1. Severe pressure on abdomen by massaging over the uterus 2. Kick, jumping, blow in the abdomen 3. Violent exercise I.e., horse riding, skipping, jumping from a height, cycling 4. Cupping 5. Very hot and cold hip bath alternatively |
|
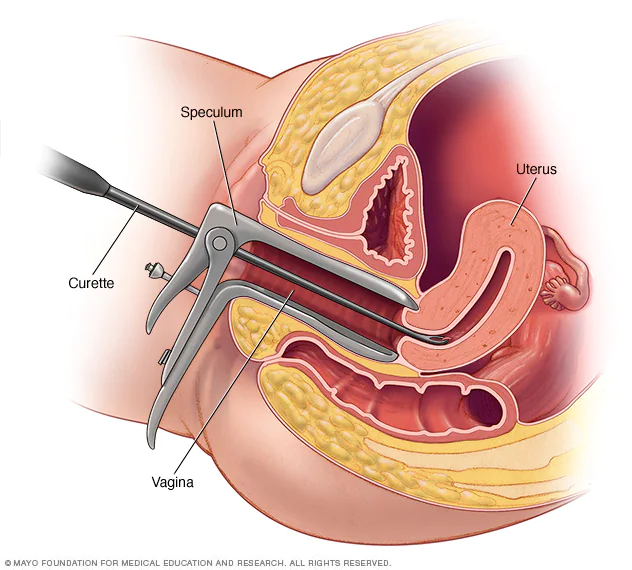
Local 1. Curettage 2. Dilation of cervix 3. Abortion sick 4. Air insufflations 5. Rupture of the membrane 6. Electricity 8. Syringing (e.g Enema syringe with hand-bulb & Higginson’s syringe) Mnemonic: CARES |
Complications of criminal abortion:
| Injury 1. Abrasion around the genitalia 2. Laceration and perforation of the upper vagina, cervix, and uterine wall 3. Cervical necrosis |
| Hemorrhage 1. Hemorrhage from external genitalia, cervix, uterus 2. Peritoneal hemorrhage |
| Infection 1. Cervicitis, salpingitis 2. Septicemia, pyemia 3. Thrombi-phlebitis |
| Shock 1. Hemorrhagic shock 2. Neurogenic shock 3. Vagal inhibition |
Causes of death in criminal abortion: (Reddy)
|
Immediate death 1. Vagal inhibition 2. Air embolism 3. Hemorrhage 4. Fat embolism 5. Amniotic fluid embolism |
| Delayed death 1. Septicemia 2. Pyemia 3. Confined local infection and toxemia 4. General peritonitis 5. Tetanus |
| Remote death 1. Jaundice and renal failure 2. Bacterial endocarditis 3. Pulmonary embolism |
Feature present in the case of recent criminal abortion:
1. There may be the discharge of milk/colostrum's/squeezing of breast
2. Body temperature may be raised
3. Abdominal wall may be tender
4. Uterus may not be palpable per abdomen
5. Labia majora and minora will be congested and abrasion, laceration present
6. Vagina may show small blood clots
7. Cervix congested and os remains dilate for few days
Clinical Examination (Ref. Review book)
1. Since, most of the abortifacients are irritants, the woman may show signs of ill health, GIT disturbances, and exhaustion.
2. In case of sepsis, there will be pyrexia with chills and rigor, pain abdomen, and increased pulse rate (100–120/minute).
Local Examination (Review book)
1. Appearance of the perineum, vulva, and vagina is noted.
2. Presence/absence of injuries (abrasions/contusions/lacerations) is noted.
3. Condition of os is noted. It remains dilated for a few days and may also show some injuries due to instrumentation.
4. Presence of recent tears, the marks of forceps, or other instruments in and around genitalia should be noted.
5. Character and amount of discharge are noted. In case of sepsis, offensive purulent vaginal discharge or a tender uterus with patulous os may be found.
Laboratory investigations: Serum and urine give positive results for the test for hCG up to 7–10 days.
Post-mortem findings in case of death due to criminal abortion:
1. External evidence: marks of general violence, injection mark
2. Cyanosis: due to shock/air embolism
3. GIT and urinary tract: irritant of ecbolic
4. Local examination:
|
Vagina - Laceration of the mucous membrane |
|
External os - Soft or not - Evidence of dilation - Laceration, bruise |
|
Cervix - Length - Anything passes into the cervical canal - Any fluid - Foreign substance - Any tear/laceration |
|
Uterus - Size, shape, weight, thickness - Foreign substance - Any tear/laceration |
5. Microscopic examination: Section of the vaginal and uterine wall
6. Chemical examination:
- Viscera
- Half of the uterus and appendage should be preserved, labeled, sealed, and sent to the chemical examiner
Duties of a doctor in case of criminal abortion:
1. The doctor should keep all the information obtained by him as a professional secret.
2. He must ask the patient to make a statement about the induction of criminal abortion. If she refuses to make a statement, he should not pursue the matter
3. He must consult a professional colleague
4. He must treat her to the best of his ability
5. If the women's condition is serious, he must arrange to record the dying declaration.
6. If the woman dies, he should not issue a death certificate, but he should inform the police.
Justifiable/Therapeutic abortion
Abortion is justifiable only when it is done in good faith to save the life of the woman if it is materially endangered by the continuance of pregnancy.
Therapeutic method:
1. Electrical vacuum aspiration & MANUAL VACUUM ASPIRATION
2. Low rupture of membrane
3. Uterus paste injection (soap+thimol+KI=paste) into the cervical canal
4. Dilation of cervix and oxytocin infusion, or direct injection of ten units of oxytocin into the uterus.
5. Dilation of the cervix and evacuation of the uterus by curettage, during the first three months.
6. Amniotic fluid replacement therapy
7. Prostaglandins:
Prostin E2 (PGE2), and prostin F2 (PGF)2 induce labour and abortion. They can be given intravenously or orally. Intra-amniotic injection of 25 mg. prostaglandin F2 is used for second-trimester abortions.
8. ABDOMINAL HYSTEROTOMY
9. Mifipristone (RU 486) inhibits the action of progesterone. This causes the breakdown of the endometrium and detachment of the embryo from the uterine wall. It is not very effective after seven weeks.
MTP (Medical termination of pregnancy)/justifiable abortion/lawful abortion.
The abortion which is done in good faith, to save the life of the woman, if it is materially endangered, by the continuance of pregnancy is called MTP/justifiable abortion/lawful abortion.
Indications:
|
Therapeutic When the continuation of pregnancy endangers the life of the women or may cause serious injury to her physical or mental health. Like Uterine fibroid, cervical cancer, hypertension, Rheumatic heart disease, DM, Hyperthyroidism, Pulmonary Tuberculosis |
|
Eugenic When there is a risk of the child being born with serious physical or mental abnormalities: 1. If the pregnant woman in the first 3 months suffer from: - German measles - Smallpox or chickenpox - Toxoplasmosis - Viral hepatitis - Any severe viral infection 2. If the pregnant woman is treated with teratogenic drugs e.g., thalidomide, cortisone, aminopterin, antimiotic, antidepressant drugs. 3. Mother is treated by X-ray or radio-isotope 4. Insanity of the parents |
|
Humanitarian Pregnancy by rape |
|
Social Factor When pregnancy has resulted from the failure of contraceptive methods in case of a married woman, which is likely to cause serious injury to her mental health. |
|
Environmental Factor When the social or economic environment, actual or reasonably expected can injure the mother's health. |
Procedures/Rules of justifiable abortion:
1. Only a qualified registered medical practitioner possessing prescribed experience can terminate the pregnancy.
Chief Medical Officer of the district is empowered to certify that a doctor has the necessary training to do abortions. A medical practitioner can qualify if he has assisted in the performance of twenty-five cases of M.T.P. in a recognized hospital.
2. The pregnancy should be terminated in hospital recognized by government for this purpose.
3. The doctors must be satisfied that these are the proper indications for induced abortion.
4. The consent of women is required before the conduction of abortion; written consent of the guardian is required if the woman is a minor or mentally ill. Consent of the husband is not necessary.
5. Abortion cannot be performed on the request of the husband if the woman herself is not willing.
6. The woman need not produce a proof for her age. The statement of the woman that she is over eighteen years of age is accepted.
7. Professional secrecy has to be maintained.
8. If the period of pregnancy is below 12 weeks it can be terminated by the opinion of a single doctor, if the period of pregnancy is between 12-20 weeks, two doctors must be agreed that there is an indication. Once the opinion is formed, termination can be done by anyone doctor.
9. In an emergency, pregnancy can be terminated by a single doctor, even without required training (even after 20th weeks), without consulting a 2nd doctor in a private hospital which is not recognized.
10. It is enough for the woman to state that she was raped, and it is not necessary that a complaint was lodged with the police.
| Non-governmental institutions may take up an abortion if they obtain a license from the Chief Medical Officer of the district. |
| The termination of pregnancy by a person who is not a registered medical practitioner (person concerned), or in an unrecognized hospital (the administrative head) shall be punished with rigorous imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than two years, but which may extend to seven years. |
Abortionist
Abortionist is a person who performs abortion either lawful or criminal.
Types:
1. Expert or medical qualified abortionist
2. Semi-skilled abortionist e.g., mid-wives, nurse, chemist, etc.
3. The unskilled abortionist
MEDICOLEGAL IMPORTANCE OF PLACENTA:
(1) It gives an idea of the length of gestation.
(2) In criminal abortion, often pieces are retained in the uterus.
(3) The transfer of poisons, bacteria, antibodies, etc. across the placenta may result in death, disease or abnormalities of the fetus.
Complication of MTP
Immediate
- Hemorrhage,
- Shock,
- Perforation of uterus, bowel,
- Cervical laceration
Delayed
- Menstrual disturbance
- Sterility,
- Psychological disorder,
- Amateur labour

Comments (0)