Pregnancy
It is a condition of having a developing embryo/fetus in the female when an ovum is fertilized by spermatozoa.
Duration of Pregnancy
9 calendar months plus 7 days from the 1st day of the last menstrual period
280 days or 40 weeks from LMP
Ways of attaining pregnancy
1. Sexual intercourse with a potent male
2. Artificial insemination
Different types of Pregnancy
- Pregnancy (True Pregnancy)
- Pseudocyesis/phantom pregnancy/false pregnancy
- Super-foetation
- Super-fecundation
Medico-legal importance of pregnancy:
A. In a civil case
- Nullity of marriage
- Inheritance of property
- During the divorce
- To get more compensations
- Working pregnant women leave the facility.
Explanation:
| Nullity of marriage - If at the time of marriage a woman is pregnant, then the marriage may be declared null and void. |
| If a woman had no access to her husband within the reasonable period matching with the duration of pregnancy then a decree of divorce may be allowed to the husband. |
| Inheritance of property - When pregnancy is followed by the death of the husband, the widow may claim a greater share of the ancestral property of the husband. |
| In divorce cases, pregnant women are allowed a higher maintenance allowance. |
| Compensation cases - Death of the husband of a pregnant woman may allow her a higher compensation. |
| Pregnancy beyond the scope of lawful wedlock makes the future baby illegitimate. |
| Working pregnant women are allowed additional leave facilities. |
B. In a criminal case
- Execution of death sentence
- In case of rape, kidnapping, seduction
- Charge of adultery against the man who is responsible for the pregnancy
- Trail in the court
- In case of suicide, homicide, abortion, blackmail
| Execution of death sentence - When a pregnant woman is awarded capital punishment after being convicted in a criminal case, the execution of the punishment may be deferred until 6 months pass after the birth of the child of the pregnant convicted and condemned woman, so that, she can rear the child till that period. In some cases, capital punishment may be commuted to imprisonment. |
| When pregnancy is claimed to be the result of rape, kidnapping, and seduction. |
| Pregnancy in an unmarried girl of 16 years or less and in a married girl of 15 years or less point towards the commission of the offense of rape. |
| Pregnancy may be the cause of the killing of an unmarried woman or a widow (Homicide). |
| Pregnant unmarried women or widows may also commit suicide. |
| Questions of pregnancy is intimately related to abortion or concealment of birth cases. |
DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY:
- The presumptive signs
- The probable sign
- The positive signs
I. PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS:
1. Amenorrhoea: This is the earliest and one of the most important symptom of pregnancy.
| Amenorrhea refers to the absence of menstrual periods; it may be either primary (meaning a woman never developed menstrual periods) or secondary (absence of menstrual periods in a woman who was previously menstruating). |
| Other causes of amenorrhoea (Other than Pregnancy) 1. During the lactation period after delivery 2. Hormonal, Psychological imbalance 3. When there is an intense desire for Pregnancy 4. Severe TB, Severe Malnutrition 5. Ovary, Uterus carcinoma |
2. CHANGES IN BREASTS:
| After the second month, breasts begin to increase in size and become nodular due to hypertrophy of the mammary alveoli. |
| Superficial veins are seen as more distinct and enlarged |
| Nipples more deeply pigmented and more erectile |
| Areola which is pink in the virgin gradually becomes dark-brown. |
| Around the nipple, the sebaceous glands become enlarged by the end of the second month to form small rounded dark-colored tubercles (MONTGOMERY'S TUBERCLES). |
| COLOSTRUM is secreted usually in the third month, which can be expressed from the breasts by gentle massage. Colostrum is a thin, yellowish fluid consisting of fat globules and large phagocytic cells filled with droplets of fat. |
3. MORNING SICKNESS: It usually appears about the end of the first month and disappears 6 to 8 weeks later. Nausea and vomiting are usually present in the morning and pass off in a few hours.
4. QUICKENING:
From about the 16th to 20th week, the pregnant woman feels slight fluttering movements in her abdomen, which gradually increase in intensity. These are due to movements of the fetus, and their first appearance is known as "quickening.
Quickening has special medicolegal importance in that, if criminal abortion is caused in a woman, who is quick with the child, then the duration of the punishment of imprisonment is increased and may extend up to 7 yrs.
Medicolegal importance of quickening
- It is a presumptive sign of pregnancy.
- It indicates that the baby is alive.
- If criminal abortion is caused in a woman, who is quick with the child then the duration of the punishment of imprisonment is increased and may extend up to 7 yrs.
5. PIGMENTATION OF THE SKIN:
The vulva, abdomen, and axillae become darker due to the deposit of pigment, and a dark line extends from the pubis to beyond the umbilicus, the so-called linea nigra.
6. CHANGES IN THE VAGINA:
The mucous membrane of the vagina changes from pink to violet, deepening to blue as a result of venous obstruction, after the fourth week. This is known as Jackquemier's sign or Chadwick's sign.
7. URINARY DISTURBANCES:
During the early weeks of pregnancy, the enlarging uterus exerts pressure on the bladder and produces frequent micturition.
8. FATIGUE: Easy fatigue is very frequent.
9. SYMPATHETIC DISTURBANCES: Salivation, perverted appetite, and irritable temper are common.
II. PROBABLE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY:
1. ENLARGEMENT OF THE ABDOMEN: During pregnancy, the abdomen gradually enlarges in size after the twelfth week.
| By the end of the third month, the uterus fills the pelvis, and between the third and fourth months appears over the brim. |
| In the fifth month, it is midway between the symphysis and umbilicus. |
| At the end of the sixth month, it is at the level of the umbilicus, and at the seventh month it is midway between the umbilicus and the xiphisternum, and |
| At the end of the eighth month, it reaches the xiphoid cartilage. |
| During the last two months, the uterus sinks into the pelvis and tends to fall forward due to its weight. |
Striae gravidarum are pinkish or slightly bluish, curved, irregular, depressed lines arranged more or less concentrically, sometimes radially around the umbilicus, gradually becoming broader.
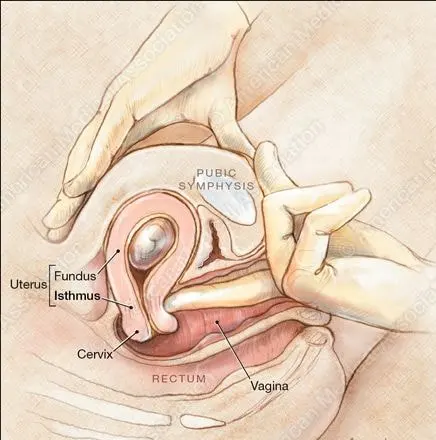
2. UTERUS:
Hegar's sign is positive at about the sixth week. If one hand is placed on the abdomen and two fingers of another hand in the vagina, the firm hard cervix is felt, and above it, the elastic body of the uterus, while between the two the isthmus is felt as a soft compressible area. This is the most valuable physical sign of early pregnancy.
| Isthmus, part of the uterus is appreciated as a soft compressible zone in between the very soft uterine body and firm and tough cervix below. |
3. CERVIX:
From the second month, the cervix progressively softens from below upward, which is well marked by the fourth month. This is known as Goodell's sign. There is a shortening of the cervix towards the last months of pregnancy. The orifice becomes circular instead of being transverse and admits the point of the finger to a greater depth.
4. INTERMITTENT UTERINE CONTRACTIONS (Braxton-Hick's sign):
Intermittent, painless uterine contractions are difficult to be observed before the third month but are easily felt after the fourth month. Each contraction lasts about a minute and relaxation for about two to three minutes. They are present even when the fetus is dead.
5. BALLOTTEMENT:
It means to toss up like a ball. This is positive during the fourth and fifth months of pregnancy as the fetus is small in relation to the amount of amniotic fluid present. To obtain vaginal ballottement, two fingers are inserted into the anterior fornix and a sudden upward motion is given. This causes the fetus to move up in the liquor amnii and after a moment, the fetus drops down on the fingers like a ball bouncing back. External ballottement can be obtained by imparting a sudden motion to the abdominal wall covering the uterus; in a few seconds, the rebound of the fetus can be felt. This can be negative if the amniotic fluid is scanty.
A sharp upward pushing against the uterine wall with a finger inserted into the vagina for diagnosing pregnancy by feeling the return impact of the displaced fetus.
6. UTERINE SOUFFLE:
This is a soft blowing murmur, which is synchronous with the mother's pulse. It is heard by auscultation on either side of the uterus just above the inguinal ligament, towards the end of the fourth month. It is due to the passage of blood through the uterine vessels.
Uterine souffle must not be confused with fetal heart sound, which is more rapid in its rate and does not synchronize with the mother's pulse.
7. BIOLOGICAL TESTS:
They are based on the reaction of test animals to chorionic gonadotropins contained in the pregnant woman's blood or urine.
They are:
1) The rapid rat test.
2) The Aschheim- Zondek test.
3) Freidman test.
4) Hogben or female toad test
5) Male frog test.
6) Galli-Mainini test. They are also positive in hydatidiform mole, chorionic epithelioma, and ectopic pregnancy.
8. IMMUNOLOGICAL TESTS (accuracy 98%):
The hormone chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) and human chorionic somatomammotropin (HCS) are secreted by the syncytial trophoblastic cells into the fluids of the mother. It can be detected in maternal blood on about the eighth day after impregnation.
HCG is a glycoprotein and acts on the same receptors as LH. An early morning urine specimen will contain the highest level of HCG and is preferable for testing. Tests are positive 12 to 15 days after implantation.
A. Inhibition (Indirect) Latex slide Test
B. Direct Latex slide test
C. Hemagglutination inhibition tube test.
Radioimmunoassay and ELISA tests can detect pregnancy with a high degree of accuracy.
III. Positive Signs of Pregnancy:
1. Foetal Parts and Movements:
Fetal movements are felt by placing the hands on the abdomen by 24 weeks. Fetal parts can be identified by abdominal palpation by 36 weeks.
2. Foetal Heart Sounds:
They are important and definite signs of pregnancy. They are heard between 1 to 20 weeks for the first time. The sounds are like the ticking of a watch placed under a pillow. Their rate is usually about 160 at fifth and 120 at the ninth month. They are not synchronous with the mother's pulse.
Fetal heart sounds are not heard:
- When the fetus is dead,
- When there is an excessive quantity of liquor amnii (Hydramnios cases)
- When the abdominal wall is very fat,
- When the examination is made before 18 weeks of pregnancy.
3. Placental Souffle:
This is a soft murmur heard over the placental site, the rate of which corresponds to that of fetal heart sounds.
4. Funic or Umbilical Souffle:
This is a blowing murmur synchronous with fetal heart sounds and is supposed to be produced in the umbilical cord.
5. X-ray Diagnosis:
At about 15th to 16th weeks, fetal parts can be detected with certainty, but occasionally parts are detected as early as ten weeks.
The shadows to be searched in the pelvis of the mother are:
- Crescentic or annular shadows of the skull.
- A series of small dots in a linear arrangement of the vertebral column.
- A series of fine curved parallel lines of the ribs, and
- Linear shadows of the limbs.
Radiological signs of fetal death are :
- Spalding's sign.
- Collapse of the spinal column due to the absence of muscle tone.
- Presence of gas in the heart and great vessels.
6. Ultrasonography:
| Gestational sac is seen as a white ring by the 6th week. |
| Fetal heartbeat can be made out by the 10th week, and |
| Fetal head and thorax by the 14th week. |
Laboratory test diagnosis of pregnancy: (Ref Lecture)
1. Bio-assay: To detect HCG in urine
2. Immuno-assay: Hemagglutination inhibition test, radio-immunoassay
3. ELISA
Confirmation of pregnancy (Ref Endeavour)
1. Immunological Test (Pregnancy Test)
2. Ultrasonography of abdomen
3. In the later period (3rd trimester) by FHS (Fetal Heart Sound), fetal movement, palpation of fetal parts.
Signs/symptoms of last trimester of pregnancy:
Symptoms
1. Amenorrhea persists
2. Frequently micturition
3. Progressive enlargement of the abdomen
3. Lightening: Due to enlargement of presenting parts
4. Fetal movement: More prominent
Signs
1. Cutaneous change
2. Uterine shape change: From cylindrical to spherical
3. Fundal height: Between umbilicus & xiphoid process.
- At 36th week corresponds to the level of the xiphoid process.
- At the 40th week, it comes down, due to enlargement of presenting parts.
4. Braxton Hick contraction: More
5. Fetal movement: Easily felt
6. Fetal heart sound
7. Palpation of fetal parts
Signs of Pregnancy in the Dead :
The presence of an embryo, fetus, placental tissue, membranes, or any other product of conception is positive proof.
The uterus is thickened and increased in size.
A well-formed corpus luteum is found in one of the ovaries.
Even in an exhumed body which has been reduced to a skeleton, fetal bones will be found in the remains.
Pseudocyesis (Spurious or Phantom pregnancy):
It is a condition in which a woman shows most of the signs of pregnancy, without being pregnant.
It is usually observed in patients nearing menopause or in younger women who intensely desire children. Most of the women suffer from some form of psychic or hormonal disorder.
Features:
1. Most of them suffer from psychic and hormonal disorders.
2. Woman shows most of the signs and symptoms of pregnancy.
3. She may have false Labour pain.
In which women it occur:
- Childless women
- Women near to menopause
Diagnosis
- Absence of positive signs of pregnancy
- Immunological test of pregnancy: Negative
- Ultrasonography: Absence of fetus
|
Super-fecundation It means fertilization of 2 ova discharged from the ovary at the same menstrual period by 2 separate acts of coitus committed at short intervals Medicolegal importance There may be the question of paternity as there is fertilization in two different sexual acts which can be confirmed by DNA testing of the fetus. |
|
Super-foetation It means fertilization of 2nd ovum in a woman who is already pregnant. |
.
Posthumous Child:
It is a child born after the death of its father, the mother being conceived by the said father.
Legal issues involved are:
- Legitimacy,
- Inheritance of property,
- Compensation case for slander against the mother.
Delivery:
It means expulsion or extraction of the child at birth.
Medico-legal importance of Delivery
- Abortion
- Infanticide
- Legitimacy
- Feigned delivery
- Divorce
- Blackmail
- Concealment of birth, etc.
Signs of recent delivery in Living / (In Dead too)
| 1. General indisposition: For the 1st 2 or 3 days, the woman is pale, ill-looking exhausted |
| 2. Breast changes: These are full, enlarged, and tender with a knotty feeling, and colostrum or milk may be expressed. The areolae are dark, nipples enlarged, and superficial veins prominent, striae gravidarum and Montgomery's tubercles are present. The presence of colostrum corpuscles in milk strongly indicates that delivery has taken place within a few days. |
| 3. The abdomen: The abdominal walls are pendulous, wrinkled, and show linea albicans, especially in flanks. They are irregular, white, or silvery subcutaneous scars. They are simply evidence of previous prolonged dissension of the abdomen. |
| 4. Perineum: It is sometimes lacerated |
| 5. Labia: They are tender, swollen, and bruised or lacerated. |
| 6. Vagina: Smooth-walled, relaxed, show recent tears which heals by 17 days. The rugae begin to reappear about the third week. |
| 7. The uterus: Immediately after delivery, the contracted and retracted body of the uterus feels like a hard muscular tumor, the upper border of which lies about 3 cm below the umbilicus. It then diminishes in size by about one-and-half cm a day. On the sixth day, it is midway between the umbilicus and pubis, by the 14th day at the level of the pubes and returns to normal condition in nine weeks. Uterus becomes normal in weight in 6 to 8 weeks. |
| 8. The Cervix: It is soft and dilated and its edges tom and lacerated transversely. The internal os begins to close in the first 24 hours. The external os is soft and patent and admits two fingers. At the end of a week, one finger is admitted with difficulty and is closed in two weeks. |
| 9. The Lochia: It is a discharge from the uterus which lasts for two or three weeks. It has a peculiar sour, disagreeable odor. During the first 4 to 5 days, the discharge is bright-red and contains large clots (lochia rubra). During the next four days, it becomes serous and paler in color (lochia serosa). After the ninth-day color becomes yellowish-grey or turbid (lochia alba) until its final disappearance. |
| 10. Intermittent Uterine Contractions: They are usually present for the first 4 to 5 days. |
| 11. If blood or urine gives a positive pregnancy test, it is strong corroborative evidence that pregnancy has recently been terminated. |
SIGNS OF REMOTE DELIVERY IN THE LIVING:
1. ABDOMEN:
The abdominal walls tend to be lax and show multiple white scars on the lateral aspects.
Linea nigra is commonly present.
2. BREASTS:
The breasts are lax, soft, and pendulous, frequently wrinkled if the woman has nursed her baby, and occasionally show linea albicans. The nipples are enlarged, the areolae dark, and Montgomery's tubercles are usually present.
3. VULVA:
The vagina is partially open as the labia do not completely close the orifice.
The perineum may show the scar of an old tear.
The vaginal rugae are absent and the walls are relaxed.
4. UTERUS:
The external OS shows an increase in the opening and depression at the site of the laceration.
The OS appears like a transverse slit, whereas in the virgin it is a small dimple in the middle of the cervix.
SIGNS OF REMOTE DELIVERY IN THE DEAD:
1. Uterus:
The uterus is larger, thicker, and heavier. The walls are concave from inside forming a wider and rounded cavity. The body of the uterus is twice the length of the cervix.
2. Cervix
Cervix is irregular in form and shortened cicatrices. The external OS is not well defined.
Complication of delivery
- Hemorrhage
- Shock (Neurogenic & hemorrhagic)
- Retention of placenta
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Infection- Inflection of vagina, cervix, uterus & peritoneum
- Septicemia & pyemia
Artificial insemination
It is the artificial introduction of semen into the vagina, cervix, or uterus to produce a pregnancy, unattained or unattainable by unnatural sexual intercourse is called Artificial insemination (about 5% male infertile)
Types:
1. A.I.H (Artificial Insemination Homologous/Husband)
2. A.I.D (Artificial Insemination Donor)
3. A.I.H.D (Artificial Insemination Husband & Donor)
Indication of A.I:
1. When the husband is impotent and sterile.
2. Hypospadias is and epispadias.
3. Rh incompatibility of husband and wife.
4. Husband is suffering from hereditary disease.
5. Double penis
Precaution of A.I:
1. Consent of husband and wife
2. Donor identity must be secreted
3. Donor must not know
4. Donor must be mentally and physically healthy and above 25 years
5. No relationship between Donor and Recipient due to the question of incest.
6. Race and character must same
7. Witness or 3rd person must be present
8. Consent of donor wife
9. Same blood group as husband and should not Rh incompatibility
10. There should not be more than 10 children of the same donor.
Complication of A.I:
1. Psychological (mother)
2. Mental trauma of children

Comments (0)