
A firearm is any weapon which discharges a missile by the expansive force of the gases produced by burning of an explosive substance.
Ballistic is the science of projectile & conditions affecting that motion
Forensic ballistics is the science dealing with the investigation of firearms, ammunition and the problems arising from their use.
Parts of Firearms
A. Stock/Butt
B. Breach
- Hammer
- Trigger & Trigger guard
- Front & Rear sight
- Safety catch
- Loading & emptying of chamber
C. Barrel (Hallow cylindrical length of gun)
- Chamber
- Taper/Leed (Anterior end of chamber is taper)
- Bore
The bore is a hallow cylindrical metallic tube extending from leed/taper end of chamber to the open end of weapon. (Inner Diameter of barrel is called bore)
- Muzzle (Anterior end of bore is muzzle end of barrel)
Bolt: Bolt is a sliding rod that pushes a cartridge into the firing chamber as it closes & locks.
Muzzle velocity: The velocity of missile as it emerges from muzzle end is known as muzzle velocity.
Classification of Firearm:
According to the condition of barrel:
A. Rifled weapons:
1) Rifles
- Air and gas-operated rifles.
- 0.22 rifles.
- Military and porting rifles.
2) Single-shot target-practice pistols
3) Revolvers
4) Automatic pistols
5) True automatic weapons (machine guns)
B. Smooth- bored weapons (shotgun).
1) Cylinder bore
2) Choke bore
3) Paradox (hammered, hammerless
4) Breech loader
5) Muzzle loader
6) Country made
According to firing action:
1) Over-bolt action
2) Under-bolt action
3) Lever action
4) Pump action or autoloading model
Rifle:
A rifle is a gun with a long barrel, the bore of which is rifled.
Rifling
Grooving on the inner surface of barrel of firearm is known as rifling.
Grooving are twisted spirally from breach to muzzle. (4-7 in number)
Importance of rifling
Rifling gives the bullet a spinning motion
Greater power of penetration
A straight course (trajectory) and
Prevents it from unsteady movement as it travels in the air.
Choking/Choking of barrel
In some smooth-bored guns, the terminal few cm (7-10 cm) of the bore near the muzzle end is slightly constricted. This is called choking of the barrel.
Advantage of choking
Effective range & penetration capacity of pellets are increased.
Cartridge
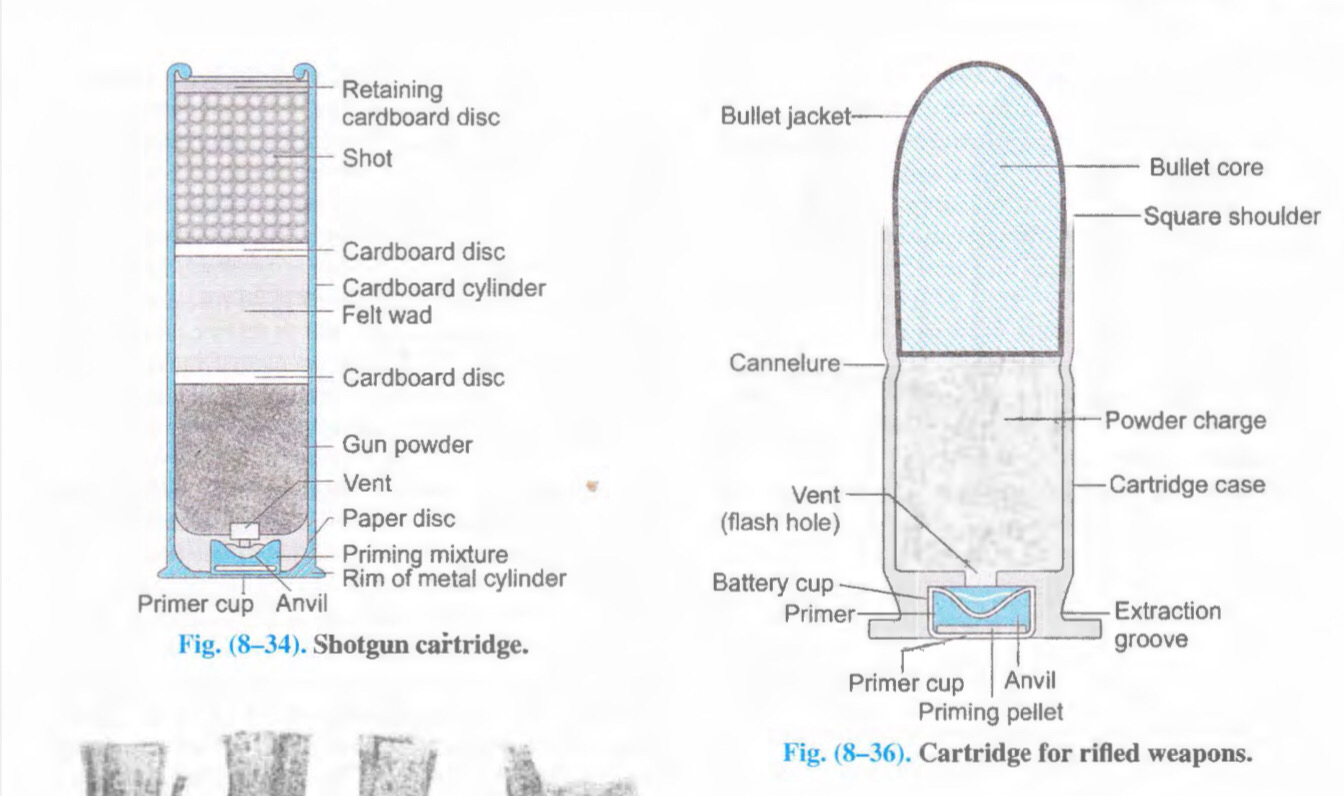
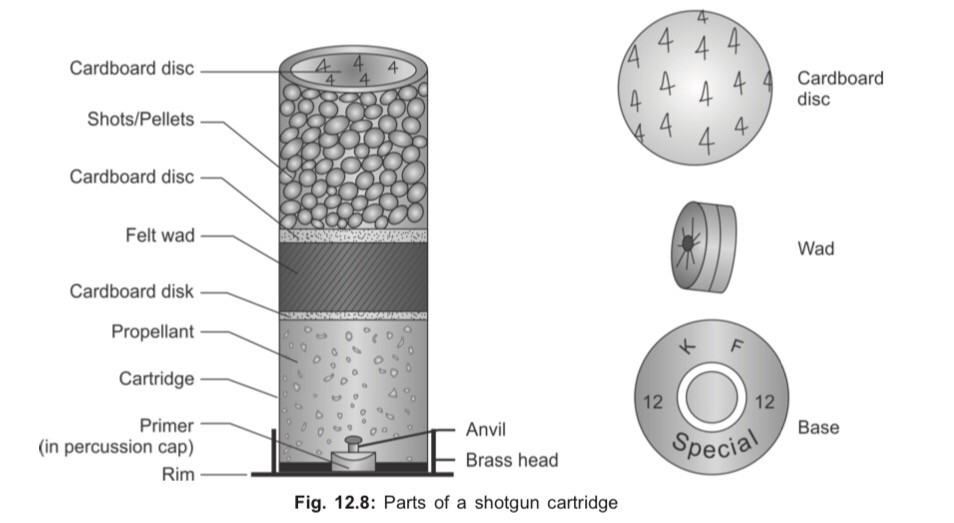
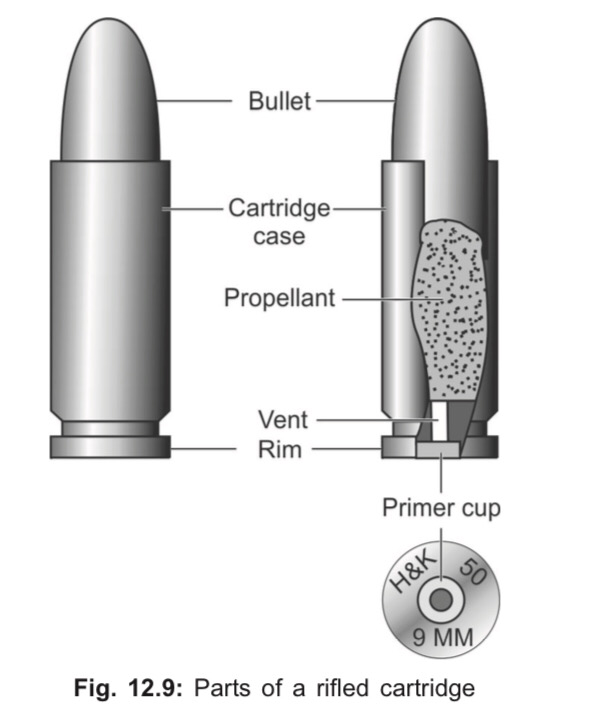
Cartridge consists of:
i. Cartridge case with percussion cap containing primer
ii. Propellant charge (gunpowder)
iii. Projectile (bullets/pellets)
iv. Wads (in smooth bore weapons only)
Blank cartridge:
Cartridge with primer, gunpowder and wadding, but without any bullet.
It is used in:
Starter pistol in sports
Stage/movie performance
For signaling
Training purpose
Gun powder
It is the mixture of explosive substances which propels the bullet forward by the enormous pressure created as a result of expansion of gases by its explosion.
Types & composition
1. Smokeless power- composed of nitrocellulose/nitroglycerin
2. Black powder- composed of Potassium nitrate (75%), Charcoal (15%), Sulfur (10%)
3. Semi-smokeless - Black powder (80%) & Smokeless powder (20%)
Primer is the highly explosive mixture in percussion cap at the base of cartridge.
Bullet
Bullet is the projectile of a rifled firearm that leaves the muzzle when it discharges.
RICOCHET BULLET:
A ricochet bullet is one which before striking the object aimed at, strikes some intervening object first, and then after recocheting and rebounding (glancing) from these, hits the object.

Comments (0)