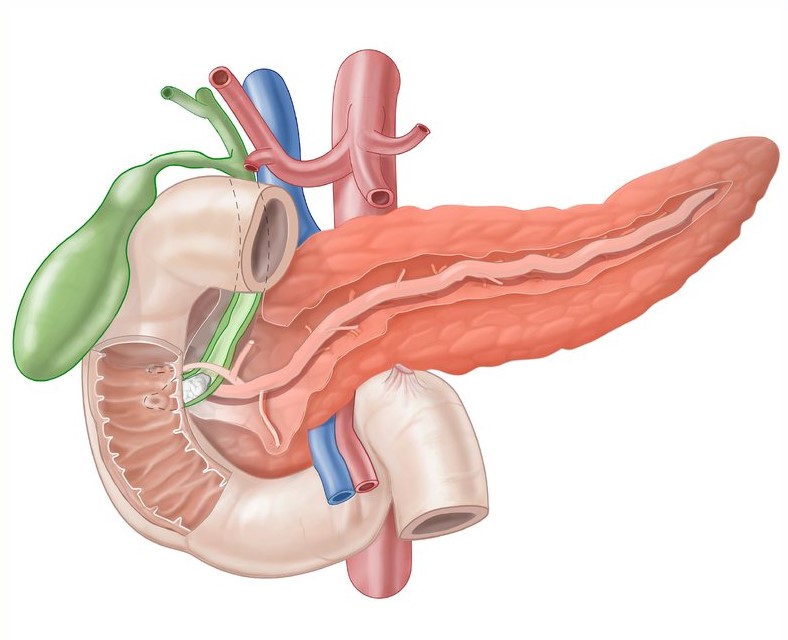
Pancreas
The pancreas is a soft lobulated gland, consisting of both exocrine and endocrine parts with very little connective tissue.
Situation: It occupies the posterior part of the epigastrium and left hypochondrium.
The pancreas is a mixed gland because it has both exocrine and endocrine parts. The function of the exocrine part is the secretion of pancreatic juice and the endocrine part is the secretion of the hormone.
Structure of the pancreas:
- Exocrine part of the pancreas
- Endocrine part of the pancreas
The Exocrine part of the pancreas is a compound racemose gland & is devoid of a definite fibrous capsule. The intercalary duct is lined by flattened epithelium. The junction between the alveolus & the duct is lined by cubical cells which are known as centro-acinar cells.
The Endocrine part of the pancreas is composed of numerous islets of Langerhans. About one million or more islets are found in the human pancreas & they are more numerous in the tail.
There present 4 types of major cells:
| Alpha cell: Secrete glucagon, which is diabetogenic. |
| Beta-cell: Secrete insulin, which is anti-diabetogenic. |
| Delta cell: Secrete somatostatin, which inhibits the release of both glucagon & insulin. |
| PP cell: Secrete pancreatic polypeptide hormone, which stimulates the secretion of gastric & intestinal enzymes & inhibits intestinal motility. |
Two minor cell types are also found in the periphery of the islets cell mass:
D1 cell: Secrete vasoactive intestinal polypeptide.
Enterochromaffin cell: Secrete serotonin.
Presenting Parts of Pancreas:
- Head
- Neck
- Body
- Tail
Junction between head and neck In front, separated by the groove for gastro-duodenal artery and behind, by the right margin of the groove for the portal vein.
Junction between body and tail - In front, not distinguishable; behind, separated by the junction of peritoneal and non-peritoneal areas.
Description of the parts:
HEAD: It is enlarged and lies at a lower level than the body, opposite L1 and L2 vertebrae.
It presents -
| 2 surfaces | Anterior & Posterior |
| 4 borders | Upper,lower,right & left |
| 1 process | Uncinate process |
Uncinate process: It is a triangular projection that arises from the lower and left parts of the head.
It is related -
| Anteriorly: Superior mesenteric vessels |
| Posteriorly: Abdominal Aorta |
| Superiorly: Left renal vein |
Relation of the anterior surface of the Head:
| Upper part related with transverse colon. |
| Lower part related with coils of jejunum |
| In front of the uncinate process related with Superior mesenteric vessels. |
Relation of the posterior surface of the head:
It is non-peritoneal and related to the-
- IVC and both renal veins
- Right crus of the diaphragm
- Bile duct
NECK: It connects the head with the body and is about 2 cm long. It presents-
- 2 surfaces - Anterior & Posterior
- 2 borders - Upper & lower
Posterior relation of the neck-
It is non-peritoneal and presents a shallow groove that contains a superior mesenteric vein in the lower part and a trunk of the portal vein in the upper part.
BODY: It is prismoid in appearance, triangular on cross-section, and extends from the front of the aorta to the front of the left kidney.
It presents -
Three surfaces
a) Anterior(anterosuperior),
b) Inferior (antero-inferior)
c) Posterior
Three borders
a) Superior
b) Anterior
c) Inferior
Relation of the posterior surface of the body-
It is non-peritoneal and related with-
| Abdominal aorta with the origin of superior mesenteric artery |
| Left crus of the diaphragm |
| Left psoas major & sympathetic trunk |
| Left suprarenal gland |
| Left kidney across its hilum |
| Left Supra-renal and left gonadal veins |
| Splenic vein |
Superior border
Close to the right and presents a conical projection known as tuber omentale.
Anterior border
It gives attachment to the root of the transverse mesocolon.
Inferior border
Superior mesenteric vessels emerge under the cover of the right end of this border.
TAIL: It is the most mobile part of the gland. It passes between the layers of the lieno-renal ligament and reaches the spleen and lies opposite the lower border of T12 vertebrae.
Pancreatic Duct:
- Main duct ( duct of Wirsung )
- Accessory duct ( duct of Santorini )
Artery supply of Pancreas:
Head and Neck of the pancreas are supplied by the ventral and dorsal anastomosis of superior and inferior pancreatico-duodenal arteries.
Body and tail are supplied by the pancreatic branches of the splenic artery.
Venous drainage:
These correspond to the arteries and drain into the superior mesenteric, splenic & into the trunk of portal veins.
Lymphatic drainage:
Head & neck drain into ventral and dorsal groups of pancreatico-duodenal lymph nodes.
Body & tail drain into pancreatico-splenic lymph nodes.
Nerve supply of Pancreas:
Sympathetic: Derived from superior mesenteric and coeliac plexus.
Parasympathetic: Derived from both vagus nerves.
Development of pancreas:
The pancreas is developed in two parts, Dorsal & Ventral.
Dorsal bud: Whole of the neck, body, and tails of the pancreas, and the upper part of the head are developed from here.
Ventral bud: Lower part of the head & uncinate process are developed from here.
Also read: Anatomy Question Collection
Also read: Anatomy Questions & Answers
Also read: Anatomy notes

Comments (0)