Extension & length
| 1st part (5 cm) Extends from the pylorus to the superior duodenal flexure |
| 2nd part (7.5 cm) Begins at the superior duodenal flexure as a continuation of the first part opposite to the L1 vertebrae and ends at the inferior duodenal flexure opposite to the lower border of the L3 vertebrae |
| 3rd part (10 cm) Extends from the inferior duodenal leads to the front of the aorta at the level of L3 vertebrae |
| 4th part (2.5 cm) Extends from the front of the aorta to the duodenojejunal flexure |
Duodenojejunal flexure:
Situated on the left side of L2 vertebrae, about 1.25cm below the transpyloric plane & 2.5 cm to the left of the median plane.
This flexure is kept in position by the suspensory muscle of the duodenum.
Relation of 1st Part of Duodenum
| In Front - (Peritoneal) • Quadrate lobe of the liver • Neck & body of the gall bladder |
| Behind - (Non-peritoneal) • Portal vein, bile duct & gastroduodenal artery • Inferior vena cava |
| Above - Lesser omentum |
| Below - Greater omentum |
Peculiarities of 1st part od Duodenum
| Most movable part |
| Supplied by end arteries |
| May be affected by the peptic ulcer |
| Devoid of circular mucous fold |
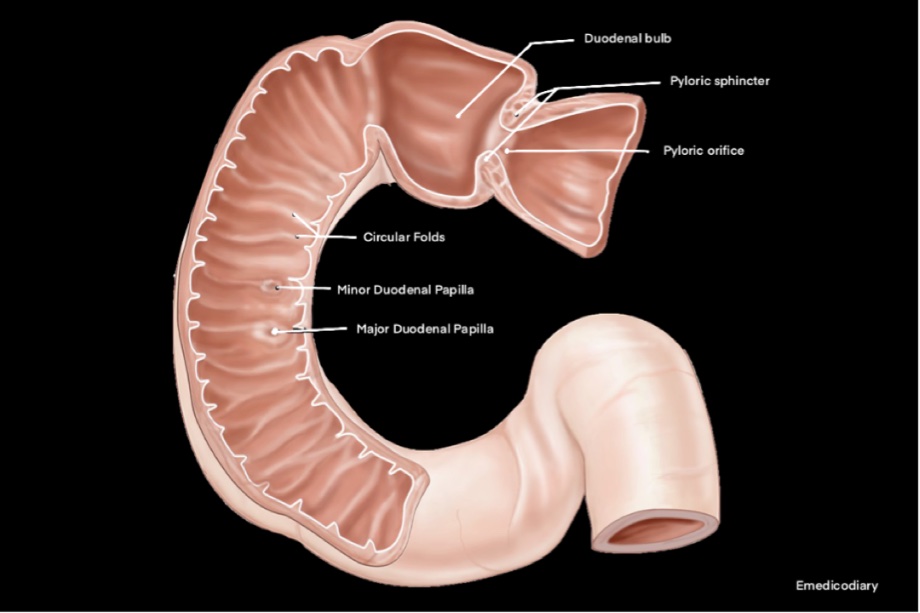
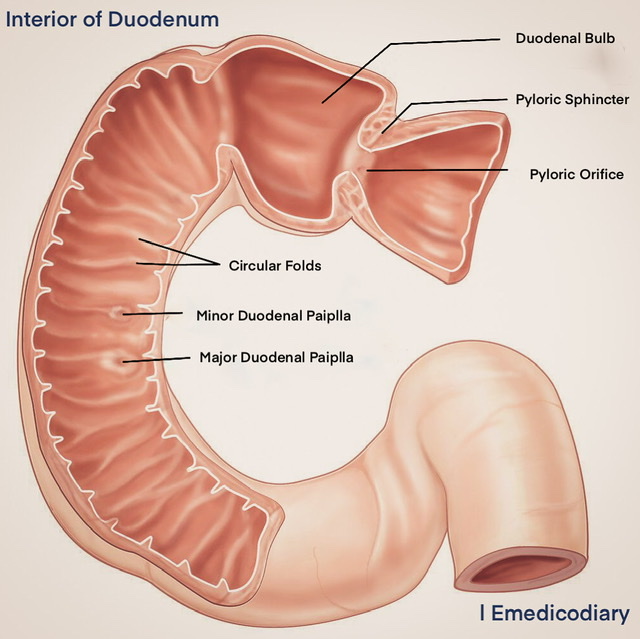
| A triangular radio-opaque shadow known as the "Duodenal cap"/"Duodenal bulb" may be observed in the first part after the Barium meal. |
Artery Supply of 1st part: Basically by the End arteries
| Supra-Duodenal branch of gastroduodenal artery: Supplies upper margin, upper 2/3 of the anterior surface, upper 1/3 of the posterior surface |
| Retroduodenal branch of gastroduodenal artery: Supplies a part of the posterior surface |
| Infra-Duodenal branch of right gastro-epiploic artery: Supplies the lower margin |
Relation of 2nd Part of Duodenum
| In front - Duodenal impression of the right lobe of the liver, fundus & body of the gall bladder - Transverse colon - A few coils of jejunum |
| Behind Anterior surface of the right kidney Right renal vessels, pelvis of the right ureter Right psoas major muscle Right edge of the inferior vena cava Sometimes, a part of the right suprarenal gland |
| Laterally - Right colic flexure |
| Medially Head of the pancreas Bile duct & the main pancreatic duct |
Interior of 2nd part of Duodenum
| Circular fold (Plica circularis) |
| Major Duodenal Papilla - conical projection arising from the posteromedial wall of the second part. Situated about 8-10 cm distal to the pylorus. |
| Minor Duodenal Papilla - small conical projection situated about 2 cm above and slightly ventral to the major papilla. Accessory pancreatic duct opens on its summit in 10% of cases. |
| Plica semicircularis |
| Plica longitudinalis |
Relation of 3rd part of Duodenum
| In front- (peritoneal except where it is crossed by mesentery) Superior mesenteric vessels & root of the mesentery |
| Behind - (non-peritoneal) Right psoas major muscle Right ureter Right gonadal vessels Inferior vena cava Abdominal aorta Inferior mesenteric artery |
| Above - Head of the pancreas Inferior pancreatico-duodenal vessels |
| Below- A few coils of the jejunum |
Structure of Duodenum:
| Serous coat is derived from the peritoneum. |
| Muscular coat consists of outer longitudinal and an inner circular layer of smooth muscle; separated by Myenteric (Auerbach's) plexus of nerves. |
| Submucous coat consists of loose areolar tissue; contains Meissner's plexus, Duodenal gland of Brunner. Racemose type of gland (CHARACTERISTICS OF DUODENUM). Secrets Bicarbonate rich fluid & an enzyme helps in the activation of trypsinogen. |
| Mucous membrane - within outwards surface epithelium, lamina propria & muscularis mucosa. |
| Surface epithelium - Simple columnar cell, occasionally goblet cells Lamina propria contains - Crypts of Lieberkuhn. |
Artery Supply:
- 1st part Supplied by the End arteries
- Rest of the parts by ventral & dorsal anastomoses of superior & inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
Venous Supply:
Corresponding to arteries & drain into superior mesenteric vein & into the trunk of the portal vein
Lymphatic Drainage:
Drain into the pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes. Efferent vessels drain into coeliac & superior mesenteric groups of pre-aortic lymph nodes.
Nerve Supply:
- Sympathetic from coeliac & superior mesenteric plexus & from T6-T9
- Parasympathetic from both vagus. Auerbach's & Meissner's plexus act as parasympathetic only.
Development:
| Mucous membrane of duodenum above & including Ampulla to Vater from:- Endoderm of Foregut |
| Mucous membrane below the Ampulla of Vater from- Endoderm of Midgut |
| The musculature & the other structures from- Splanchnic layer of the lateral plate Mesoderm. |
Clinical Facts
| First part of the duodenum is vulnerable to the formation of the peptic ulcer |
| Second part is most protected from external injuries. But sometimes small bile stones may be impacted on the summit of major papilla which produces obstructive jaundice. |
| Third part is most vulnerable to external injuries because it may be compressed between the vertebral column. |
| A loop of the small gut may Herniate into any of the recesses of the Fourth part of the duodenum. If the gut fails to return the internal hernia, thus formed produces Intestinal obstruction. |
Also read: Anatomy Question Collection
Also read: Anatomy Questions & Answers
Also read: Anatomy notes

Comments (0)