Epithelium/Connective Tissues Histology
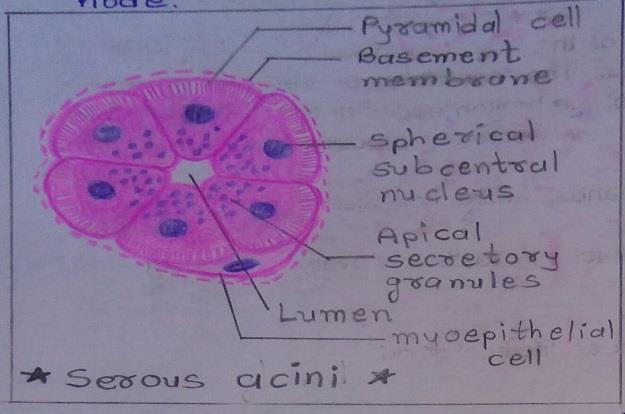
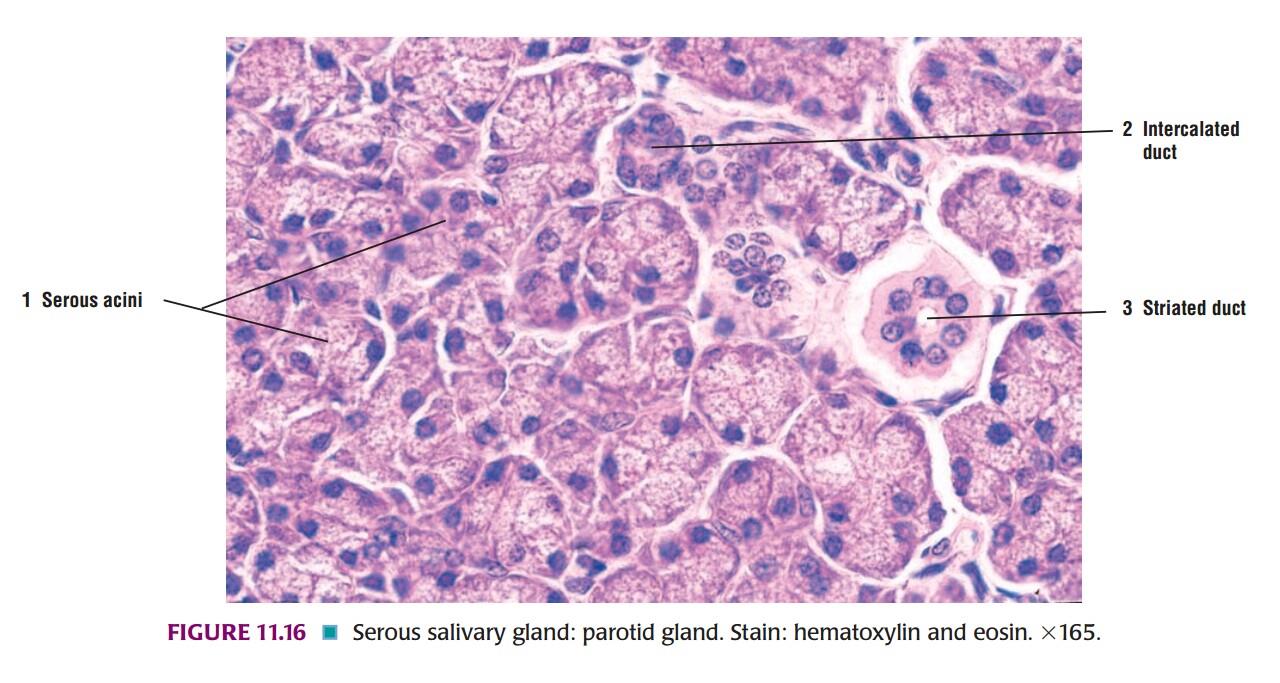
Slide 1: SEROUS GLAND
DRAWING:
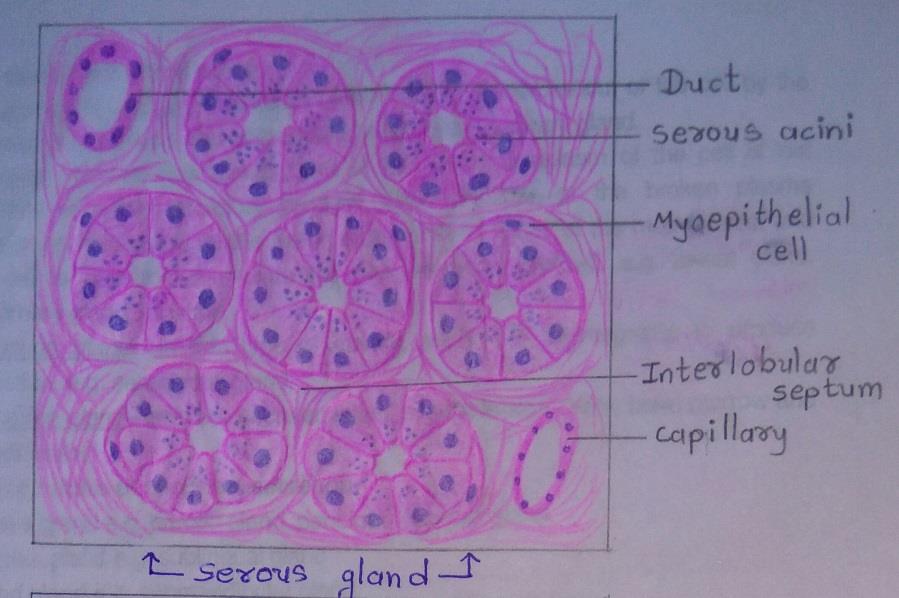
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINT:
| 1. Triangular cells with rounded nuclei. |
| 2. Their nuclei are centrally placed. |
| 3. Cell boundaries are indistinct. |
| 4. Lumen of these acini is smaller than the mucous acini. |
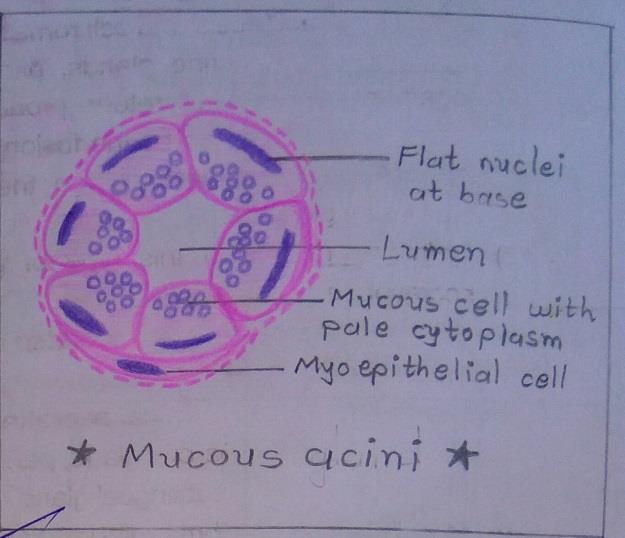
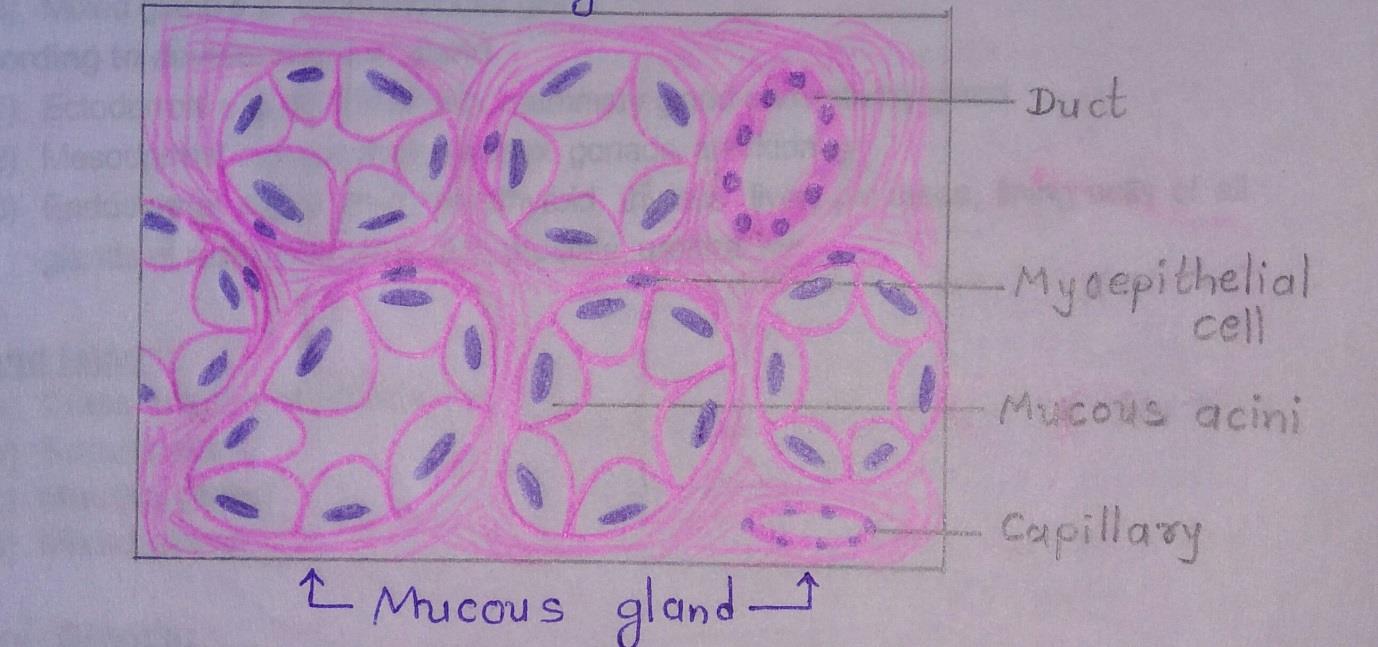
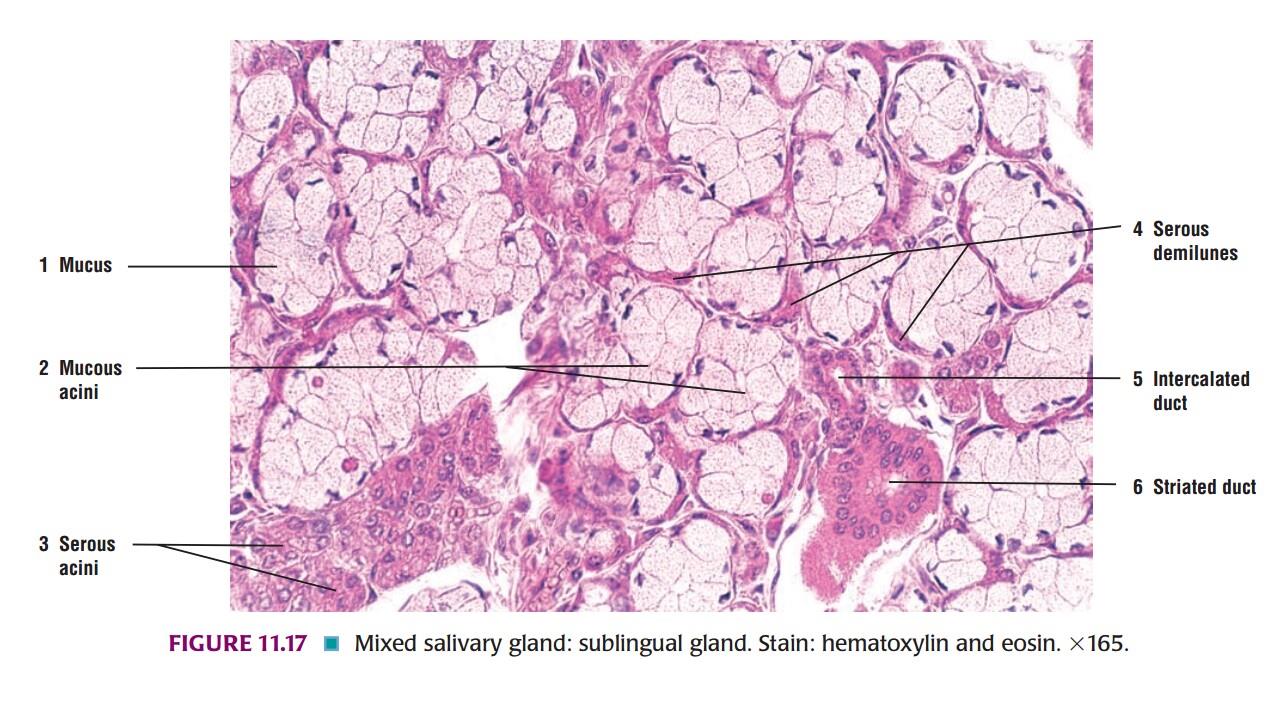
Slide 2: MUCOUS GLAND
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. Tall cells with flat nuclei at their base. |
| 2. Cell boundaries are distinct. |
| 3. Lumen of these acini is larger than the serous acini. |
| 4. Lightly stained and appear empty with H & E staining. |
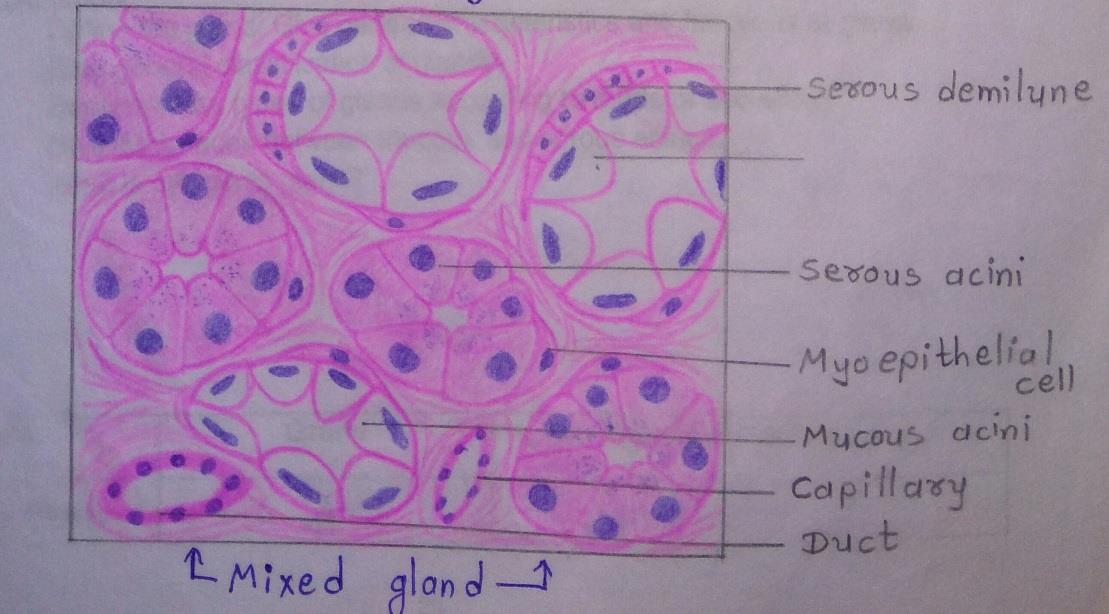
Slide 3: MIXED GLAND
DRAWING:
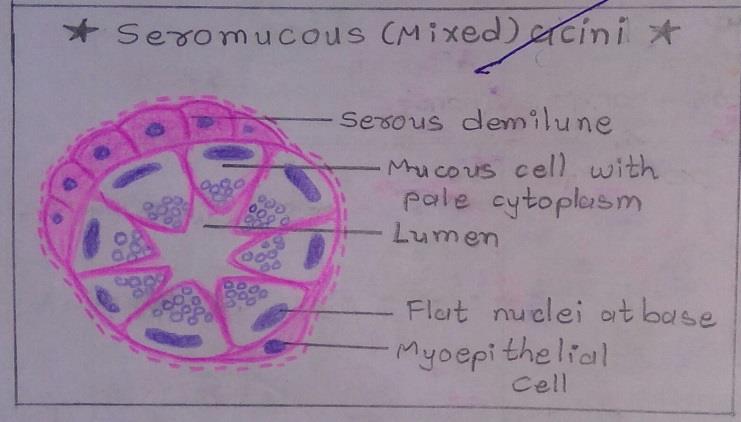
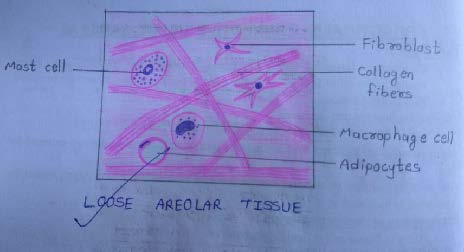
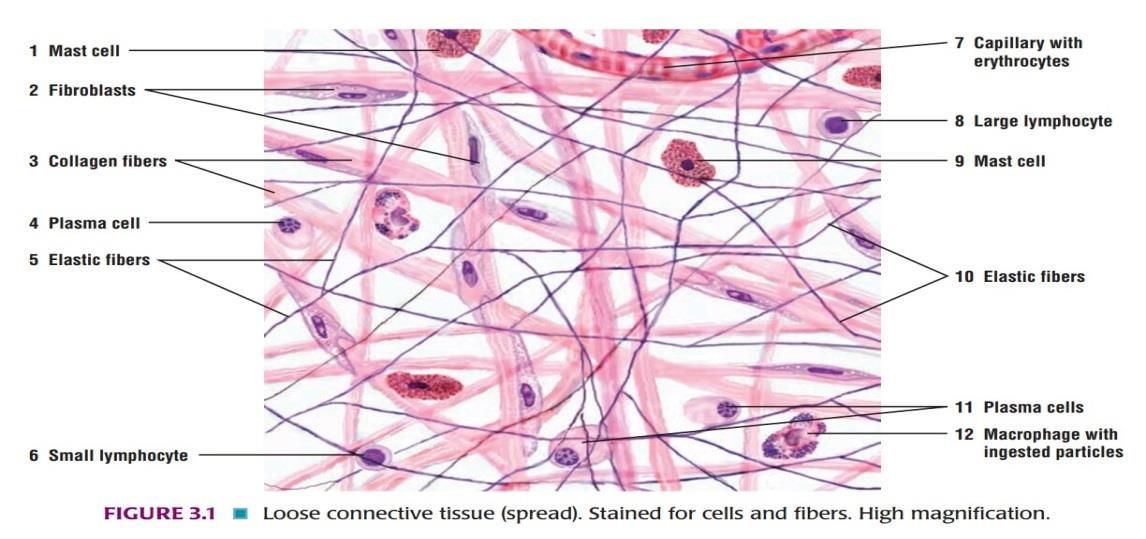
Slide 4: LOOSE AREOLAR TISSUE
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
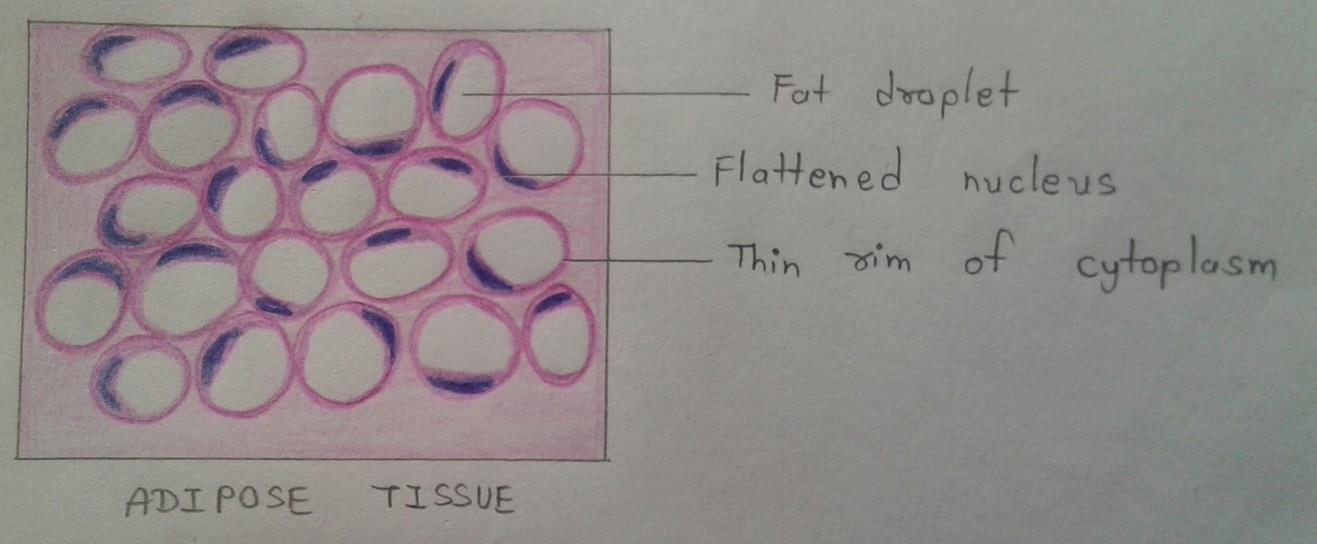
Slide 5: ADIPOSE TISSUE
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
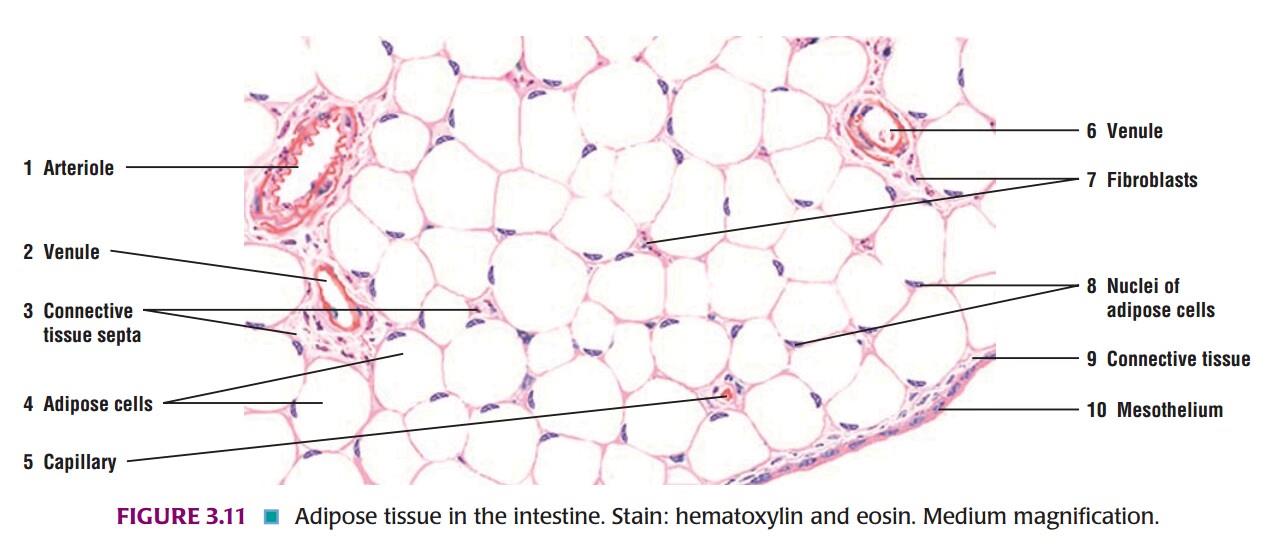
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. The cytoplasm of each cell is seen as a pink rim. |
| 2. The nucleus is flat and lies to one side(eccentric). |
| 3. In routine sections, the cells appear empty, giving it a honeycomb appearance. |
Slide 6: MUCOID TISSUE
DRAWING:
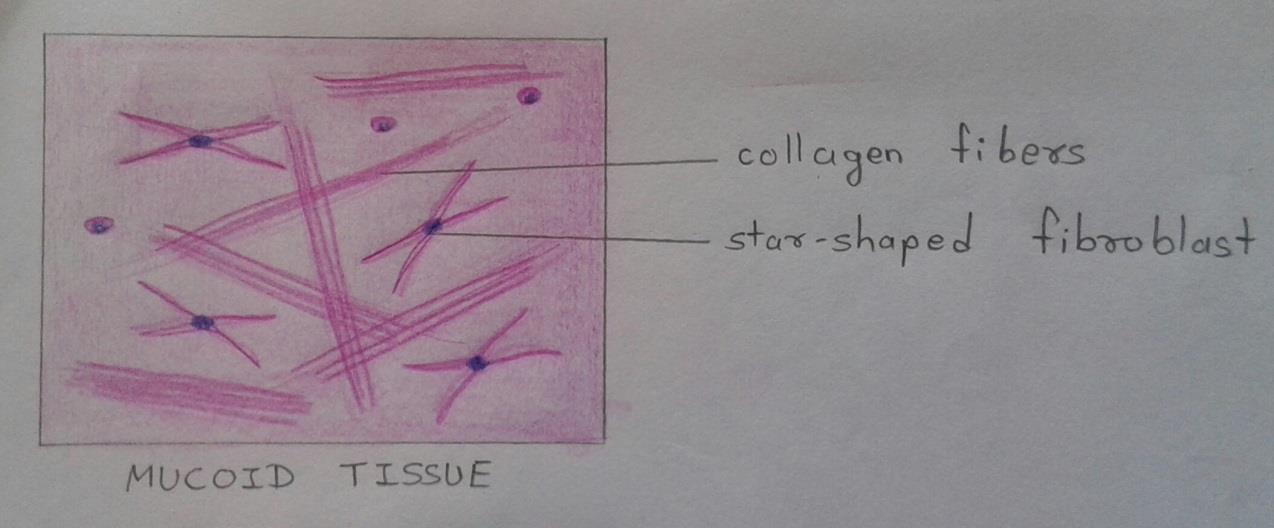
IDEAL SLIDE:
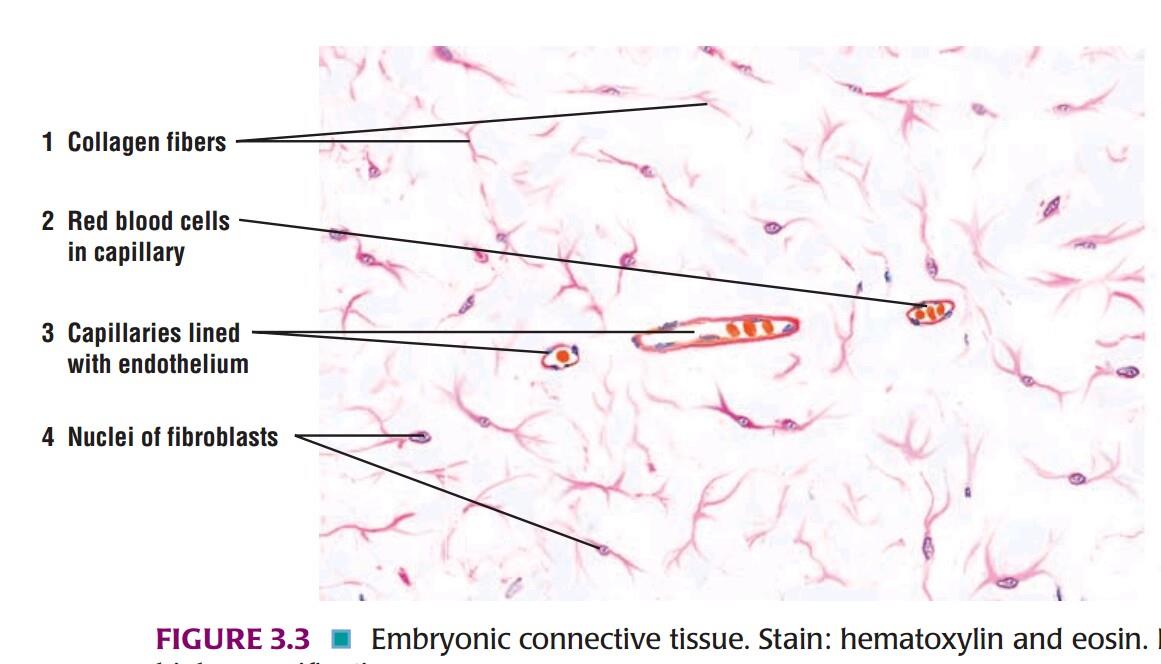
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. Component of mucoid tissue is a jelly-like group substance rich in hyaluronic acid. |
| 2. Scattered and star-shaped fibroblasts, some delicate collagen fibers, and some rounded cells. |
Slide 7: RETICULAR TISSUE
DRAWING:
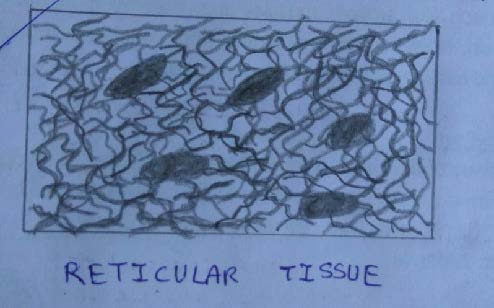
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. It contains abundant reticular fibers. |
| 2. Reticular fibers are composed of collagen type 3. |
| 3. They differ from typical collagen fibers as follow: • They are much finer and have uneven thickness. • They form a network by branching, and by anastomosing with each other. • Reticular fibers stained black with silver impregnation but type 1 collagen fibers stained brown with silver impregnation. |
Cartilage Histology
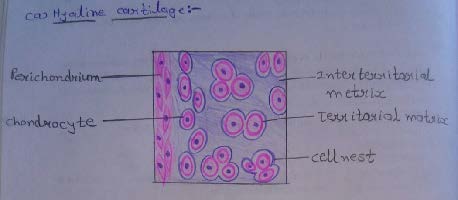
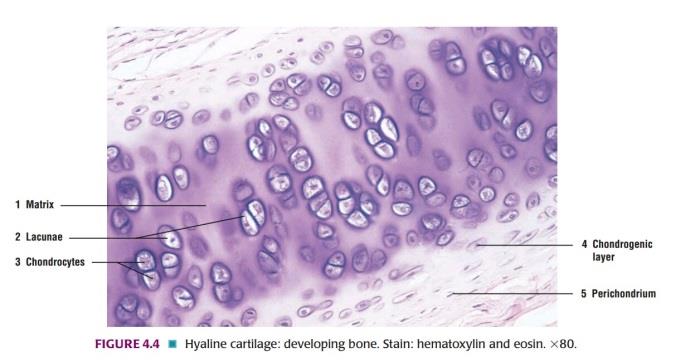
Slide 8: HYALINE CARTILAGE
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. There is a presence of isogenous cell groups of chondrocytes called as cell nest. |
| 2. Its intercellular substance appears to be homogenous. |
| 3. In H & E staining, the matrix is stained blue. |
| 4. Around cell nests, the matrix stains deeper than elsewhere is called the territorial matrix or lacunar capsule. |
| 5. The pale staining matrix separating cell nests is the interstitial matrix. |
| 6. Chondrocytes increase in size from periphery to center. |
| 7. Near the surface of the cartilage the cells are flattened and merge with the cells of the overlying connective tissue. This connective tissue forms the perichondrium. |
| 8. Using special techniques, it can be shown that many collagen fibers are present in the matrix. |
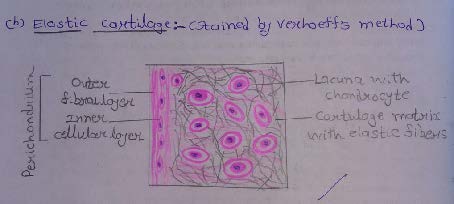
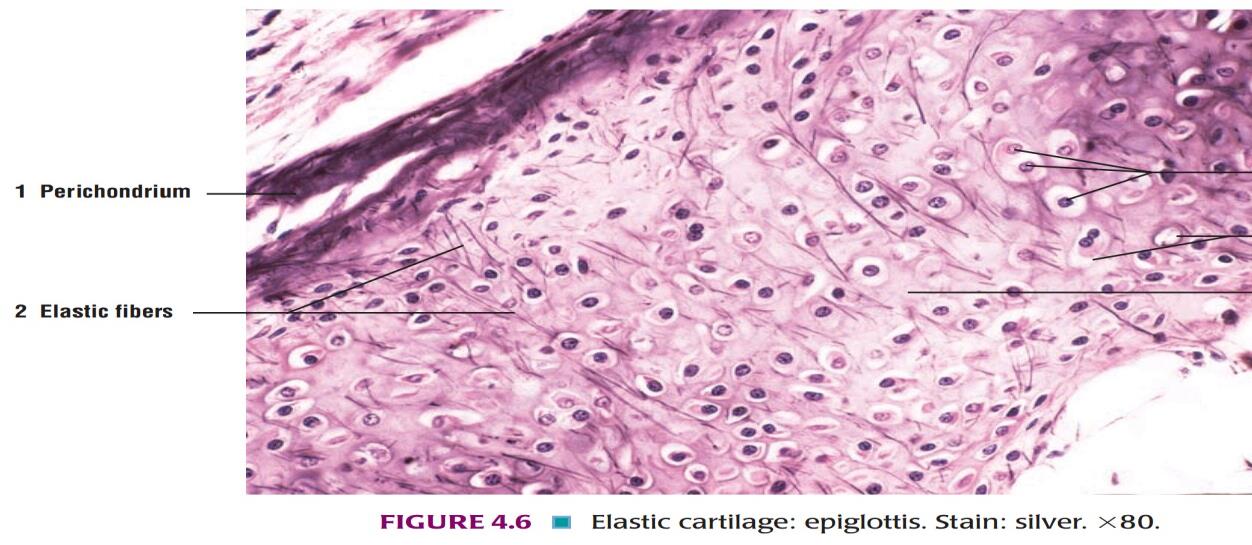
Slide 9: ELASTIC CARTILAGE
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. The main difference between hyaline cartilage and elastic cartilage is that instead of collagen fibers, the matrix contains numerous elastic fibers that form a network. |
| 2. The elastic fibers are difficult to see in H & E stained sections, but they can be clearly visualized if special methods for staining elastic fibers are used. |
| 3. Elastic cartilage is characterized by the presence of chondrocytes within the lacuna surrounded by bundles of elastic fibers. |
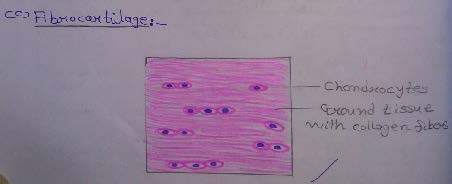
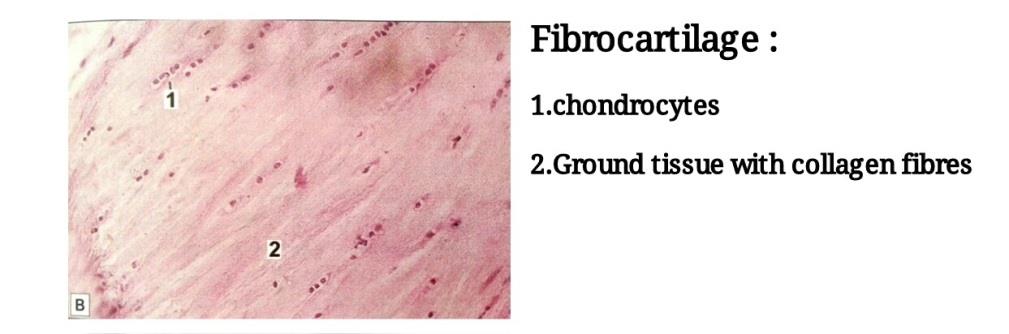
Slide 10: FIBROCARTILAGE
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. Presence of prominent collagen fibers arranged in bundles with rows of chondrocytes intervening between the bundles. |
| 2. Perichondrium is absent. |
| 3. This kind of cartilage can be confused with the appearance of a tendon. However, the chondrocytes in fibrocartilage are rounded but, in a tendon, fibrocytes are flattened and elongated. |
| 4. The collagen in fibrocartilage is different from that in hyaline cartilage in that it is type 1 collagen and not type 2. |
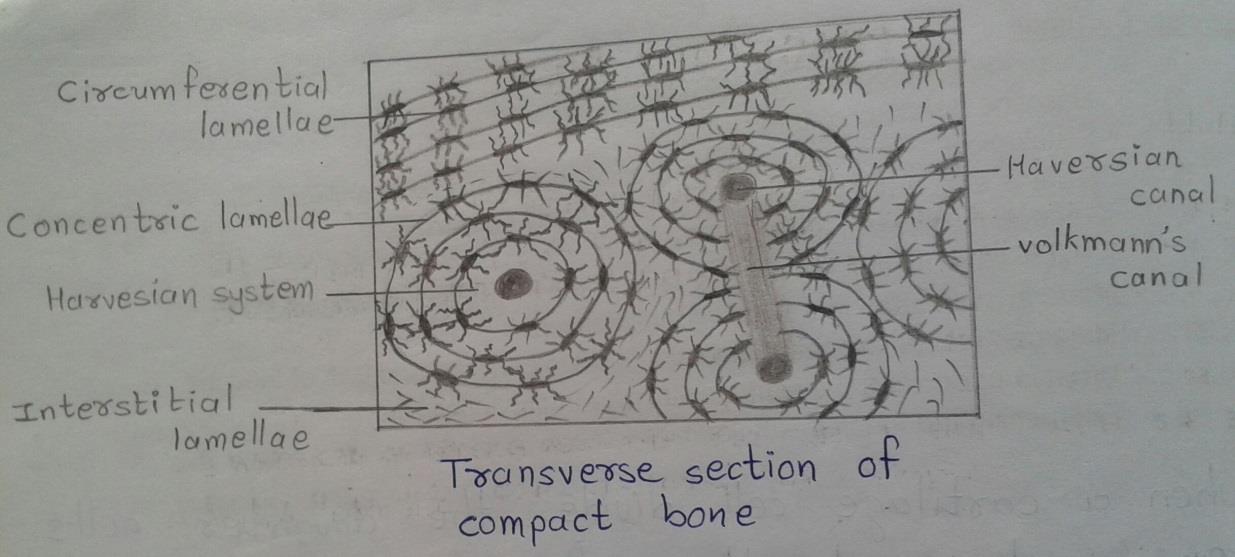
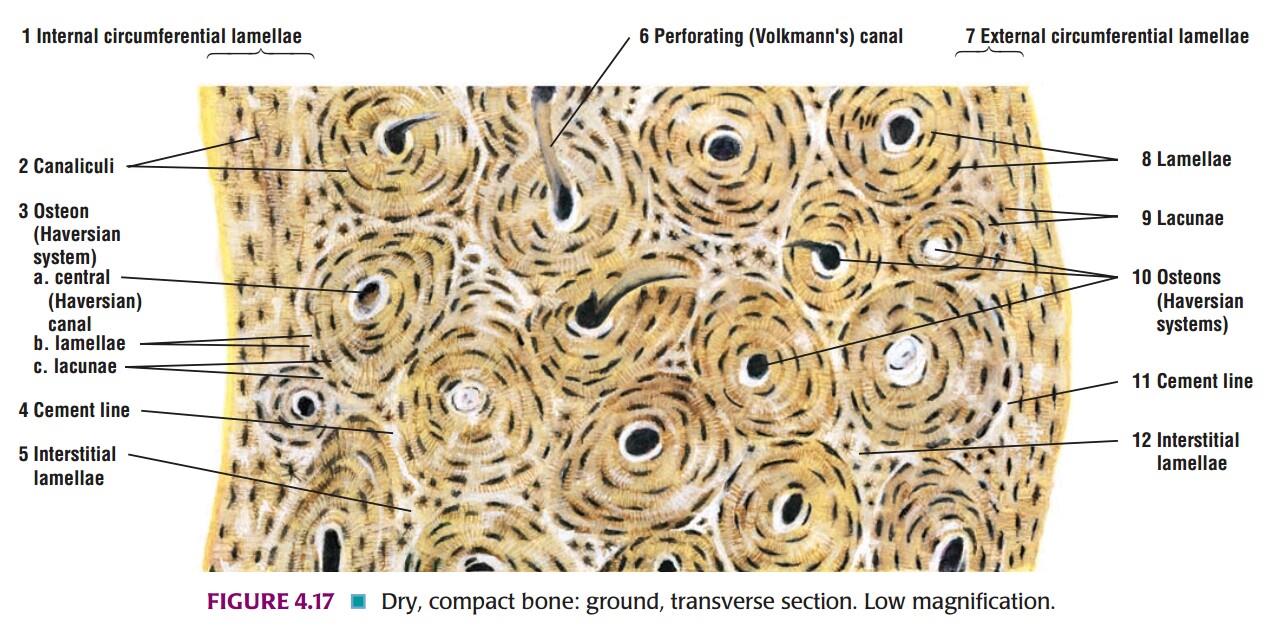
Slide 11: Transverse Section OF COMPACT BONE
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. A transverse section through compact bone shows ring-like osteons. |
| 2. At the center of each osteon there is a Haversian canal. |
| 3. Around the canal there are concentric lamellae of bone amongst which there are small spaces called lacunae. |
| 4. Delicate canaliculi radiate from the lacunae; these contain cytoplasmic processes of osteocytes. |
| 5. Interstitial lamellae fill intervals between Haversian systems. |
| 6. Near the surface of compact bone, the lamellae are arranged in a parallel manner. These are circumferential lamellae. |
| 7. Volkmann`s canal interconnecting the adjacent Haversian canal may be seen. |
Bone Histology
Slide 12: Longitudinal Section of COMPACT BONE
DRAWING:
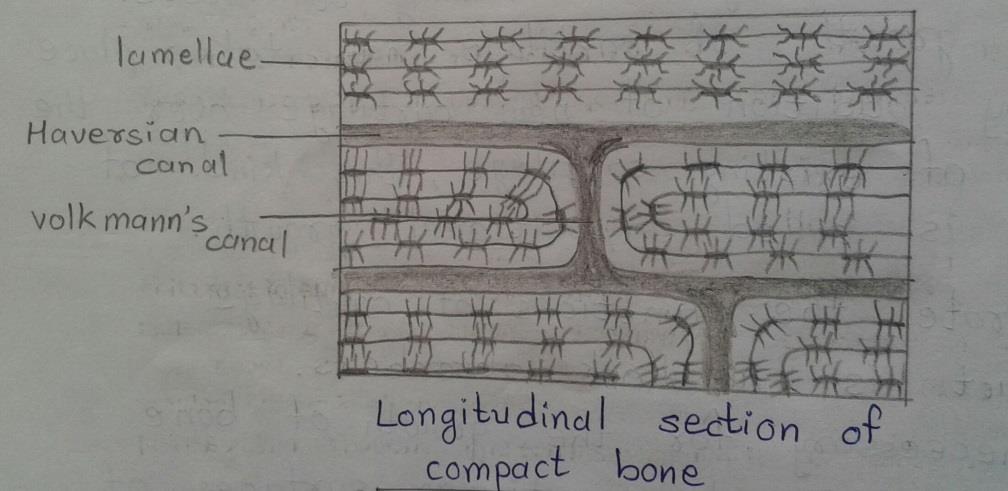
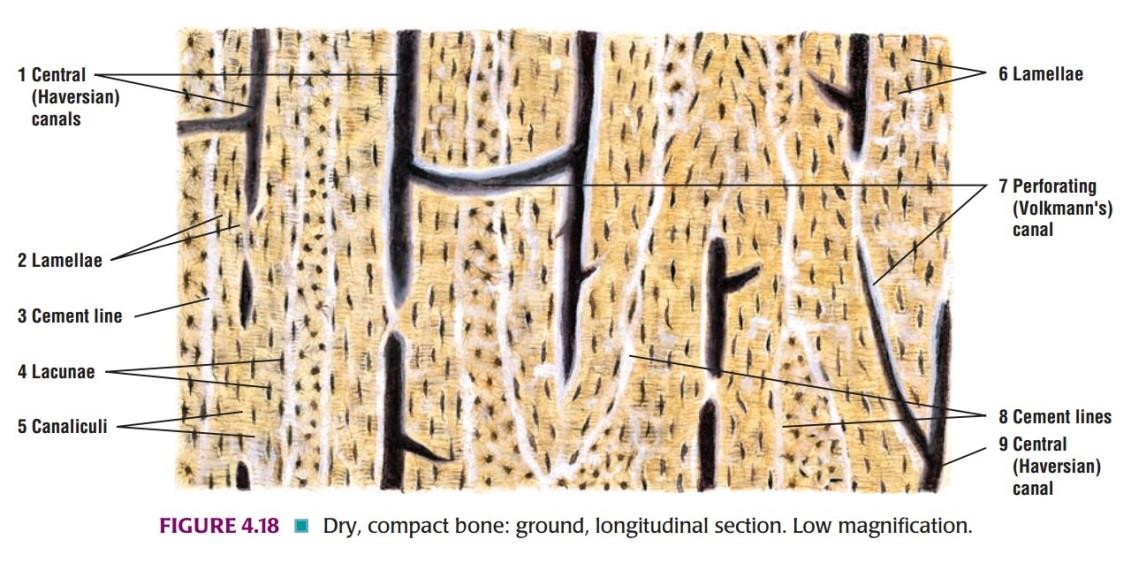
IDEAL SLIDE:
Slide 13: DEVELOPING BONE
DRAWING:
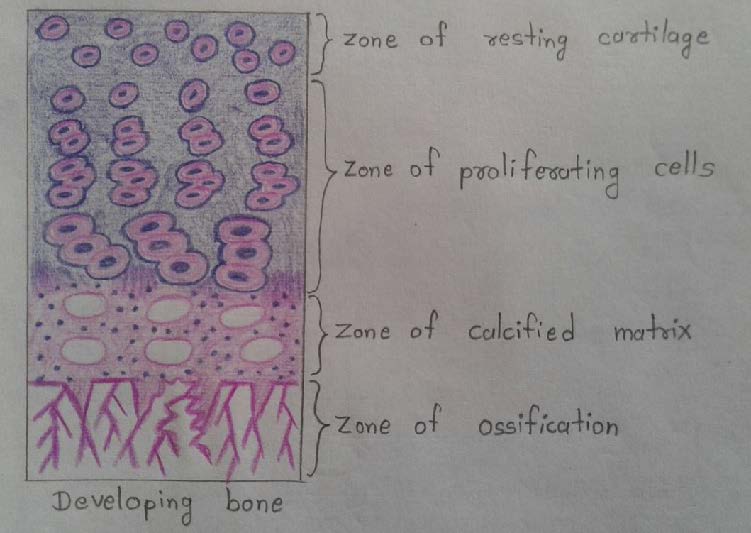
IDEAL SLIDE:
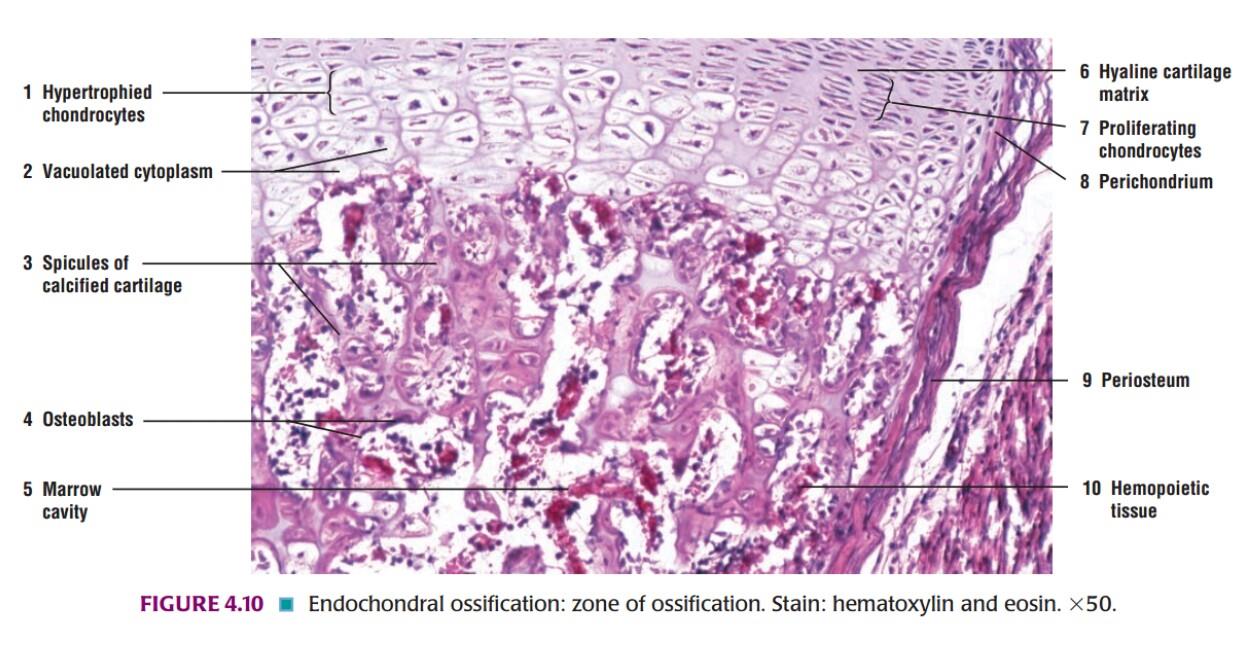
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| In the zone of resting cartilage, the cells are small and irregularly arranged. |
| In the zone of proliferative cartilage, the cells are larger and undergo repeated mitosis. |
| As they multiply, they come to be arranged in parallel columns, separated by bars of intercellular matrix. |
| In the zone of calcification, the cells become still larger and the matrix becomes calcified. |
| Next to the zone of calcification, there is a zone where cartilage cells are dead and the calcified matrix is being replaced by bone. |
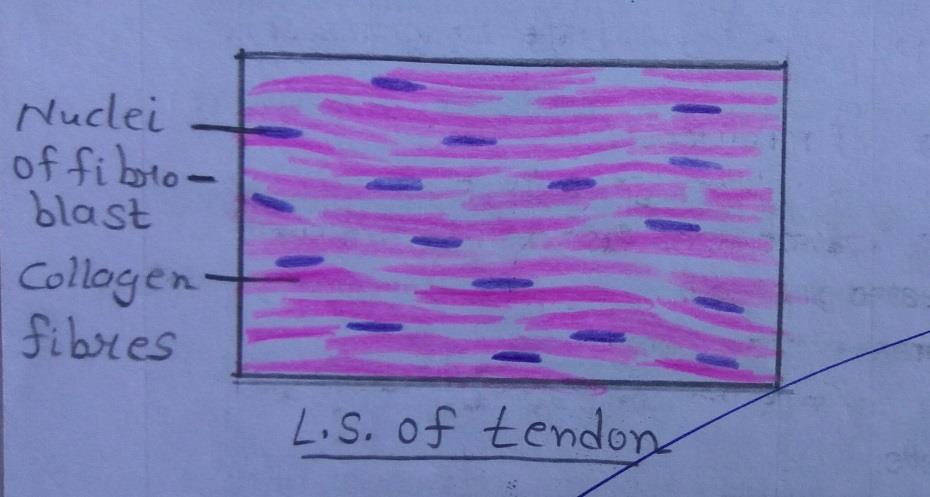
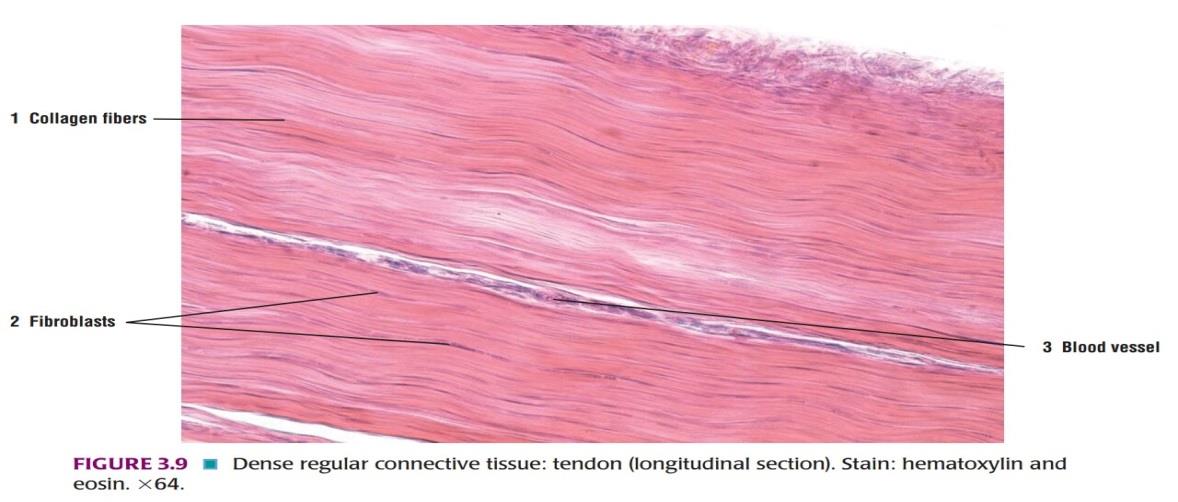
Slide 14: Longitudinal Section OF TENDON
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. Presence of collagen fibers arranged in orderly fashion parallel to each other. |
| 2. In the longitudinal section of the tendon, the fibroblasts and their nuclei are seen to be elongated. |
| 3. Ground substance is less in amount. |
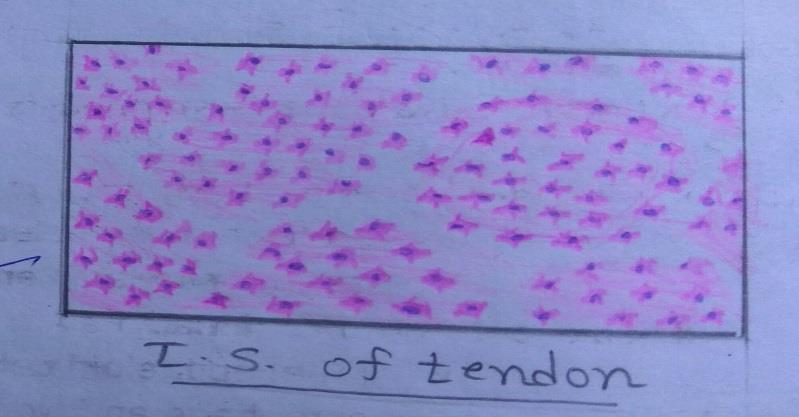
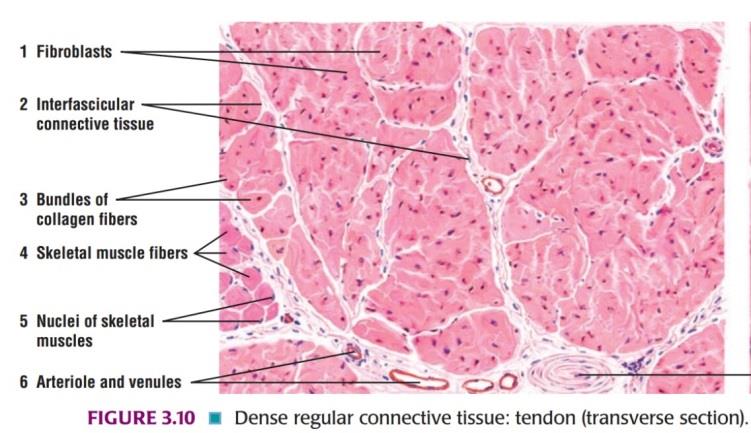
Slide 15: Transverse Section of TENDON
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1. In transverse sections, the fibroblasts are stellate shaped. |
| 2. Ground substance is less in amount. |

Comments (2)