Nervous, Eye, Ear (Systemic Histology 4)
5 years ago 9493
Plate 78: CEREBRUM
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
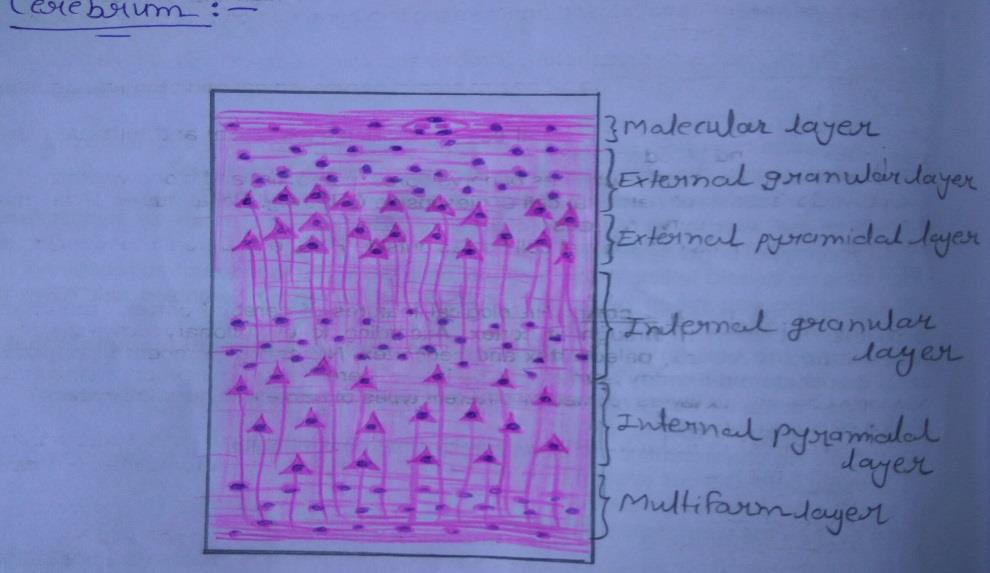
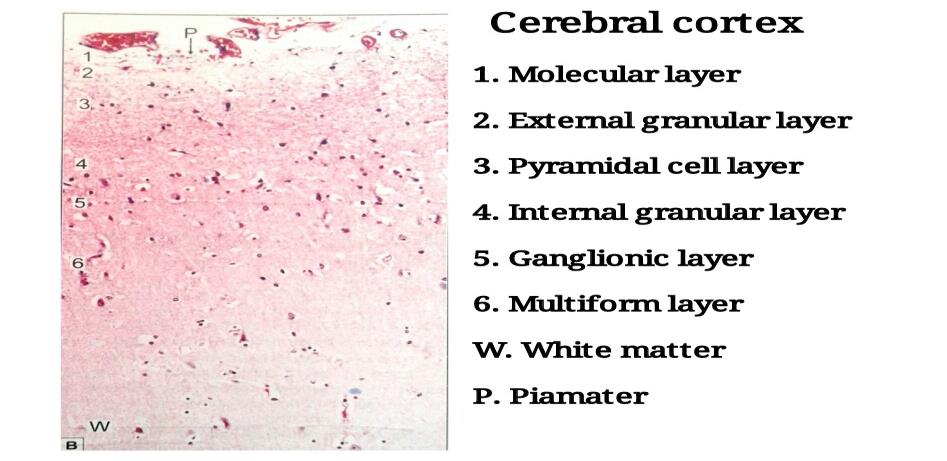
| 1) A slide of the cerebral cortex shows outer grey and inner white matter. Multipolar neurons of various shapes are arranged in six layers in the grey matter. |
| 2) From the superficial surface downwards, these laminae are: ? Plexiform or molecular layer ? External granular layer ? Pyramidal cell layer ? Internal granular layer ? Ganglionic layer ? Multiform layer |
| 3) The plexiform layer is made up predominantly of fibres although a few cells are present. |
| 4) The external and internal granular layers are made up predominantly of stellate cells. |
| 5) The predominant neurons in the pyramidal layer and ganglionic layer are pyramidal. |
| 6) The largest pyramidal cells are found in the ganglionic layer. |
| 7) The multiform layer contains cells of various sizes and shapes. |
Plate 79: CEREBELLUM
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
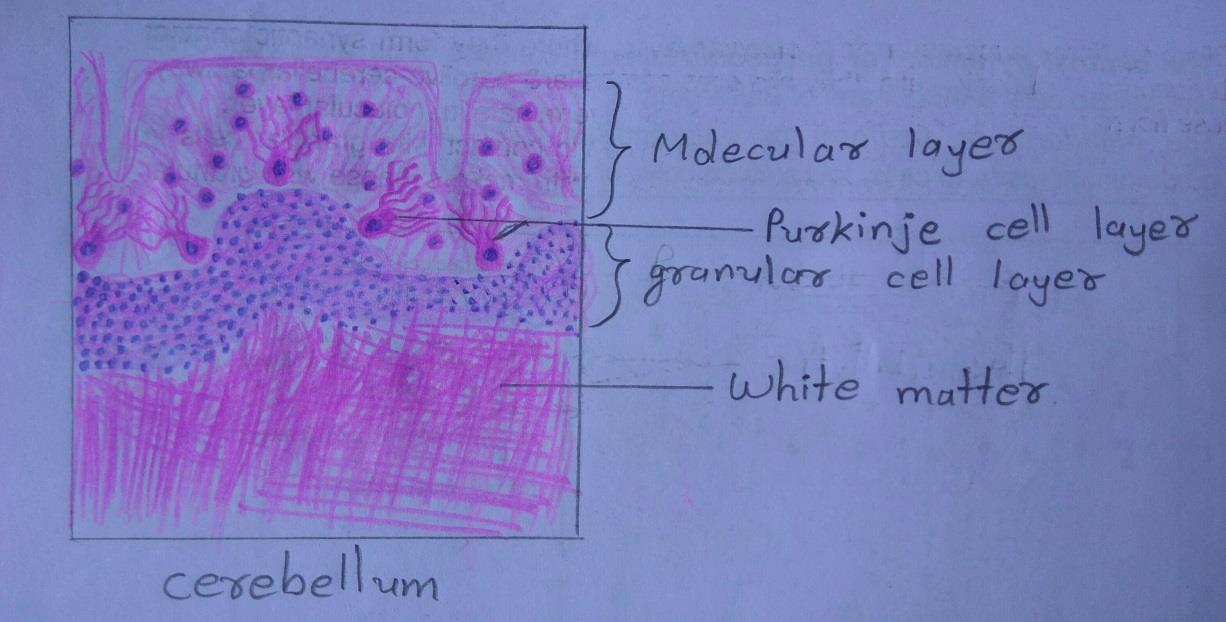
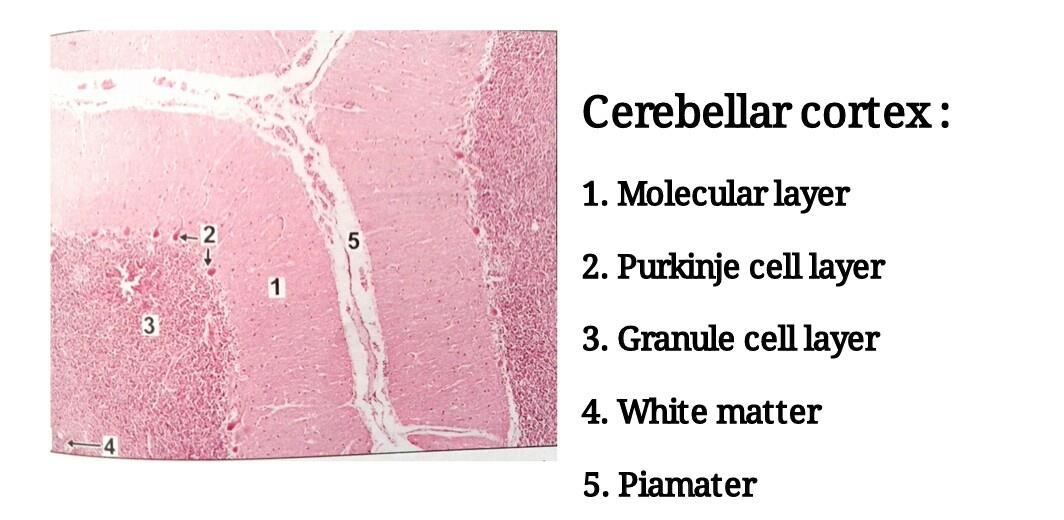
| 1) The section of the cerebellum shows leaf-like folia. |
| 2) The cortex is covered by piamater which appears as a thin layer of collagen fibres. Blood vessels may be seen just beneath the piamater. |
| 3) Outer grey mater is arranged in three layers from without inwards: Ø Molecular layer- very few nuclei of neurons seen. Many cell processes present. The appearance of the layer is pale. Ø Purkinje cell layer- single layer of big flask-shaped pink neurons Ø Granular cell layer- appears very dark blue because of presence of abundant nuclei of neurons. |
| 4) Inner white matter shows axons which appear as pink fibers. |
| 5) Nuclei of neuroglia are present both in grey and white matter. |
Plate 80: SPINAL CORD
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
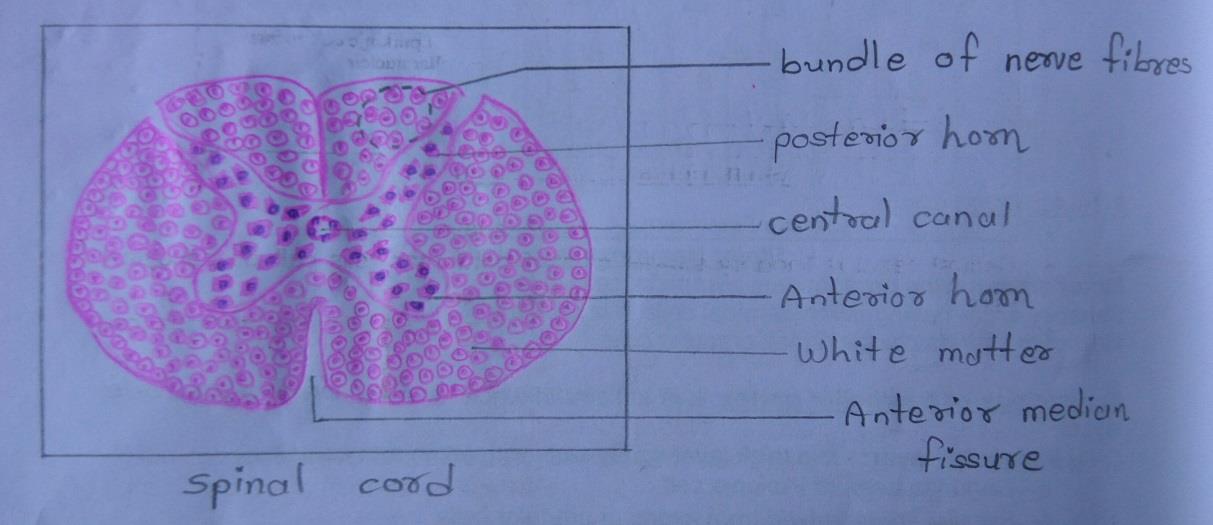
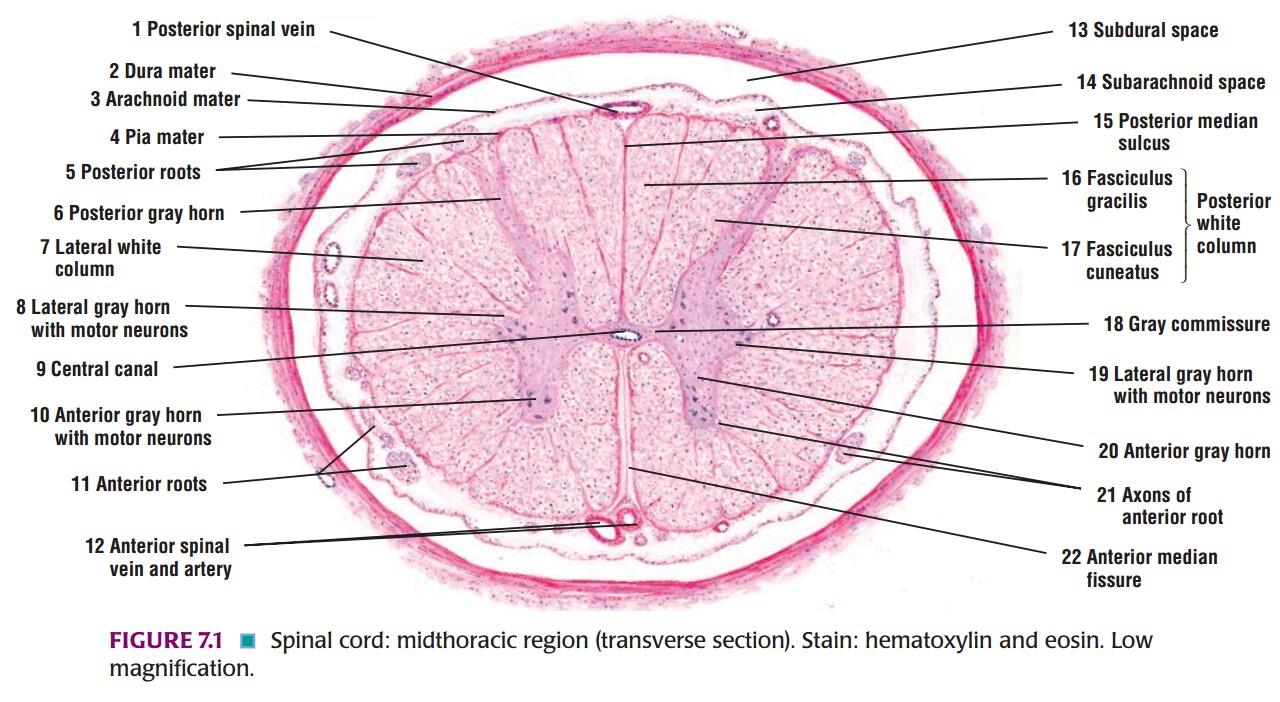
| 1) The spinal cord has a characteristic oval shape. It is made up of white matter which containing mainly of myelinated fibres; and grey matter which containing neurons and unmyelinated fibres. |
| 2) The grey matter lies towards the center and is surrounded all round by white matter. |
| 3) The grey matter consists of a centrally placed mass and projections(horns) that pass forwards and backward. |
| 4) The grey matter of the right and left halves of the spinal cord is connected across the middle line by the grey commissure that is traversed by the central canal. |
| 5) The central canal of the spinal cord contains cerebrospinal fluid. The canal is lined by ependyma. |
Plate 81: SENSORY GANGLIA
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
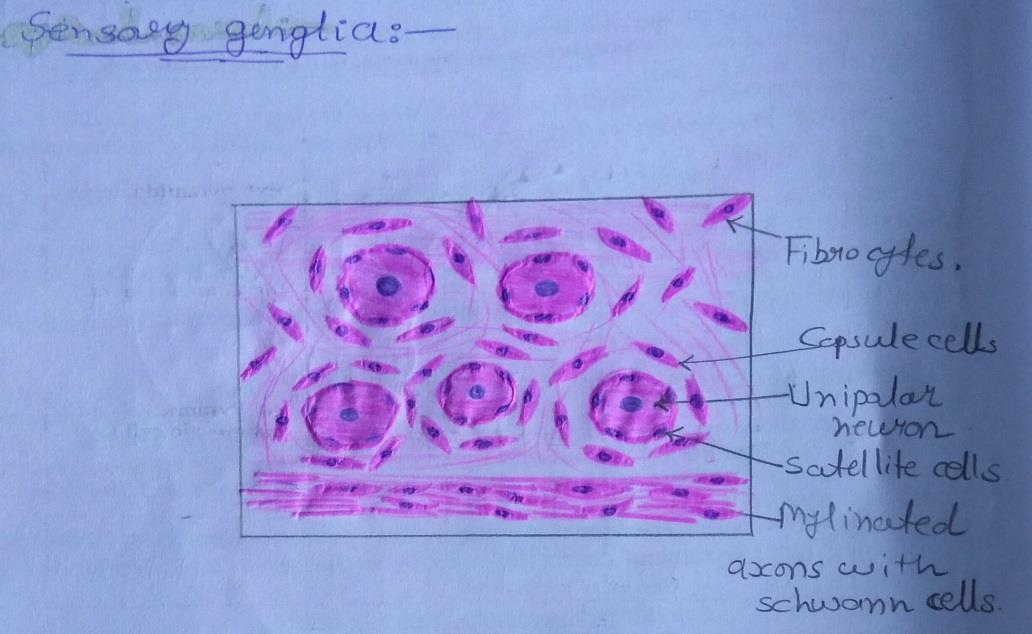
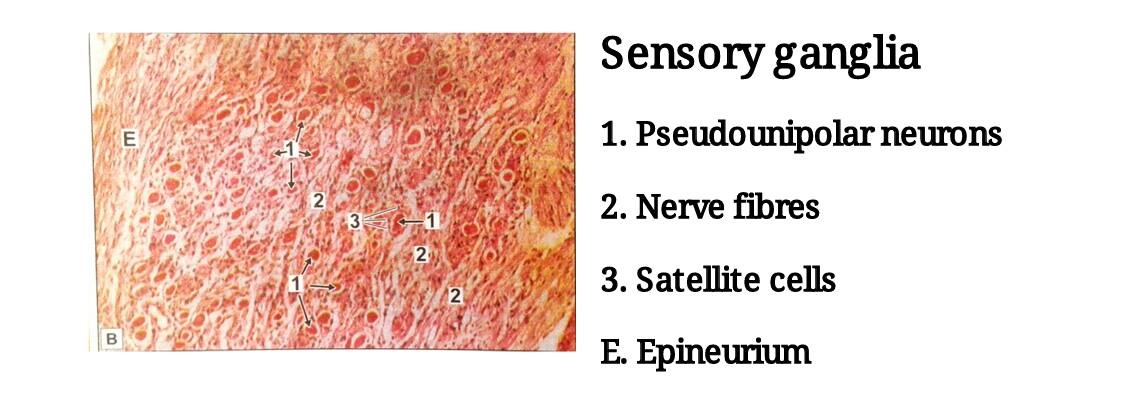
| 1) In H & E stained sections the neurons of sensory ganglia are seen to be large and arranged in groups chiefly at the periphery of the ganglion. |
| 2) The neurons of sensory ganglia can be seen to be unipolar. |
| 3) The groups of cells are separated by groups of myelinated nerve fibres. |
| 4) The cell body of each neuron is surrounded by a layer of flattened capsular cells or satellite cells. |
| 5) Outside the satellite cells there is a layer of delicate connective tissue. |
Plate 82: AUTONOMIC GANGLIA
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
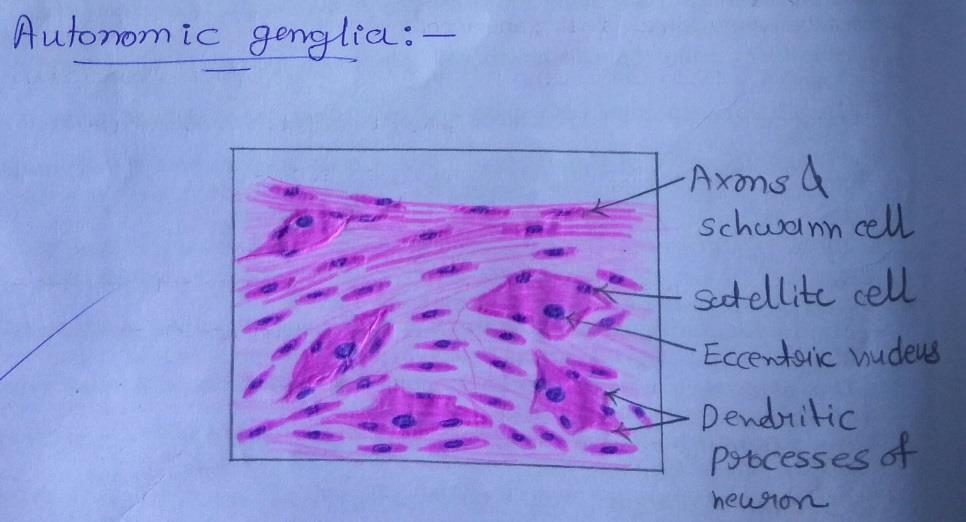
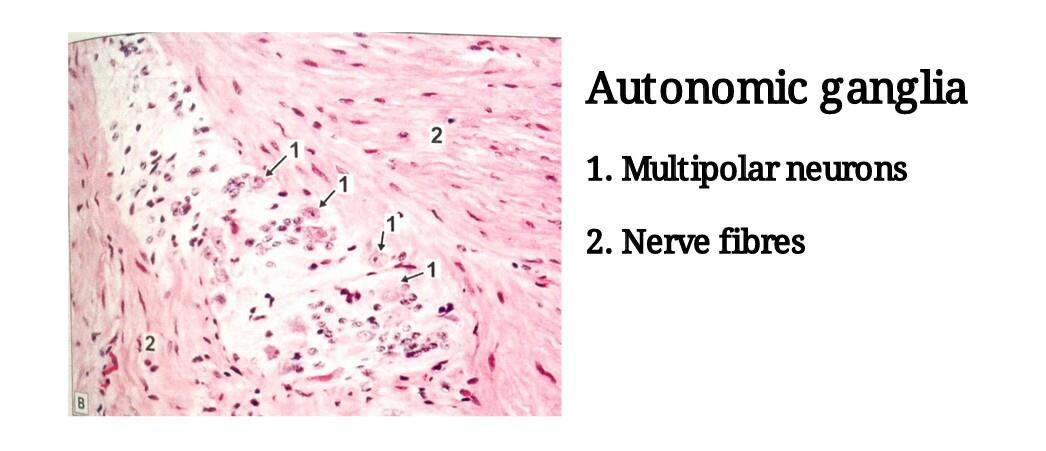
| 1) The neurons of autonomic ganglia are smaller than those in sensory ganglia, they are seen to be multipolar. |
| 2) The neurons are not arranged in definite groups as in sensory ganglia, but are scattered throughout the ganglion. |
| 3) The nerve fibers are non-myelinated and thinner. |
| 4) Satellite cells are present around neurons of autonomic ganglia, but they are not so well defined. |
Eye
Plate 83: CORNEA
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
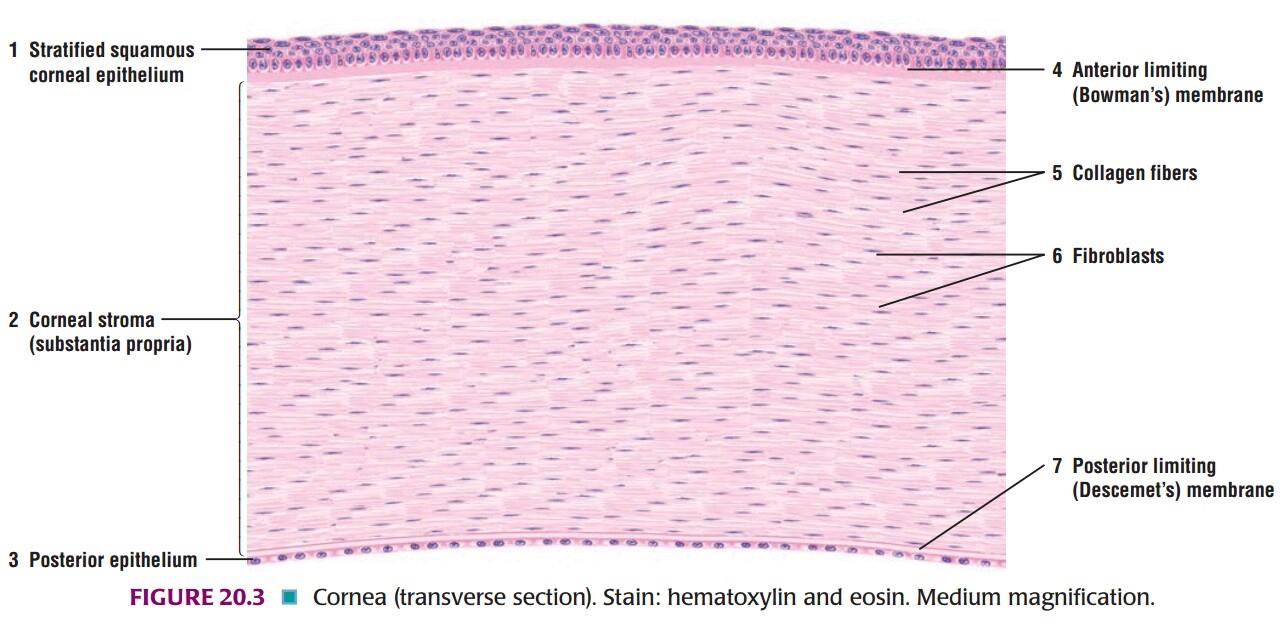
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
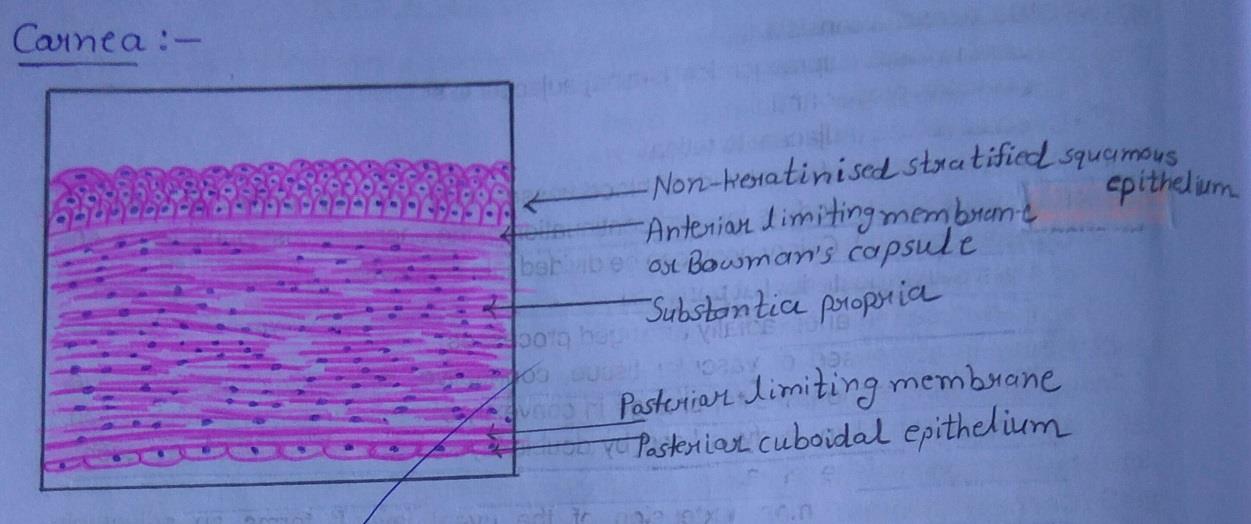
| 1) The cornea is made up of five layers: |
| Ø The outermost layer is of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. |
| Ø The corneal epithelium rests on the structureless anterior limiting lamina [also called Bowman`s membrane] |
| Ø Most of the thickness of the cornea is formed by the substantia propria made up of collagen fibres embedded in a ground substance. |
| Ø Deep to the substantia propria there is a thin homogenous layer called the posterior limiting lamina. |
| Ø The posterior surface of the cornea is lined by a single layer of flattened or cuboidal cells. |
| 2) The structure of the cornea is fairly distinctive and its recognition should not be a problem. |
Plate 84: EYELID
DRAWING:
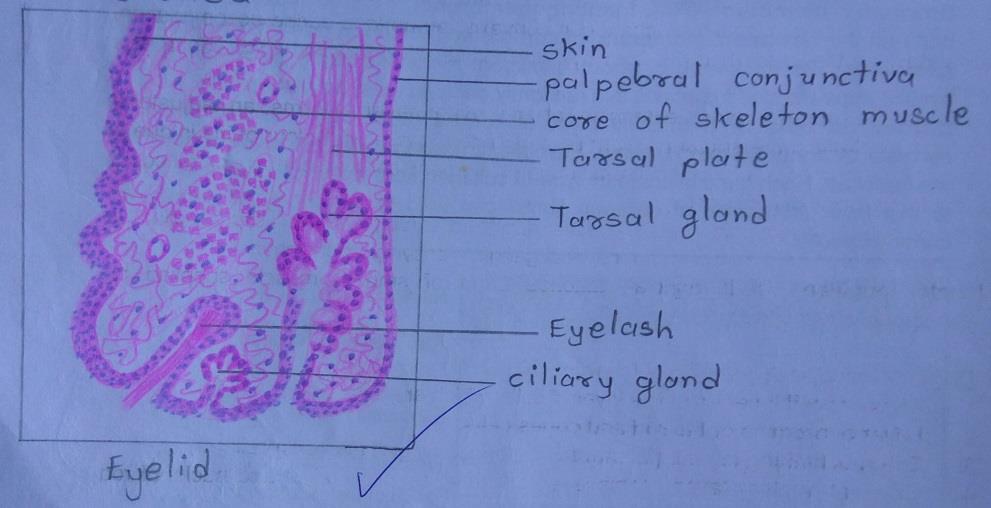
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1) Anteriorly, there is a layer of true thin skin. |
| 2) Considerable thickness of the lid is formed by fasciculi of the palpebral part of the orbicularis oculi muscle. |
| 3) The ‘skeleton’ of each eyelid is formed by a mass of fibrous tissue called the tarsus, or tarsal plate. |
| 4) On the deep surface of the tarsal plate, there are a series of vertical grooves in which tarsal glands or meibomian glands are lodged. |
| 5) Modified sweat glands, called ciliary glands or glands of Moll are present in the lid near its free edge. |
| 6) Sebaceous glands present in relation to eyelashes constitute the glands of Zeis. They open into hair follicles. |
| 7) The inner surface of the eyelid is lined by the palpebral conjunctiva. |
Plate 86: EYEBALL & RETINA
DRAWING:
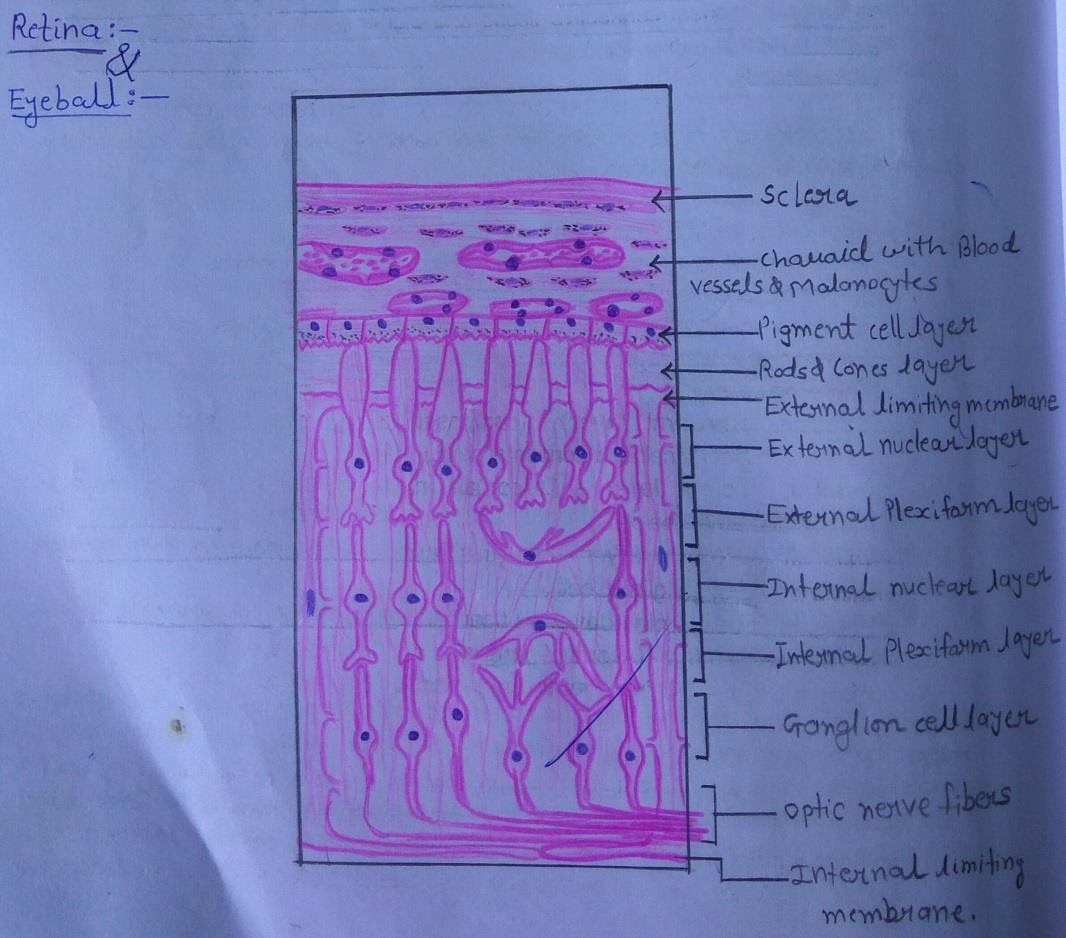
IDEAL SLIDE:
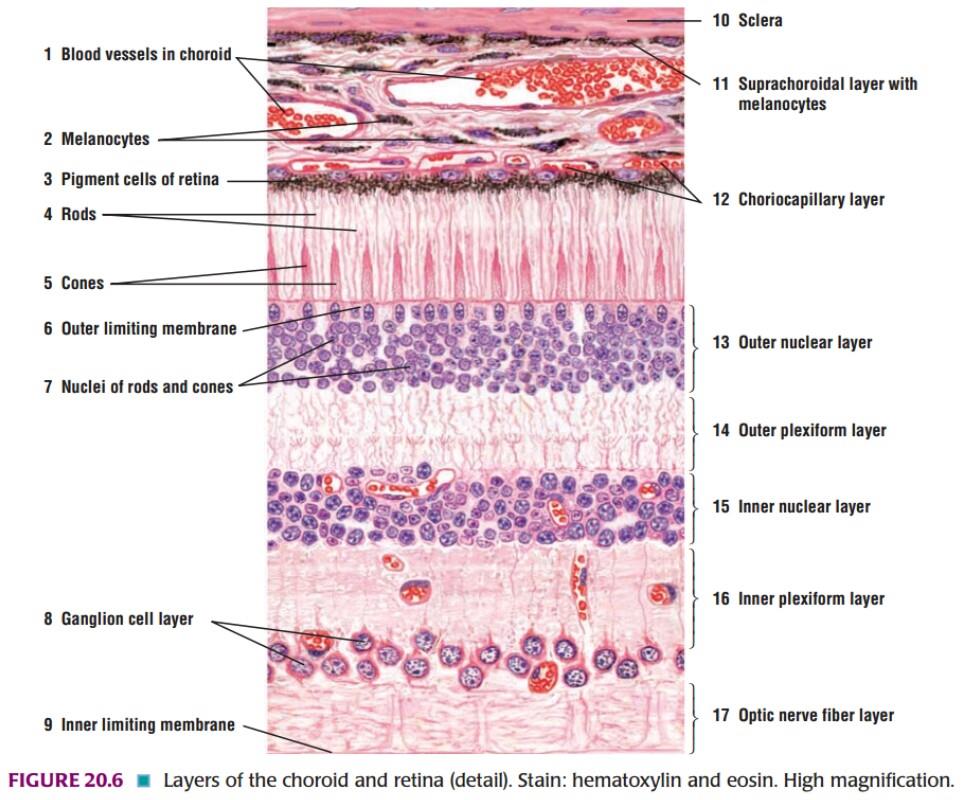
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1) The wall of the eyeball is made up of several layers as follows: Ø Sclera, made up of collagen fibers. Ø Choroid, containing blood vessels and pigment cells. The remaining layers are subdivisions of the retina. Ø Pigment cell layer Ø Layer of rods and cones Ø External limiting membrane Ø Outer nuclear layer Ø Outer plexiform layer Ø Inner nuclear layer Ø Inner plexiform layer Ø Layer of ganglion cells Ø Layer of optic nerve fibres. Ø Internal limiting membrane |
| 2) The appearance is not likely to be confused with any other tissue. |
Ear
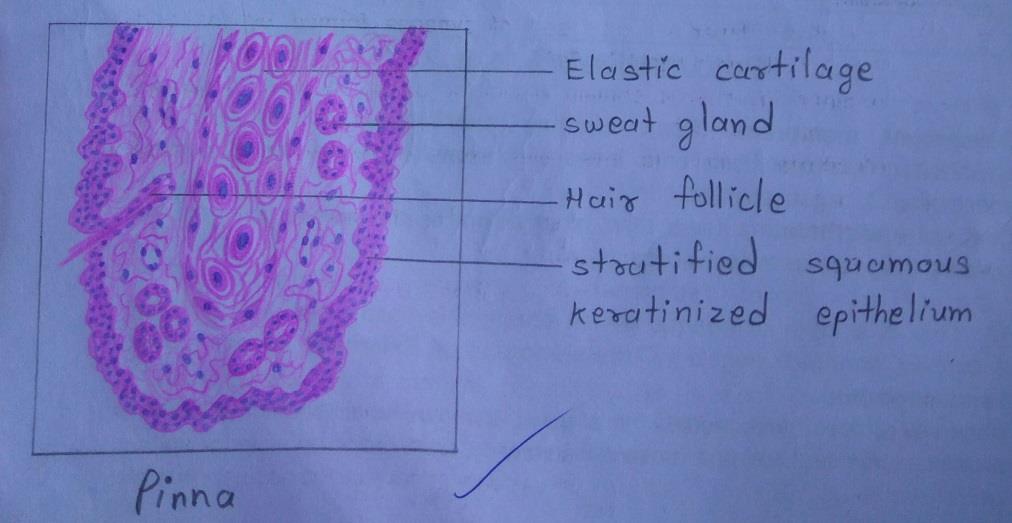
Plate 85: PINNA
DRAWING:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1) The auricle [pinna] consists of a thin plate of elastic cartilage covered on both sides by true skin. |
| 2) Epithelium is stratified squamous keratinizing, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands are present in the skin, adipose tissue is present only in lobule. |
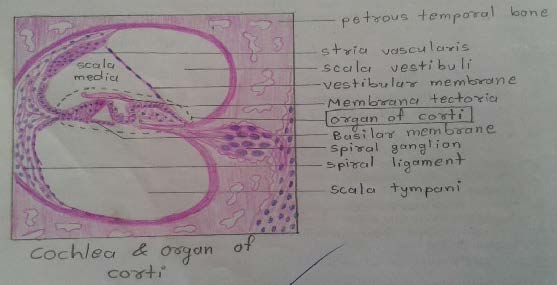
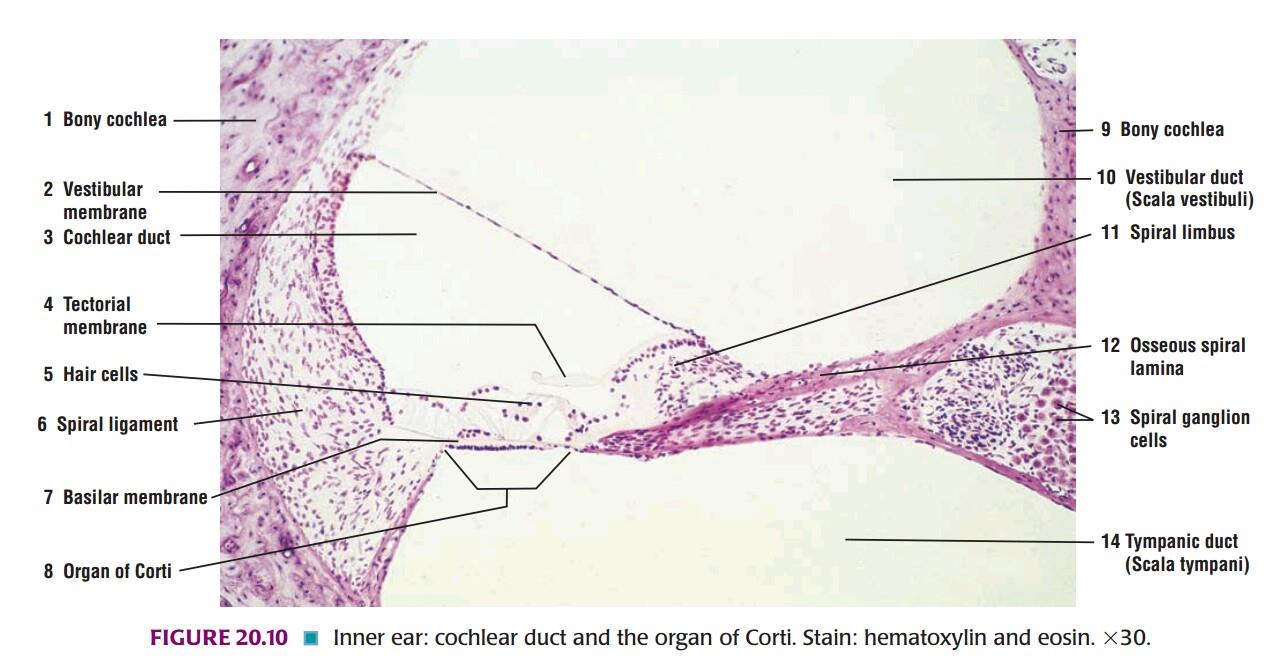
Plate 87: COCHLEA & ORGAN OF CORTI
DRAWING:
IDEAL SLIDE:
IDENTIFICATION POINTS:
| 1) The cochlea is embedded in the petrous temporal bone. It is in the form of a spiral canal. |
| 2) The cone-shaped mass of bone surrounded by these turns of the cochlea is called the modiolus which contains a canal through which fibres of the cochlear nerve pass. |
| 3) A mass of neurons belonging to the spiral ganglion lies to the inner side of each turn of the cochlea. |
| 4) The parts to be identified in each turn of the cochlea are the Scala vestibule, Scala media, the Scala tympani, the vestibular membrane, the basilar membrane, the membrane tectoria, the organ of corti and the spiral lamina. |
| 5) Outer wall of the cochlear turn is the spiral ligament and it is lined by avascularised epithelium (stria vascularis). |
Comments (0)