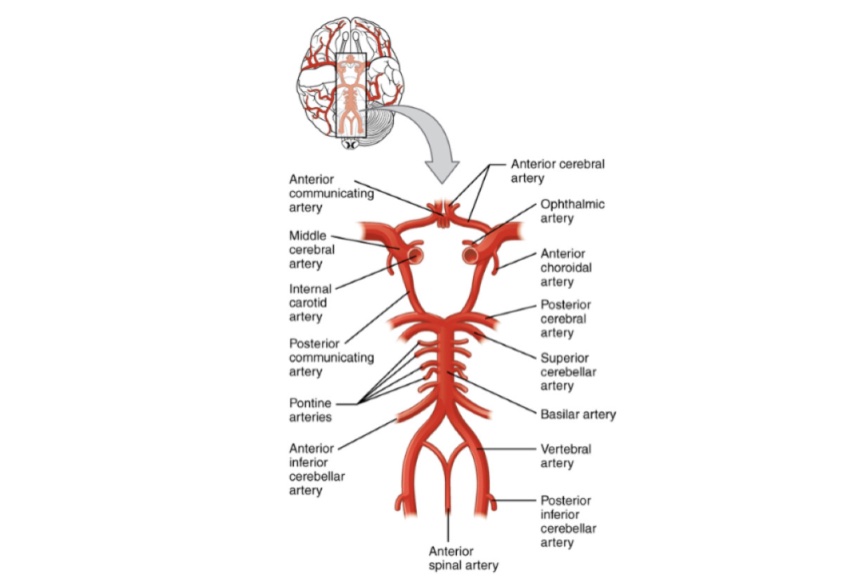
brain blood supply
Q.1 Name the arteries supplying the brain.
- Internal carotid arteries and its branches.
- Vertebral arteries: At the lower border of pons join to form the Basilar artery.
Q.2 What is the artery of Heubner?
Recurrent branch of the anterior cerebral artery which supplies anterior perforated substance.
Q.3 What are the branches of the basilar artery?
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Pontine branches
- Labyrinthine artery.
Q.4 Why the macular vision is often spared in thrombosis of the posterior cerebral artery?
Because part of the visual area responsible for macular vision lies in the region where the area of distribution of the middle and posterior cerebral artery meet and this area may receive supply directly from the middle cerebral artery or through anastomoses with branches of a posterior cerebral artery.
Q.5 Which arteries of the brain are end arteries?
Long and short perpendicular branches of cortical arteries are end arteries.
Q.6 What is the arterial supply of the cerebellum?
- Superior cerebellar Branches of basilar artery
- Anterior inferior cerebellar, branch basilar artery
- Posterior inferior cerebellar: Branch of vertebral artery.
Q.7 What is the ‘circle of Willis’?
It is an arterial circle formed at the base of the brain by interconnections between the main arteries supplying the brain.
Q.8 What is the clinical importance of the ‘circle of Willis’.
- It helps in equalizing pressure in the arteries of two sides.
- It also helps in maintaining blood supply to different parts of the brain, if the main artery of one side is obstructed.
Q.9 Name the arteries forming ‘circle of Willis’?
Anteriorly: Anterior communicating artery, joining two anterior cerebral arteries.
Posteriorly: Basilar artery as it divides into two posterior cerebral arteries.
On each side: Anterior cerebral, internal carotid, posterior communicating, and posterior cerebral arteries.
Q.10 Name the structures forming the blood-brain barrier.
- Capillary endothelium and its basement membrane
- Arachnoid layer of perivascular sheath
- Perivascular space
- Pial layer of perivascular sheath
- Neuroglia and ground substance of the brain.
Q.11 Thrombosis of central branches of cerebral arteries results in infarction. Why?
Because they are end arteries.
Q.12 What is the arterial supply of the cerebral cortex?
- Cortical branches of anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries.
- Motor area by anterior and middle cerebral artery.
- Auditory area and speech area by middle cerebral artery.
- Visual area by posterior cerebral artery.
Q.13 What are the characteristics of veins supplying the cerebrum?
- Vessel walls are devoid of muscle
- No valves are present
- Some open into cranial venous sinuses against the direction of blood flow in the sinus.
Q.14 How the basal vein is formed?
By union of anterior cerebral vein, deep middle cerebral veins, and some inferior striate vein.
Q.15 How great cerebral vein is formed and terminates?
Formed by the union of two internal cerebral veins and ends in the straight sinus.

Comments (0)