BLOOD VESSELS OF HEAD AND NECK
Q.1 What are the branches of the subclavian artery?
- Vertebral artery,
- Internal thoracic,
- Thyrocervical trunk,
- Costocervical trunk and
- Dorsal scapular. In 1/3 cases it arises with superficial cervical from thyrocervical trunk.
Q.2 What are the tributaries of the subclavian vein?
- External Jugular,
- Dorsal scapular,
- Thoracic duct on left and
- Right lymphatic duct on right.
- Sometimes, anterior jugular vein.
Q.3 Name the tributaries of the internal jugular vein?
- Inferior petrosal sinus,
- Sigmoid sinus,
- Common facial vein,
- Lingual vein,
- Pharyngeal vein,
- Superior thyroid vein and
- Middle thyroid vein.
- Sometimes, occipital vein.
Q.4 Name the tributaries of brachiocephalic vein.
Brachiocephalic vein is formed by an internal jugular vein and subclavian vein.
Right brachiocephalic:
- Vertebral.
- Internal thoracic.
- Inferior thyroid.
- First posterior intercostal
Left brachiocephalic: 1-4: Same as above.
- Left superior intercostal.
- Thymic veins.
- Pericardial veins.
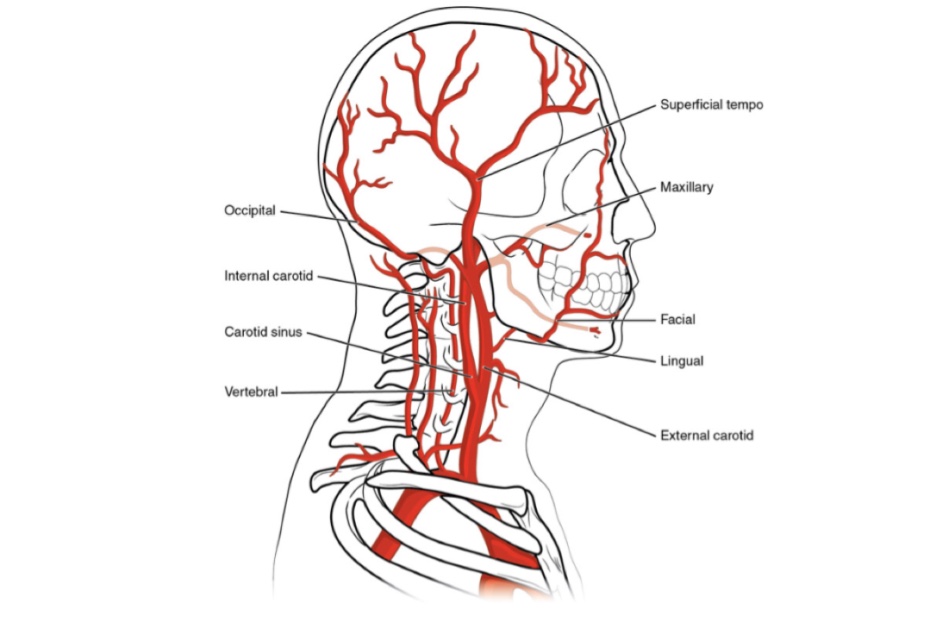
Q.5 Name the branches of the internal carotid artery.
- Cervical part: No branches.
- Petrous part:
– Corticotympanic.
– Pterygoid branch.
- Cavernous part:
– Cavernous branches to trigeminal ganglion.
– Superior hypophyseal.
– Inferior hypophyseal. - Cerebral part:
– Ophthalmic.
– Anterior cerebral.
– Middle cerebral.
– Posterior communicating.
– Anterior choroidal.
– Meningeal.
Q.6 Name the branches of the vertebral artery.
- Cervical branches:
– Spinal.
– Muscular.
- Cranial branches:
– Meningeal.
– Posterior spinal.
– Anterior spinal.
– Posterior inferior cerebellar.
– Medullary
Q.7 Name the branches of the superficial temporal artery.
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Anterior auricular
- Middle temporal
- Zygomatico-orbital
- Transverse facial
Q.8 How the retromandibular vein is formed?
It is formed by the union of superficial temporal and maxillary vein behind ramus of mandible
Q.9 How the external jugular vein is formed and what are its tributaries?
It is formed by the union of the posterior division of retromandibular vein and posterior auricular vein.
Other tributaries are:
- Posterior external jugular
- Transverse cervical
- Suprascapular
- Anterior jugular.
Q.10 Name the branches of the maxillary artery.
First part:
- Deep auricular
- Anterior tympanic
- Middle meningeal
- Accessory meningeal
- Inferior alveolar
Second part:
- Deep temporal
- Pterygoid
- Masseter
- Buccal.
Third part:
- Posterior superior alveolar
- Infraorbital
- Greater palatine
- Pharyngeal
- Artery of pterygoid canal
- Sphenopalatine
Questions on
– External carotid: In chapter Triangles or Neck.
– Venous sinuses: In chapter Meninges of Brain and CSF.
NERVES OF HEAD AND NECK
Q.1 What is the characteristic feature of cervical spinal nerves?
In the spine, each spinal nerve lies below the numerically corresponding vertebra. But the upper seven cervical nerves lie above the numerically corresponding vertebrae. The eighth cervical nerve lies below the C7 vertebra.
Q.2 How the greater occipital nerve is formed?
It is formed by the medial branch of the dorsal ramus of the second cervical nerve.
Q.3 How the cervical plexus is formed?
By ventral rami of C1-4 spinal nerves.
Q.4 What are the branches of cervical plexus?
Cutaneous branches:
– Lesser occipital nerve (C2)
– Greater auricular nerve (C2,3)
– Transverse cutaneous nerve of neck (C2,3)
– Supraclavicular nerves (C3,4)
Muscular branches:
– To prevertebral muscles: Rectus capitis lateralis and anterior from C1, longus capitis from C1-3, longus colli from C2-4.
– To sternocleidomastoid (C2).
– To levator scapulae, scalenus medius and trapezius (C3,4).
– Phrenic nerve (C3-5) to diaphragm.
– To infrahyoid muscles through hypoglossal nerve and ansa cervicalis.
Q.5 (a) How is ‘ansa cervicalis’ formed?
(b) What is its distribution?
- By union of two roots formed by C1 through hypoglossal nerve and C2,3 superficial to common carotid artery.
- b. All infrahyoid muscles except thyrohyoid.
(Questions on Cranial nerves: See Cranial Nerves in CNS)

Comments (0)