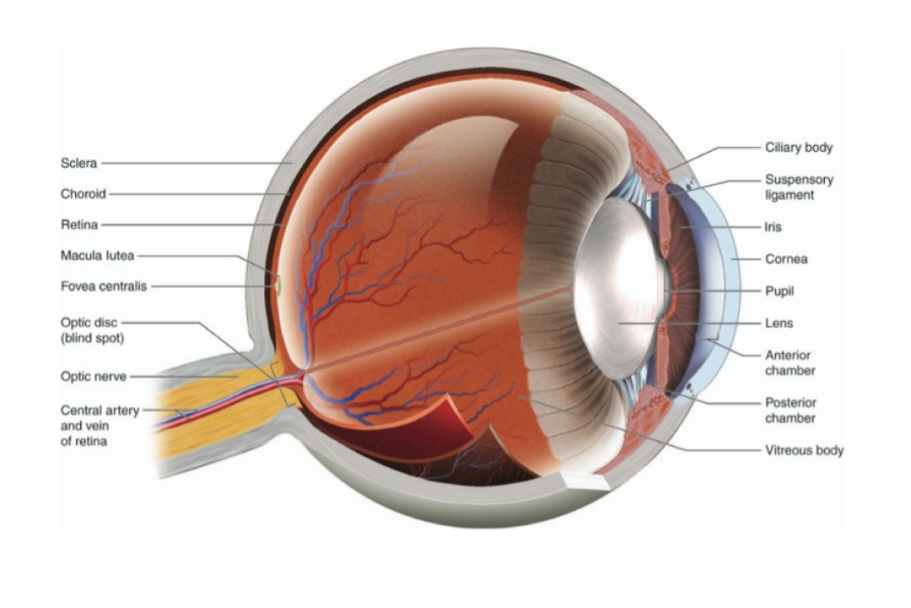
EYE
Q.1 Name the different layers of the eye.
- Outer or fibrous coat consists of sclera and cornea.
- Middle or vascular coat comprises choroid, ciliary body, and iris.
- Inner or nervous coat, Retina.
Q.2 What is the diameter of the eyeball?
The posterior five-sixths has a diameter of about 24 mm. The anterior one-sixth is much more convex and represents part of the sphere having a diameter of 15 mm.
Q.3 Name the refractive media of the eye.
From before backward:
- Cornea,
- Aqueous humour,
- Lens and
- Vitreous body
Q.4 What is ‘Lamina fusca of Sclera’?
It is a thin layer of delicate tissue between choroid and sclera.
Q.5 Name the structures piercing sclera.
- Optic nerve,
- Long ciliary nerves and arteries,
- Short ciliary nerves and arteries
- Venae vorticose
Q.6 What are the layers of the cornea seen histologically?
From before backward:
- Corneal epithelium (Stratified squamous),
- Bowman’s membrane,
- Substantia propria,
- Descemet’s membrane and
- Endothelium of anterior chamber
Q.7 Name the membrane separating the choroid from retina.
Membrane of Bruch
Q.8 What are the types of muscle fibers in the ciliary body and what is their function?
- Radial fibers.
Function: Relax the suspensory ligament of the lens, so the lens bulges and becomes more convex for near vision.
- Circular fibers.
Function: Also relax suspensory ligament of the lens.
Q.9 What is ora serrata?
The retina proper ends anteriorly, just behind the sclerocorneal junction in a wavy line called as ora serrata. It also represents the junction of the choroid with the ciliary body. Anterior to ora serrata retina continues as double-layered epithelium lining the inner surface of the ciliary body and posterior surface of iris.
Q.10 What is the nerve supply of ciliary muscle?
Parasympathetic nerves through third cranial nerve.
Q.11 What are the muscles of iris?
Has smooth muscle consisting of
- Sphincter pupillae:
Has circular muscle fibers and its contraction narrows the pupil - Dilator pupillae:
Has radial muscle fibers.
Q.12 What is the nerve supply of muscles of iris?
- Sphincter pupillae:
Parasympathetic nerve.
Preganglionic neurons in the Edinger Westphal nucleus give axons to the oculomotor nerve and its branches reach the ciliary ganglion.
Postganglionic fibers reach muscle through short ciliary nerves. - Dilator pupillae:
Sympathetic nerve.
Preganglionic neurons in T1segment.
Postganglionic neurons in the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion.
Q.13 What is the dioptric power of lens?
15 dioptres
Q.14 What is the total dioptric power of the eye?
58 dioptres
Q.15 At which layer of eye maximum refraction takes place.
Corneal surface
Q.16.1 What is ‘fovea centralis’?
This is the center of the macula. This is the thinnest part of the retina containing only cones and is the site of maximum acuity of vision.
Q.16 What is ‘Blindspot’?
It is a part of an optic disc that contains no rods or cones. This is insensitive to light.
Q.17 Name the layers of the retina.
From without inwards:
- Outer pigmented layer
- Layer of rods and cones
- External limiting membrane
- Outer nuclear layer
- Outer molecular layer
- Inner nuclear layer (Bipolar cells)
- Inner molecular layer
- Ganglion cells layer
- Nerve fiber layer
- Inner limiting membrane.
Q.18 What is the arterial supply of retina?
Supplied by an artery, Central artery of Retina.
In optic disc, it divides into branches which supplies a deeper layer of retina up to bipolar cells.
Branches of the central artery of the retina are end arteries.
Rods and cones with nuclei are supplied by diffusion from capillaries.
Q.19 Describe the circulation of Aqueous humour.
Secreted into posterior chamber from capillaries of ciliary process
↓
Through pupil enters anterior chamber
↓
Filters through spaces of iridocorneal angle (Trabecular spaces)
↓
Enters sinus venosus sclerae
↓
Anterior ciliary veins
Q.20 What is hyaloid fossa?
It is a depression in the vitreous body on which the posterior surface of the lens lies.

Comments (0)