SUPERIOR VENA CAVA
Q.1 How superior vena cava is formed?
By the union of two brachiocephalic veins behind the lower border of first costal cartilage close to the sternum.
Q.2 Name the tributaries of superior vena cava.
- Azygous vein,
- Mediastinal veins and
- Pericardial veins.
Q.3 What is the pathway for the collateral circulation in obstruction of superior vena cava?
- If obstructed above opening of azygous vein:
Venous blood from the upper half of the body is returned through the azygous vein and superficial veins of the chest are dilated up to costal margin. - If obstructed below the opening of the azygous vein:
Venous blood is returned through inferior vena cava via the femoral vein and superficial veins are dilated on chest and abdomen up to the saphenous opening in the thigh (Thoraco-epigastric vein).
Q.4 How superior vena cava is developed?
- Upper half, up to the opening of azygous vein:
Right anterior cardinal vein - Lower half, below the opening of azygous vein:
Right common cardinal vein
PULMONARY TRUNK AND ARTERIES
Q.1 What is the course of pulmonary trunk?
It begins opposite the sternal end of the left 3rd costal cartilage and the upper end lies in front of the fifth thoracic vertebra. The bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk lies below the arch of the aorta.
Q.2 What are the relations of the right pulmonary artery?
Anterior:
Ascending aorta, Superior vena cava, and Upper right pulmonary vein.
Posterior:
Oesophagus and Right bronchus.
Q.3 What are the relations of the left pulmonary artery?
Posterior:
Left bronchus and Descending aorta.
Superiorly:
Connected to the arch of the aorta by ligamentum arteriosum.
AORTA
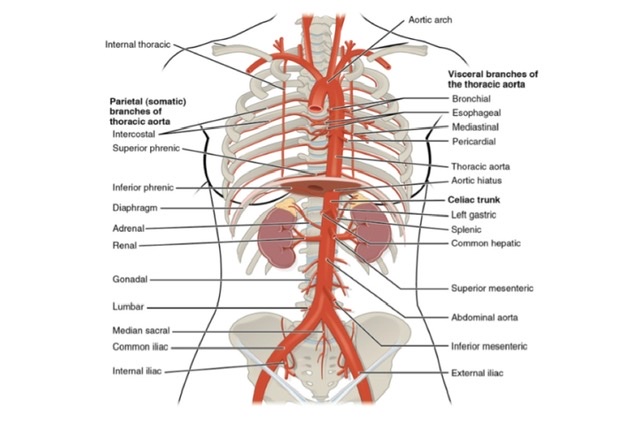
Q.1 What are the parts of aorta in thorax?
- Ascending aorta,
- Arch of aorta and
- Descending thoracic aorta.
Q.2 What is the course of ascending aorta?
It begins at the level of the lower border of 3rd costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum. It runs upwards, forwards and to right, and continues as the arch of the aorta at sternal end of upper border of second right costal cartilage.
Q.3 What is Aortic sinus?
It is dilatation of the vessel wall at the root of the aorta above each cusp of the aortic valve.
Q.4 Name the branches of ascending aorta?
- Right coronary artery: From anterior aortic sinus.
- Left coronary artery: From left posterior aortic sinus.
Q.5 What is the level of beginning and termination of the arch of aorta?
It begins behind the upper border of 2nd right sternochondral joint (lower border of T4) and ends at a lower border of the body of the 4th thoracic vertebra on the left side. Thus it begins and ends at the same level but it begins anteriorly and ends posteriorly.
Q.6 What are the posterior and to the right relations of the arch of aorta?
From behind forwards these are:
- Vertebral column
- Oesophagus
- Trachea
- Superior vena cava
- Thoracic duct
- Left recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Deep cardiac plexus.
Q.7 Name the branches of arch of aorta.
- Brachiocephalic artery: Divides into the right common carotid and right subclavian artery.
- Left common carotid,
- Left subclavian.
- Thyroid ima
- Occasionally
- Vertebral artery.
Q.8 Name branches of descending thoracic aorta.
- Posterior intercostal arteries: For 3rd-11th spaces, on both sides,
- Subcostal arteries: On both sides,
- Two left bronchial arteries,
- Oesophageal branches,
- Pericardial branches,
- Mediastinal branches and
- Superior phrenic
Q.9 What is aortic aneurysm?
It is a localized abnormal dilatation of aorta.
Q.10 What is the coarctation of the aorta?
It is the narrowing of the aorta, occurring usually immediately beyond the origin of the left subclavian artery. It leads to hypertension above the narrowing e.g., arms, neck, and head and hypotension below e.g., lower limb.
Q.11 What is the developmental origin of the aorta?
- Ascending aorta: From truncus arteriosus
- Arch of aorta:
– From ventral part of aortic sac and its left horn and
– Left fourth arch artery.
- Descending aorta:
– From left dorsal aorta below the attachment of the fourth arch artery.
– Fused median vessel.
Q.12 What is ‘ductus arteriosus’?
It is communication present in fetal life connecting the left pulmonary artery with aorta just distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery. After birth, it gets obliterated and forms ligamentum arteriosum.
Q.13 What will happen if ductus arteriosus remains patent?
It causes progressive enlargement of the left ventricle and pulmonary hypertension.
AZYGOUS AND HEMIZYGOUS VEINS
Q.1 How azygous vein is formed and terminates?
By the union of right ascending lumbar and right subcostal vein at the level of T12 vertebra and terminates at the level of T4 vertebra into superior vena cava.
Q.2 Name the tributaries of azygous vein.
- Right posterior intercostal veins.
- Right superior intercostal veins.
- Hemiazygous veins:
Present on the left side and joins azygous vein at the T8 level. - Accessory hemiazygous vein:
Present on the left side and joins azygous vein at the T7 level. - Right bronchial veins.
- Oesophageal veins.
- Mediastinal and pericardial veins.
- Right ascending lumbar veins.
- Right subcostal vein.
Q.3 Name the tributaries of hemiazygous vein.
- 9th-11th left posterior intercostal veins.
- Left ascending lumbar vein.
- Left subcostal vein.
THORACIC DUCT
Q.1 What is the length of the thoracic duct?
40 cm
Q.2 What is the extent of the thoracic duct?
Begins from Cisterna chyli near the lower border of the T12 vertebra. Ends into the angle of the junction between left subclavian and left internal jugular vein at the level of T2 vertebra.
Q.3 What are the relations of the thoracic duct in the aortic opening of the diaphragm?
- Anteriorly: Diaphragm
- Posteriorly: Vertebral column
- To the left: Azygous vein
- To the right: Aorta
Q.4 Name the tributaries of the thoracic duct.
In thorax:
- Channels from posterior mediastinal and intercostal nodes.
- Left mediastinal trunk may drain.
At root of neck:
- Left jugular trunk,
- Left subclavian trunk.
Q.5 From which areas the thoracic duct drains lymph?
- Both halves of the body below diaphragm and
- Left half above diaphragm.

Comments (0)