POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL
Q.1 What are the different layers of thoracolumbar fascia? •
- Posterior layer:
Medially attached to lumbar and sacral spines and laterally blends with the anterior layer. Covers erector spinae muscle. - Middle layer:
Medially attached to tips of the transverse process of lumbar vertebrae and laterally blends with posterior layers. It separates the erector spinae from the quadratus lumborum muscle. - Anterior layer:
Medially attached to the anterior surface of transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae and laterally blends with the posterior layer. Covers the anterior surface of the quadratus lumborum muscle.
Q.2 What is the extent of the abdominal aorta?
It extends from the lower border of the T12 vertebra to the front of L4 where it terminates into the left and right common iliac arteries.
Q.3 What are the branches of the abdominal aorta?
- Ventral branches:
– Coeliac trunk
– Superior mesenteric artery
– Inferior mesenteric artery. - Dorsal branches:
– Lumbar
– Median sacral. - Lateral branches:
– Inferior phrenic
– Middle suprarenal
– Renal
– Testicular or ovarian. - Terminal branches: Common iliac arteries
Q.4 What are the tributaries of inferior vena cava?
- Common iliac veins
- Third and fourth lumbar veins
- Right testicular or ovarian vein
- Renal veins
- Right suprarenal vein
- Hepatic veins
- Right inferior phrenic vein.
Q.5 What are the posterior relations of the gonadal arteries?
On both sides:
- Psoas major
- Genitofemoral nerve
- External iliac vessels.
On the right side, in addition, it is related to the inferior vena cava.
Q.6 What is the extent of the common iliac arteries?
Each artery begins in front of the body of the fourth lumbar vertebra and it terminates in front of the sacroiliac joint, at the level of a disc between the fifth lumbar vertebra and sacrum.
Q.7 What are the branches of the external iliac artery?
- Inferior epigastric artery
- Deep circumflex iliac artery Each artery continues into the thigh as the femoral artery deep into the inguinal ligament.
Q.8 Which veins on the left side open into the left renal vein but corresponding veins on the right side open into the inferior vena cava?
- Inferior phrenic vein
- Suprarenal vein
- Testicular vein (ovarian vein)
Q.9 What are the tributaries of common iliac veins?
- Iliolumbar vein
- Median sacral vein
Q.10 What is the pathway by which the blood reaches the heart in obstruction of the inferior vena cava?
In obstruction of the inferior vena cava communications between tributaries of inferior and superior vena cava undergo considerable enlargement. Veins involved from below are the inferior epigastric, circumflex iliac, and external pudendal. Blood from them passes into the lateral thoracic, internal thoracic, and posterior intercostal passing over the abdominal wall. Communication is also established through azygous and hemizygous veins and vertebral venous plexus.
Q.11 What is Cisterna chyli?
It is a 5-7 cm long lymphatic sac, situated in front of L1,2 vertebrae, to the right of the abdominal aorta. It continues upwards as a thoracic duct.
Q.12 How the lumbar plexus is formed?
- It is formed by ventral rami of the upper four lumbar nerves.
- The first lumbar nerve also receives a contribution from the subcostal nerve.
- The L4 nerve gives a contribution to the lumbosacral trunk (L4,5) which forms part of the sacral plexus.
Q.13 What are the branches of the lumbar plexus?
- Iliohypogastric nerve (L1),
- Ilioinguinal nerve (L1),
- Genitofemoral nerve (L1,2).
- The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (L2, 3).
- Femoral nerve (L2,3,4).
- Obturator nerve (L2,3,4).
- Lumbosacral trunk (L4, 5).
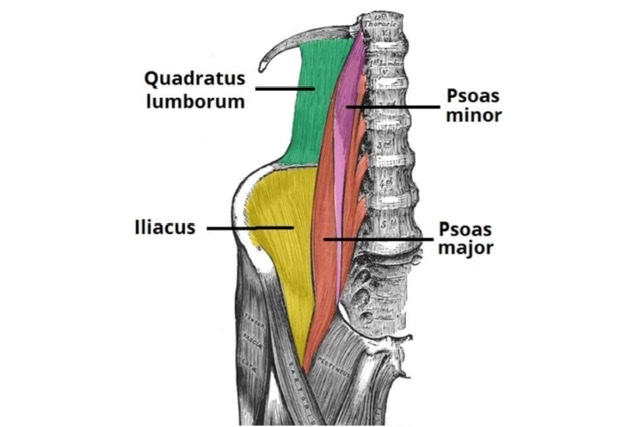
Q.14 Name the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall.
- Psoas major
- Psoas minor
- Iliacus and
- Quadratus lumborum.
Q.15 What are the actions of psoas major?
- Helps in maintaining posture at the hip. Balances trunk while sitting.
- With iliacus, the flexor of the hip joint.
- One psoas causes lateral flexion of the trunk on that side.
- Lateral rotation of the hip.
Q.16 What are the boundaries of the lower lumbar triangle?
Also called Petit’s triangle, formed by the latissimus dorsi and the posterior border of the external oblique muscle of the abdomen. The base is formed by the iliac crest.

Comments (0)