Leg & Foot (Viva)
LEG AND FOOT
Q.1 Name the bony prominences felt in the leg and foot.
- Medial and lateral condyles of the tibia.
- Tibial tuberosity:
In front of the upper part of the tibia, 2.5 cm below the line passing between tibia condyles. - Head of fibula:
Posterolaterally at the level of tibial tuberosity. - Anterior border and medial surface of tibia.
- Medial malleolus of tibia:
On the medial side of the ankle. - Lateral malleolus of fibula.
- Peroneal trochlea:
About a finger breadth below lateral malleolus. - Sustentaculum tali:
About a finger breadth below the medial malleolus. - Tuberosity of navicular bone:
2.5 to 3.5 cm antero-inferior to medial malleolus. - Tuberosity of base of fifth metatarsal:
On the lateral border of the foot.
Q.2 What are the parts of the deep fascia of the leg?
- Intermuscular septa:
– Anterior and posterior intermuscular septa:
Divide leg into three compartments anterior, lateral and posterior.
– Superficial transverse fascial septum:
Separates superficial and deep muscles of the back of the leg. Also forms flexor retinacula.
– Deep transverse fascial septum:
Separates tibialis posterior from long flexors of toes.
- Retinacula:
– Extensor retinacula: Superior and inferior.
– Peroneal retinacula: Superior and inferior.
Q.3 What are the attachment of inferior extensor retinacula?
It is a Y-shaped retinacula.
- Stem: Attached to anterior and articular part of the superior surface of the calcaneum.
- Upper band: Attached to the anterior border of the medial malleolus.
- Lower band: Attached to plantar aponeurosis.
Q.4 Name the structures passing deep to inferior extensor retinacula.
- Tibialis anterior
- Extensor hallucis longus
- Deep peroneal nerve
- Anterior tibial vessels.
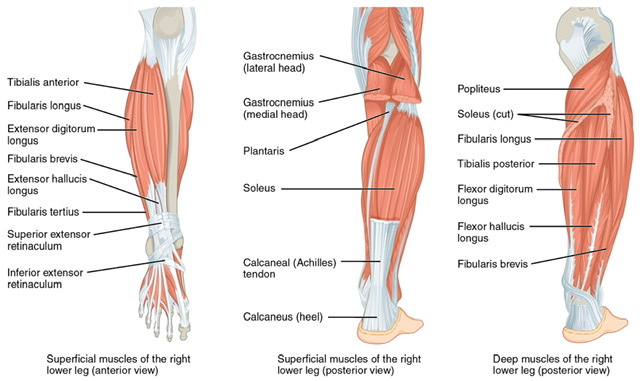
Q.5 Name the muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg.
Superficial muscles:
- Gastrocnemius,
- Soleus and
- Plantaris.
Deep muscles:
- Popliteus,
- Flexor digitorum longus,
- Flexor hallucis longus and
- Tibialis posterior.
Q.6 Name the structures passing under the flexor retinaculum.
From medial to lateral and above downwards are:
- Tibialis posterior tendon
- Flexor digitorum longus tendon
- Posterior tibial vessels
- Tibial nerve
- Flexor hallucis longus tendon.
Q.7 What is Tendocalcaneus?
It is a long tendon, receiving the insertion of fibers of soleus, gastrocnemius, both medial and lateral head.
Q.8 What is the insertion of the tibialis anterior?
Tibialis anterior is inserted into the medial side of medial cuneiform and base of the first metatarsal.
Q.9 Where is peroneus longus inserted?
It is inserted into the lateral side of medial cuneiform and base of the first metatarsal.
Q.10 Name the muscles found in different layers of the sole of the foot.
From without inwards:
First layer:
- Flexor digitorum brevis
- Abductor hallucis
- Abductor digiti minimi.
Second layer:
- Flexor digitorum accessorius
- Lumbricals: Four in number Third layer:
- Flexor hallucis brevis
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis
- Adductor hallucis Fourth layer:
Three plantar and four dorsal interossei.
Q.11 What is plantar aponeurosis and what are its functions?
It is the thickened central part of the deep fascia of the sole.
Functions:
- Provides attachment to the skin of the sole.
- Gives origin to muscles of the first layer of the sole.
- Protects the digital vessels and nerves and deeper muscles.
- Helps in maintaining the longitudinal arch of the foot.
Q.12 What are the functions of interossei of sole?
- Dorsal interossei: Abductors of the toes.
- Plantar interossei: Adductors of the toes.
Also read: Anatomy Question Collection
Also read: Anatomy Questions & Answers
Also read: Anatomy notes

Comments (0)