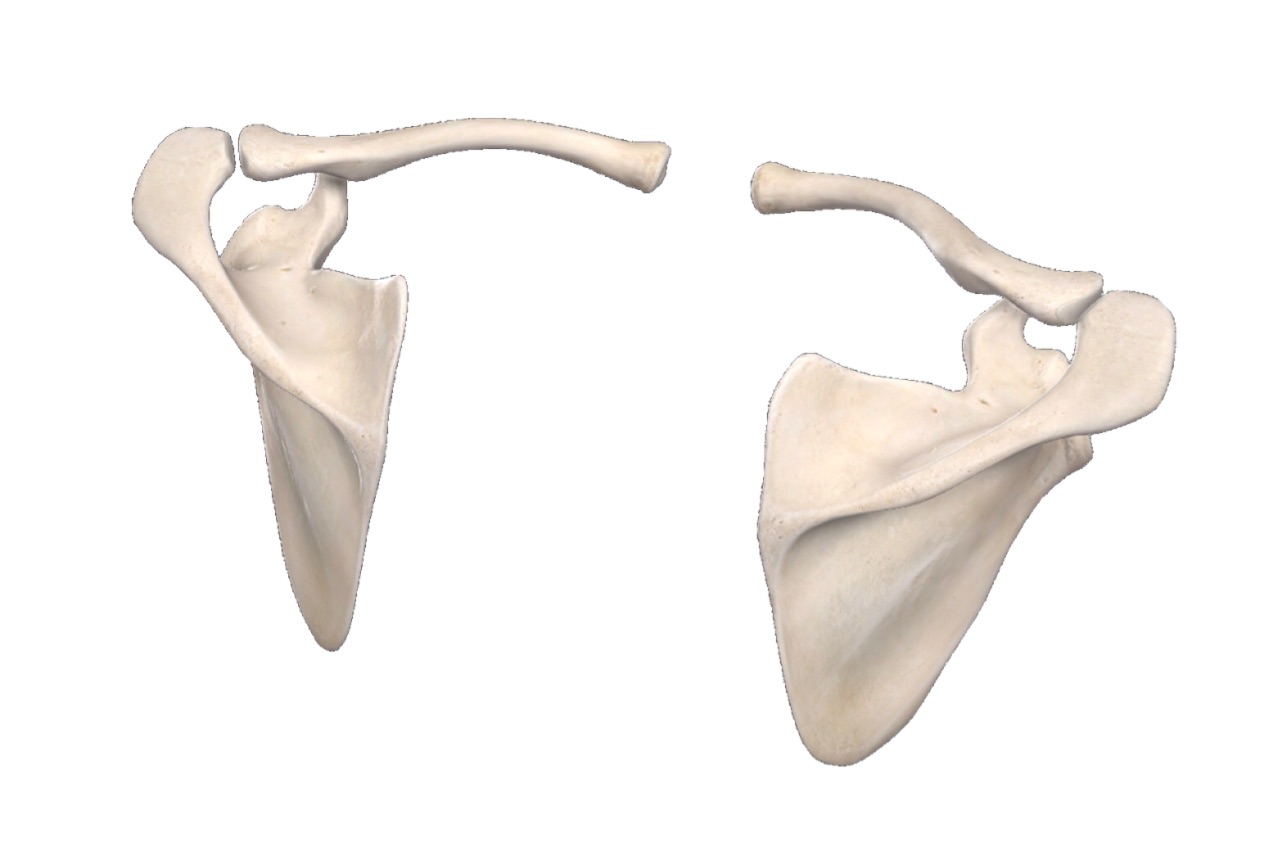
Clavicle & Scapula (Viva-related)
CLAVICLE
Q.1 What are the characteristic features of the clavicle?
- It is a long bone that lies horizontally in the body.
- It has no medullary cavity.
- It is subcutaneous throughout.
- It is the first bone to ossify in the body of the fetus.
- Only long bone that ossifies in membrane except sternal and acromial end.
- It is the only long bone which ossifies from two primary centers.
- It is the most commonly fractured bone in the body.
Q.2 How will you determine the side to which the clavicle belongs?
- It was two ends, lateral and medial. The lateral end is flat and the medial end is large and quadrilateral.
- Shaft is convex forwards in medial 2/3 and concave forwards in lateral 1/3.
- The inferior surface is grooved longitudinally in the middle 1/3.
Q.3 What is the nutrient artery supplying clavicle?
- Nutrient branch from the suprascapular artery
Q.4 What are the muscles attached to the medial part of the clavicle?
- Clavicular part of pectoralis major: From anterior surface of medial half.
- Clavicular head of sternocleidomastoid: From the upper surface of the medial part.
- Lateral part of sternohyoid: Posterior surface of medial end.
Q.5 What are the functions of the clavicle?
- Transmits force from the upper limb to the axial skeleton.
- Provides attachment to muscles.
- Acts as a strut holding arm free from the trunk.
Q.6 Name the structures attached to the edges of the groove for subclavius.
- Clavipectoral fascia
Q.7 To which structure the medial end of the clavicle articulates?
- Manubrium sterni
- First costal cartilage
Q.8 At which site the clavicle fracture occurs commonly?
- At the junction of the middle and outer third, which is the weakest point.
SCAPULA
Q.9 What is the extent and position of the scapula?
- It lies on the posterolateral aspect of the chest wall.
- It extends from II to VII rib.
Q.10 How will you determine the side to which scapula belongs?
- The lateral angle is large and has a glenoid cavity.
- Lateral thickest border runs from the glenoid cavity above to the inferior angle below.
- The dorsal surface is convex and is divided into supraspinatus and infraspinatus fossa by a triangular spine.
- The costal surface is concave.
Q.11 Name the structures passing above and below the suprascapular notch.
- The suprascapular notch is converted into a foramen by the suprascapular ligament.
- The suprascapular artery passes above the ligament and suprascapular nerve below the ligament.
Q.12 Name the structures attached to Acromion.
- Trapezius: Inserted on its medial border
- Deltoid: Originates from the lateral margin, tip, and the upper surface.
- Coracoacromial ligament: Attached to apex of acromion.
Q.13 What are the structures attached to the coracoid process?
Muscles:
- Short head of biceps: Origin from the tip of the coracoid process.
- Coracobrachialis: Origin from the tip of the coracoid process.
- Pectoralis minor: Insertion on medial border and superior surface.
Ligaments:
- Coracoacromial ligament: To lateral border.
- Coracoclavicular ligament: Conoid part to knuckle of process. Trapezoid part to ridge between pectoralis minor and coracoacromial ligament.
- Coracohumeral ligament: To root of the coracoid process.
Q.14 Name the muscles inserting on the medial border of the scapula?
On coastal surface:
Insertion of two digitations of the serratus anterior.
On dorsal surface: Insertion of
- Levator scapulae: Above root of spine
- Rhomboideus minor: Opposite the root
- Rhomboideus major: Below the root
Q.15 Which muscle originates from supraglenoid tubercle?
- Long head of biceps
Q.16 Which muscle originates from infraglenoid tubercle?
- Long head of triceps
Q.17 How many ossification centers are present in scapula?
- Eight
Also read: Anatomy Question Collection
Also read: Anatomy Questions & Answers
Also read: Anatomy notes

Comments (0)