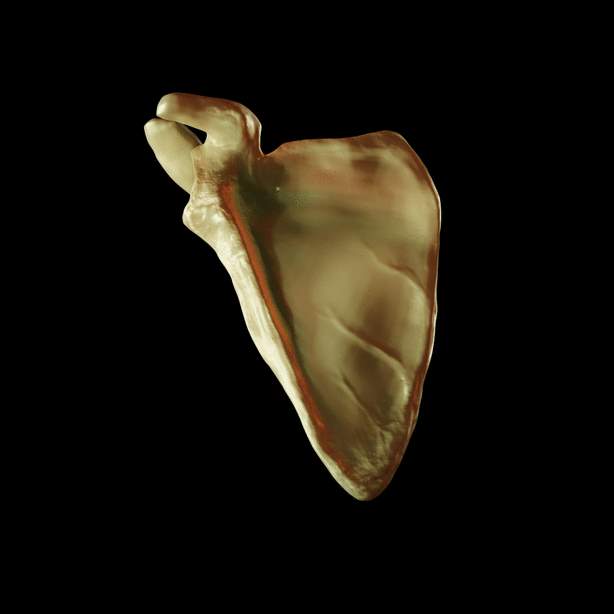
Scapula
• Flat Type of bone
• Located on the upper part of the posterior lateral aspect of the thorax at the level of 2nd – 7th ribs.
Parts of scapula
1. Body
2. Three processes:
• Spinous,
• Acromion
• Coracoid process
Body of Scapula
1. Two surfaces
• Costal surface
• Dorsal surface
2. Three borders
• Superior border
• Lateral Border
• Medial border
3. Three angles
• Inferior
• Superior
• Lateral angle
Costal surface
| It is concave and directed medially and forward. |
| 3-4 oblique ridges are presents which gives attachment to the intramuscular tendon of the subscapularis muscle. |
| The medial border of the costal surface along with the inferior angle gives insertion to the serratus anterior muscle. |
Dorsal surface
| It is convex backward |
| Shelf-like projection called spinous process divides this surface into two parts. |
| • Upper smaller part is called the supraspinous fossa. • Lower larger part is called infra spinous fossa. |
| Spinoglenoid notch communicates the Supraspinous fossa and infra spinous fossa. |
| Suprascapular nerve and vessels pass from the supraspinous fossa to the infra spinous fossae through the spinoglenoid notch. |
Muscular Attachment of Doral Surface
| From Supraspinous fossa - Supraspinatus muscle arises |
| From Infraspinous fossa - Infraspinatus muscle arises |
| Upper 2/3rd of dorsal surface near lateral border - Teres minor muscle arises |
| Lower 1/3rd of dorsal surface near lateral border - Teres major muscle arises |
| Similarly, the inferior angle of the dorsal surface gives origin to the latissimus dorsi muscle. |
Superior border
| Shortest border. |
| Extended between superior angle and inferior angle. |
| Near the root of the coracoid process a notch is present called suprascapular notch. |
| Superior transverse ligament converts the suprascapular notch into the suprascapular foramen. |
| The superior border near the suprascapular notch gives origin to the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle. |
Note:
| Above the superior transverse ligament suprascapular artery passes. It means the Suprascapular artery doesn't pass through Suprascapular foramen. |
| Below the superior transverse ligament, the suprascapular nerve passes through the suprascapular foramen. |
Lateral border
| Thickest border. |
| Extend from the inferior angle to the glenoid cavity. |
| A tubercle called infraglenoid tubercle is present at its upper part just below the glenoid cavity. |
| From Infraglenoid tubercle, the Long Head of the Triceps muscles arises. |
| From Supraglenoid tubercle, the Long Head of Biceps Brachii muscle. |
Medial border
| Extend from the superior angle to the inferior angle. |
| Costal surface of the medial border → Gives insertion to the serratus anterior. |
| Dorsal aspect of medial border from the superior angle to the root of the spinous process → Gives insertion to the levator scapulae. |
| Dorsal aspect of the medial border opposite to root of spinous process → Gives insertion to the Rhomboideus minor muscle. |
| Dorsal aspect of the medial border from the root of the spinous process to the inferior angle → Gives insertion to the rhomboideus major muscle |
Inferior angle
Lies over the 6th or 7th ribs.
Superior angle
Lies over the 2nd rib.
Lateral angle
| It is also called as head of scapula. |
| There is the presence of a cavity called the glenoid cavity. |
| Glenoid cavity articulates with the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint which is Ball & Socket type of synovial joint. |
| At the margin of this joint there is a fibrocartilaginous rim called the glenoid labrum. |
| There is a presence of tubercle called supraglenoid tubercle from where the long head of biceps brachii arises. |
Spinous process
• Shelf-like bony projection.
• Lies the dorsal surface of the scapula.
• It divides the dorsal surface of the scapula into two parts i.e
Supraspinatus fossa &
Infraspinatus fossa
Parts of spinous process:
1. Two surfaces
(Superior & Inferior surface)
2. Three border
(Anterior, Posterior & Lateral border)
| Superior surface: • Forms lower boundary of supraspinous fossa. • Gives origin to the supraspinatus muscle. |
| Inferior surface: • Forms upper boundary of infraspinous fossa. • Gives attachment to the infraspinatus muscle. |
| Anterior border: • It is attached to the dorsal surface of the scapula. |
| Lateral border: • Gives boundary to the Splenoglenoid notch through which suprascapular nerve and vessel pass. |
| Posterior border: • It is called the crest of spine. • It has two lips. One is the upper lip and another is lower lip. |
| • Trapezius is inserted into the upper lip. • Deltoid is origin from the lower lip. |
Acromion process
Consist of
• A tip
• Two borders (Medial & Lateral border)
• Two surface (Superior & Inferior surface)
| In Tip • Coracoacromial ligament is attached. |
| Medial border • A circular facet is present which articulates with the clavicle to form the acromioclavicular joint. • Gives insertion to the trapezius muscle. |
| Lateral border • Gives origin to the deltoid muscle. |
| Superior surface • Rough & subcutaneous |
| Inferior surface • Rough & related to subscapular bursa. |
Coracoid process
•It is sharply projected forward and slightly laterally.
• Give attachment to three muscles.
• Give attachment to three ligaments.
Muscles
• Short head of biceps brachii and coracobrachialis arises from the tip of this process.
• Pectoralis minor muscle inserted into the medial border of the upper surface.
Ligament
• Lateral border gives attachment to the coracoacromial ligament.
• Its knuckle gives attachment to the conoid part of the coracoclavicular ligament.
Between pectoralis minor muscle and coracoacromial ligament the trapezoid part of the coracoclavicular ligament is attached.
The root of the Glenoid cavity gives attachment to the coracohumeral ligament.
Also read: Anatomy Question Collection
Also read: Anatomy Questions & Answers
Also read: Anatomy notes

Comments (0)