MBBS questions collection of Abdomen
Abdomen
Anterior abdominal wall
- What is rectus sheath? Give its formation and contents.
- Steps of dissection of rectos sheath. What is actuate line?
- Arteries of the anterior abdominal wall. SH: Epigastric artery.
- Structures in hypogastric region. Situation: Liver, stomach, Rt.kidney.
- Hernia, indirect inguinal hernia, and direct inguinal hernia . Difference between them.
- Boundary and content of inguinal canal with clinical importance.
- Divide the abdominal into the different regions (draw and level ) with content.
- What is Hesselbach's triangle?
The diaphragm
- What is diaphragm? Give its nerve supply.
- Major opening of the diaphragm with vertebral level and structures passing. Through them.
- Nerve supply of diaphragm on the embryological background.
- Development of diaphragm.
- SN: central tendon.
- The action of the diaphragm.
Stomach
- Draw and label the different part of stomach. Give lymphatic drainage of the stomach.
- Draw and level of the stomach. What is gastric pit?
- Blood supply nerve supply and lymphatic drainage of the stomach.
- What is stomach bed? Give formation of it. Draw and label.
- What is the gastric pit? Branch of celiac trunk. Clinical importance of stomach.
- Give the histological structure of stomach. The mucosa of stomach.
- Give the histological feature of the oesophagus.
- Rotation of stomach in embryonic life. Development of stomach.
- What is the gastric canal?
Duodenum
- Write the visceral relations of the first part of duodenum. Explain blood supply of duodenum on development background. What is duodenal cap?
- Relation of first part of duodenum . Histological feature s of duodenum. Intestinal villi.
- Describe second part of duodenum with clinical importance. Extention and structures open into it.
- What is duodenal cap? Give its clinical importance.
- Blood supply and development of duodenum.
Jejunum and Ileum
- Macroscopic and microscopic difference between jejunum and Ileum.
- Macroscopic and microscopic difference between small and large intestine.
- Different positions of the appendix with structure, blood supply and clinical importance.
- Congenital megacolon.
- Mention the different positions, artery supply and clinical importance of vermiform appendix
Anal Canal
- Describe anal canal. Interior of anal canal . Interior features of upper 15 mm of anal canal with clinical importance.
- Give the internal features of upper 15 mm of anal canal. Mention the significance of pectinates line.
- What is anal column? Give its development.
- SN: Pectinate line . Hemorrhoids pudendal canal .
- Give blood supply, lymphatic drainage, nerve supply and clinical importance if anal canal.
- Formation and nerve supply of external and internal anal sphincter.
- Boundary and contents of ischiorectal fossa with clinical importance.
- Development of anal canal.
- Five important between upper and lower part of anal canal.
- What is imperforated anus.
Liver
- What is the anatomical and physiological lobe of the liver? Support os liver.
- What is hepatic lobule, portal lobule and portal acinus's with functional importance?
- Write about parts, nerve supply, and histology of gall bladder, write a note on common bile duct.
- Relation of Rt lateral surface of liver with clinical importance.
- Development of liver , formation, and tributaries of portal vein.
- Give formation and distribution of portal vein. Mention sites of Porto Caval anastomosis.what are esophageal varices.
- Draw and level a classical hepatic lobule . Histological structure of Liver.
- Sites of portosystemic anastomosis in our body. Relation of interior surface of liver.
- Short note: portal vein.
Pancreas
- Parts of pancreas. Gross anatomy of head of pancreas.
- Blood supply and development of pancreas.
- What is annular pancreas?
- Histological structure of pancreas. What is pancreatic acini?
- Mention relations of head and neck of pancreas.
Spleen
- SN: a) visceral surface of the spleen. B) splenic pulp. C) red and white pulp
- Histological features of spleen.
- Mode if blood supply if spleen.
- Ligaments of spleen and their content.
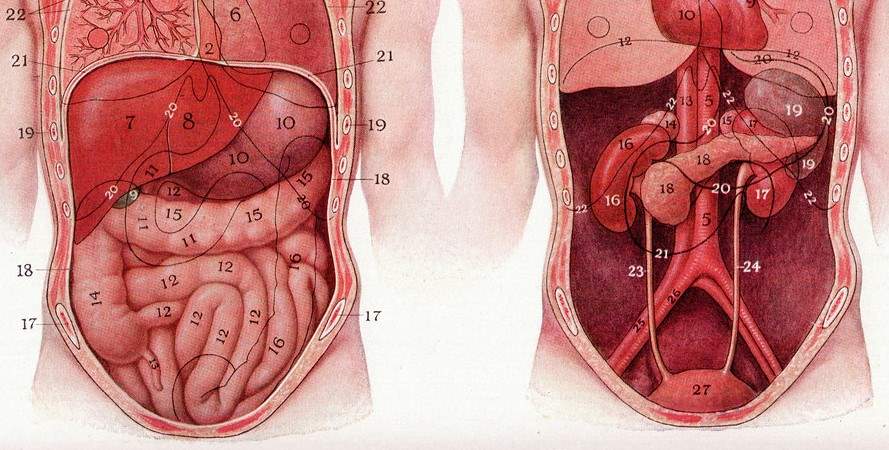
Kidney
- Draw and label a coronal section through the kidney showing naked eye give sources of development of adults kidney. What is agenesis of the kidney.
- Different parts of uriniferous tubules. What is renal sinus?
- What is nephron? Draw and label different parts of it.its dev.
- Distribution of renal sinus fascia. Factors responsible for ascend s of kidney.
- Blood supply and development of kidney . Development anomalies of the kidney.
- Draw and label a coronal section of kidney showing its different microscopic structures.
- Derivation of mesonephric and paramesonephric ducts of kidney in both sexes.
- Short note: a) Polycystic kidney b)Ectopia varicose
- Relation of right (anterior surface)and left kidney (posterior).
Suprarenal gland
- Describe suprarenal gland. Dev of suprarenal gland. Histological structure if suprarenal gland.
Ureter and urinary bladder
- Course and relations of pelvic part of ureter. What is urectal fistula?
- SH: Trigone of urinary bladder. Boundary and clinical importance.
- Development of urinary bladder. Histological structure of urinary bladder.
Prostate
- Mention the anatomical lobes and histology of prostate.
- Write about prostate. Capsule of the prostate.
- Histological structure and clinical importance of prostate.
- Name the lobes of the prostate. Which lobe is more imp. Clinically and why?
Urethra
- Mention different parts and development of male urethra. What is hypostasis?
- Features of prostatic part of urethra.
Male genitalia
- Parts of male genitalia. Transverse section of penis.
- Homologous part of male and female genitalia. Give its dev and structures.
Penis
- Parts of penis. Support and blood supply, nerves supply of penis.
- What is erectile tissue? Name different erectile tissue of penis.
Female genitalia
Uterus
- Give the normal position and primary supports of uterus. What is uterus didelphys? Mention formation and clinical importance of pouch of Douglas.
- Parts and normal position of uterus.
- What is anti-flexion and anti version of uterus? What is uterus bicorn is? What is uterus didelphys?
- Supports of uterus. Ectopic pregnancy
- Histological features of endometrial of uterus. What is ovulation?
- Draw and label different parts of uterus. Discuss structure of endometrium of uterus at different stages of menstrual cycle.
Vagina
- Fornices of vagina with clinical importance. What is vaginal fornix?
Uterine tube
- Histological structure and development of uterine tube.
- Clinical importance of uterine tube. Parts and blood supply of uterine tube.
Ovary
- Explain location and development of ovary. Draw and label light microscopic features of ovary.
- Histological structure of ovary.
- Boundary of ovarian fossae. What is ovarian fimbriae?
Others
- Epiploic foramen, spermatic cord. Pouch of Douglas physiological umbilical hernia.
- Mention the boundaries and characteristics of trigone of urinary bladder. What is pelvic kidney.
- Boundary and contents of deep perineal pouch.
- What hypospadias and pudendal block? Name the retroperitoneal structure.
- Define cloaca . Mention it’s derivatives in both sexes.
- Stomodeum and proctodeum
- Define porta- caval anastomosis. Mention three porta- caval anastomosis with clinical importance.
- Content of the spermatic cord.
- What is Hydrocele?
- Name the genital ducts in both sexes and mention their derivatives.
Also read: Anatomy Question Collection
Also read: Anatomy Questions & Answers
Also read: Anatomy notes
Comments (0)