Vascular System
Circulation
The process of blood & lymph flow through a closed system of vessels is called circulation.
Type of circulation
• Systemic circulation
• Pulmonary circulation
• Portal circulation
Systemic circulation
Passage of blood from the left ventricle through the aorta to tissues & from the tissue to the right atrium is called systemic circulation.
Pathway
| Left ventricle → Aorta → Artery → Arterioles → Capillary → Venule → Vein → Right atrium |
Pulmonary circulation
Passage of blood from the right ventricle through the lungs to the left atrium of the heart is called the pulmonary circulation. It takes deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs & returns oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
Pathway
| Right ventricle → Pulmonary artery → Lung → Pulmonary vein → Left atrium |
Difference between systemic & pulmonary circulation
| Systemic circulation |
Pulmonary circulation |
| Blood flow from the left ventricle to body tissue to the right atrium |
Blood flow from the right ventricle to lung & from the lung to the left atrium |
| Start from ventricle |
Starts from right ventricle |
| Ends at right atrium |
Ends at left atrium |
| Artery - carry oxygenated blood |
Artery - carry deoxygenated blood |
| Vein - carry deoxygenated blood |
Vein - carry oxygenated blood |
Less distensible
So offer high resistance
So High blood pressure system
|
More distensible (high elastic fibers)
So offer less resistance
So low-pressure system |
Portal circulation
The system of blood circulation from one set of capillary of one structure(organ) to another set of capillary of another structure(organ) is called the portal system. In another way, the passage of blood through two sets of capillaries before draining into the heart is called portal circulation.
Portal circulation begins in capillaries & also end in another set of capillaries.
Example:
Hepatic circulation:
• Begin from capillaries around the digestive system
• Carry nutrients from GIT to liver for metabolism
• End at the capillary of the liver called liver sinusoids.
Type of portal system
|
1. Arterial portal system
Example: Renal portal system
|
|
2. Venous portal system
Example: Hepatic portal system & hypophyseal portal system
|
|
Hepatic portal system
From capillary plexuses of gut to hepatic sinusoid
|
|
Function
Enables the blood to take up products of digestion from alimentary canal & to covey them to the liver cells
|
|
Renal portal system
From glomerular plexus to peritubular plexus
|
|
Functions
Helps reabsorption of some essential constituents of glomerular filtrate back to blood
|
Hypophyseal portal system
From capillary plexuses of the hypothalamus to sinusoid of anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)
|
Functions
Transport the releasing & inhibiting hormones secreted from the hypothalamus to anterior pituitary gland for the regulation of secretion from the anterior pituitary gland.
|
Suprarenal portal system
From cortical sinusoids to medullary sinusoids
|
Function
Conveys some chemical substances from cortex to medulla
|
Anastomosis:
Anatomically, the connection between two adjacent blood vessels by collateral channels is called anastomosis.
Type of anastomosis
• Arterial anastomosis (Inter-arterial anastomosis)
• Venous anastomosis
• Arterio-venous anastomosis (Vascular Shunt)
| Anastomosis |
Features |
Examples |
| 1. Arterial anastomosis |
|
|
| • Actual |
Blood spurts in both directions
from the cut end of the anastomosis. |
Between Rt. & Lt. gastric arteries
Anterior & posterior intercostal arteries
Ovarian arteries
Uterine arteries |
| • Potential |
Blood spurts in one direction from
the cut end of the vessel |
Between rt. & Lt. coronary arteries
Cortical arteries of cerebral hemisphere |
| 2. Venous anastomosis |
Communication between veins
Common & frequently available anastomosis |
Dorsal venous arch of hand
Dorsal venous arch of foot
Between cephalic & basilic vein through the median cubital vein
Azygos vein which connects superior vena cava with inferior vena cava |
| 3. Arterio-venous anastomosis |
When arterioles directly communicate
with venules by anastomosing channels
without passing through capillary beds |
Tip of nose, lips ear lobules, fingertip
Mucous membrane of nose & alimentary canal
Erectile tissue of sexual organ
Thyroid gland
|
Importance of anastomosis:
• Allow an equalization of blood pressure over territories in which they are connected.
• Provide alternative channels of supply to a particular area.
• Provide equal distribution of blood
• Regulate temperature between the environment & body by adjusting the blood flow of the cutaneous bed.
End artery / No anastomosis
In a certain portion of the body, arteries don’t form any anastomosis with neighboring vessels called as end arteries.
No collateral circulation, only one route in the end artery.
Types of end artery
|
Anatomical (True) end artery
True end artery are those whose terminal branches do not anastomose.
|
|
Example:
Central artery of retina
|
Functional end artery
Terminal branches of these arteries anastomose with neighboring arteries but this anastomosis is not enough to keep tissue alive if any one of these arteries block.
|
Example
Coronary arteries of heart
Splenic artery of spleen
Renal artery for kidney
Arteries of liver
Arteries of lung
Central arteries of brain
|
Significance of end artery
Occlusion of the central artery of retina leads to necrosis & is followed by permanent blindness.
Any blockage of these arteries causes serious nutritional disturbance resulting in the death of the tissue supplied by the vessels (Describe as necrosis, infarction, or gangrene).
Anatomically, the right & left coronary arteries of the heart are not end arteries, they do anastomose with each other but functionally, they behave like end arteries because during occlusion of any one of these, another artery do supply the collateral circulation but this collateral supply is not enough to meet the oxygen & nutrients demand of the blocked area leading to myocardial infarction.
Components of the circulatory system
Blood vascular system
| Heart |
| Arteries |
• Large/Elastic arteries
Example
Aorta & its branches
• Medium-sized/Muscular arteries
Example
Femoral artery, Brachial artery, Radial artery
• Arterioles
Example
Branches of muscular arteries
|
| Capillaries |
• Continuous/somatic
Example
In skin, muscle & nervous system
• Fenestrated/visceral
Example
In kidney, intestine, endocrine gland, pancreas
• Discontinuous/ sinusoidal
Example
In liver, spleen, bone marrow & adrenal medulla
|
| Veins |
• Large vein
Example
Superior & Inferior Vena cava
• Medium vein
Example
Radial vein, Femoral vein
• Small vein
Example
Tributaries of medium vein
|
Components of Lymphatic vascular system
| 1. Lymphatic capillaries |
| 2. Lymphatic vessels |
3. Terminal lymphatic duct
• Thoracic duct
• Right lymphatic duct |
Functional classification of blood vessels
| Types |
Examples |
| Distributor vessels |
Arteries |
| Resistance vessels |
Arterioles |
| Exchange vessels |
Capillaries |
| Capacitance (Reservoir) vessels |
Veins |
Overall course:
Heart
↓
Arteries
• Large artery (elastic)
• Medium-sized artery (muscular)
• Small artery
↓
Arteriole
↓
Metarteriole
↓
Capillary
↓
Venule
↓
Vein
↓
Heart
Artery
Artery is a complicated series of tubes through which heart transport blood to all parts of the body by repeated contraction.
Classification
• Large artery/ Elastic artery
• Medium-sized artery/ Muscular artery
• Small artery
• Arterioles
Large artery/ Elastic artery
• Main characteristics feature is composed of elastic fibers.
• Large artery is known for its elasticity.
• Contain an abundant amount of elastic fibers.
Why abundant elastic fibers in large arteries?
Abundant elastic fibers are present for strength & elasticity needed to withstand the force by which heart pump blood, & prevent bursting of an artery.
When heart ejects the huge amount of blood with great pressure, large arteries have to stretch (increase) their lumen’s diameter for the accommodation of such a huge volume of blood & withstand the pressure.
Similarly between heart contraction, the elastic walls of large arteries recoil (contract to normal), so to continue the further pumping of blood to far distance even when ventricles are relaxed, to maintain blood pressure.
|
During ventricular contraction, the resulted arterial hydrostatic pressure is called systolic blood pressure.
Systolic blood pressure - is the direct resultant effect results from ventricular contraction.
|
| During the ventricular relaxation (in between two contractions), the resulted arterial hydrostatic pressure is called diastolic blood pressure. |
But even in ventricular relaxation, blood vessels exert pressure, why?
This is because due to the elastic recoil tendency of large arteries which further pump the accumulated blood present in their lumen during ventricular relaxation.
Thus diastolic blood pressure - results from the elastic recoil tendency of large arteries.
Blood vessel has the highest blood pressure when heart contract, & lowest when the heart relaxes and the variation in pressure produces a pulse, which can only be felt in arteries.
Large arteries are found nearly around the heart like
• Pulmonary artery
• Aorta
• Brachiocephalic trunk
• Carotid artery
• Subclavian artery
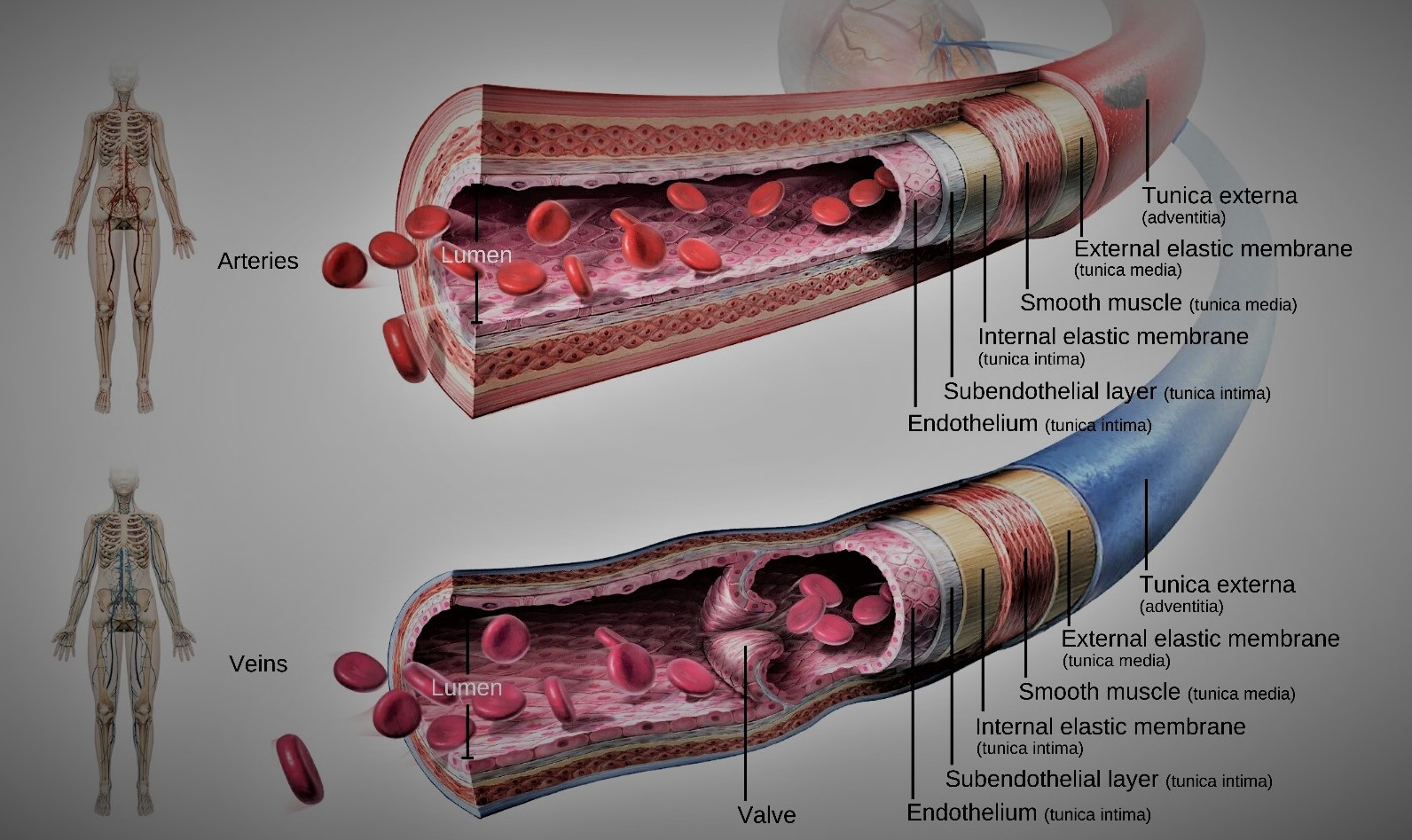
Histological layer of large/elastic artery
Tunica adventitia (Outer layer)
• Consists of connective tissue in which collagen & elastic fibers are prominent.
Tunica media (Middle layer)
• Consists of circular smooth muscle cells (spindle-shaped)
• Maximum Elastic & collagen fibers present
• External elastic lamina - composed of yellow elastic fibers (present between tunica media & tunica adventitia)
Tunica intima (Inner layer)
Consists of
• Endothelial lining (of Simple Squamous Epithelium)
• A sub-endothelial layer of connective tissue
• Internal elastic lamina (composed of elastic fibers) - which separates tunica intima & tunica media.
Note:
| External elastic lamina & internal elastic lamina - composed of elastic fibers. |
| As elastic fibers are the prominent feature of the large artery and found in every layer (more abundantly in the middle layer), in the histological side, we cannot distinctly see internal & elastic lamina as these also composed of elastic fiber. |
Medium-sized artery/ Muscular artery
Features
• Know for its thickest middle layer (tunica media) composed of an abundant amount of smooth muscle cells, so that they can contract & relax (dilate) as per the amount of blood needed.
• Supply to specific parts of the body according to which they are named after.
Example
- Brachial artery
- Radial artery
- Femoral artery
- Splenic artery
Note:
| These circular smooth muscles layer is innervated by the sympathetic nervous system which controls vasoconstriction/vasodilation of vessels. |
| There is little/no parasympathetic effect on blood vessels. |
|
• Strong rapid firing of sympathetic impulse - causes vasoconstriction
• Weak weak firing of sympathetic impulse - causes vasodilation
|
| So, sympathetic nerve supply is solely responsible for vasomotor function (vasodilation/vasoconstriction) |
Histological layer of Muscular artery
Tunica adventitia (outer layer)
• Consists of connective tissue with collagen & elastic fibers
Tunica media (middle layer)
Consists of
• Huge circular layer of smooth muscle cells (spindle-shaped) for which medium-sized is known as muscular artery.
• Some elastic & collagen fibers
• External elastic lamina - which separate tunica media from the tunica adventitia
Tunica media (inner layer)
Consists of
• Inner endothelial lining of (simple squamous)
• Middle subendothelial layer of connective tissue
• Internal elastic lamina - composed of elastic fibers (which separate it from tunica media)
Difference between Large artery (elastic) & Medium-sized artery (muscular)
| Large artery |
Medium-sized artery |
| Internal elastic lamina is not distinct from tunica media |
Internal elastic lamina is prominent |
| External elastic lamina is not distinct |
External lamina is distinct |
| Tunica media is mostly composed of elastic fibers with relatively few smooth muscle fibers |
Tunica media is composed of circularly arranged layer of smooth muscle fibers with some elastin |
| They can stretch & recoil according to pressure change |
They can contract & relax changing the lumen’s diameter as per the need regulated by sympathetic nerve fibers |
| They are the conducting arteries |
They are the muscular arteries |
Note:
| Elastic fibers - yellow in color |
| Elastic fibers are made up of elastin protein. |
| Elastic fibers are present where elasticity is required (stretch & recoil phenomena) like in lungs, pulsating arteries. |
| Only arteries have pulsation (not present in veins & capillaries), so arteries have a relatively good amount of elastic fibers than in those veins. |
| Smooth muscle fibers are spindle-shaped with a single nucleus centrally placed. |
| The lumen of all blood vessels are lined by Simple Squamous Epithelium which is named as Endothelium (in case of blood vessels). |
| Vasa vasorum (Vessel of vessel) - Supply large arteries as they need their own blood supply. |
All arteries carry oxygenated blood except
• Pulmonary artery - which carries deoxygenated from heart to lung for the oxygenation process
• Umbilical artery - which carries deoxygenated blood from fetus to mother
|
| Arterioles help in regulating blood pressure by contraction of smooth muscles present in their walls. |
| When an artery is cut, blood spurts out in a rapid manner which coincides with heartbeat/pulse. |
Atherosclerosis:
Atherosclerosis is the condition of hardening of arteries due to deposition of plaques inside the tunica intima.
Atheroma or plaque is mainly composed of cell debris containing lipids (cholesterols & fatty acid), and calcium for hardening.
Long term persisting diabetes mellitus (high blood sugar), cholesterols, high blood pressure, stress & smoking, all are involved in damaging endothelium of arteries leading to atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is characterized by progressive inflammation of the walls of arteries.
Initially, when there is damage in the endothelial lining of blood vessels, accumulation of WBC (especially macrophages) occurs which takes up a huge amount of oxidized Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)- bad cholesterol.
After the accumulation of high cholesterol content, macrophages now called as foam cells.
These formed plaques later calcified making stiffness (hardness) to arteries.
Veins are not subjected to develop atheroma/ plaques as veins do not have the same hemodynamic pressure as arteries.
Thrombosis
Formation of the blood clot inside the blood vessel making obstruction to blood flow is called thrombosis.
Embolism is the formation of a piece of loose clot (called an embolus) that travels around through your blood circulation and could occlude the vessels of certain organs.
Example:
• Ischemic stroke (in brain)
Summary On Histological structure of blood vessels
Tunica intima
• Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels
• In vessels larger than 1mm, a sub-endothelial connective tissue basement membrane is present
Tunica media
• Smooth muscle & elastic fiber layer, regulated by the sympathetic nervous system
• Controls vasoconstriction/ vasodilation of vessels
Tunica adventitia
• Collagen fibers that protect & reinforce vessels
• Large vessels contain vasa vasorum
| |
Arteries |
Vein |
Capillary |
| Wall layers |
Tunica adventitia
Tunica media
Tunica intima |
Tunica adventitia
Tunica media
Tunica intima |
Only Tunica intima present |
Arteries & arterioles have thicker walls than veins & venules because they are closer to heart & receive blood that is surging at far greater pressure.
Capillary
Capillaries are simple microscopic vessels, endothelial tubes that connect the arterial end & venous sides of the circulation.
Features of capillary:
• Has no smooth muscles - so no contraction/relaxation
• Only one layer i.e tunica intima & underlying basal lamina
• No tunica media & tunica adventitia
Sites where capillaries are absent
Capillaries supply almost every cell, except for
• Epithelial cells resting on the basement membrane
• The epidermis of skin, hair & nails
• Cornea of eye
• Cartilage
These structures have no direct blood supply.
Note:
| When branching of arteries occurs, the cross-sectional area increases decreasing the velocity of blood flow (with low blood pressure). |
| Capillaries have a lot of branching with a maximum cross-sectional area. Thus capillaries have slowest blood flow for an excellent exchanging process. |
| When venules combine to form veins, the cross-sectional area of blood vessels decreases increasing the velocity of blood flow. |
Classification of capillary
1. Continuous capillary:
| Lack pores on its wall |
| Epithelial lining along with basal lamina is continuous without pores on its wall. |
| Most abundant capillaries found all over the body |
| Found in skin, muscle, lung and nervous system (brain & spinal cord) |
Continuous capillaries of nervous tissue is so special that its permeability is highly selective. The endothelial lining with tight junction forms the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB). Due to this, even drugs cannot bypass this barrier. So its highly complicated to treat brain patients by use of drugs.
2. Fenestrated capillary
| Presence of pores (fenestrae) through the walls of the endothelial cells, like cheese |
| Fenestration usually covered with thin glycoproteins diaphragm or may not be. |
| Endothelial lining (cell to cell connection) is continuous but present many tiny small-small pores. on the vessel wall. |
| But the basal lamina is continuous. |
| Found in areas involved in active filtration (kidney), absorption (intestine), or endocrine hormone secretion. |
|
Found in
• Renal glomeruli
• Intestinal villi
• Endocrine glands
|
In the glomerulus of the nephron, ultra-filtration of blood occurs for urine formation.
But protein & RBC cannot cross the barrier |
Similarly, blood vessels in intestinal villi receives nutrients from digested food. But cannot absorbs fat (as fat globules are bigger in size).
Thus, fats are transported through lacteal (lymph vessels in the digestive system) |
| Exocrine glands have their own ducts for transport of their secretion. But, endocrine glands drain their secretion through blood vessels. |
3. Sinusoidal capillary / Discontinuous capillary
| Larger capillaries with much more larger lumen. |
| Usually large fenestrated with larger intercellular clefts; incomplete basement membrane |
| Protein & RBC can pass. |
| Both endothelial lining & basal lamina is not continuous. |
| Permits maximal exchange of macromolecules as well as cells between tissues & blood. |
|
Found in
• Liver (Hepatic sinusoid)
• Bone marrow
• Spleen
• Adrenal medulla
|
Function of capillary
• Transfer of O2 & other nutrients from blood to tissues.
• Transfer of Co2 & metabolic waste products from tissues to the blood.
Normally plasma protein cannot cross the wall of capillaries. In certain pathological conditions, plasma protein can cross the capillary wall into the interstitial space decreasing the osmotic colloidal pressure within blood vessels and increasing the osmotic colloidal pressure around the interstitial space draining wall into the space from blood vessels causing edema.
Thus, the main function of plasma protein is to maintain osmotic colloidal pressure within the blood vessels to preserve/hold the water content for maintaining blood volume.
However physiologically, protein & RBC can cross the wall of sinusoid capillaries.
• In liver - plasma protein can cross and drain in blood vessels.
• In Red-bone marrow - RBC can cross
| The liver is the main site of plasma protein formation. All proteins are synthesized in the liver except gamma-globulin which is formed by lymphocytes & plasma cells. |
| Red-bone marrow is the site where formed elements of blood are formed. |
| The spleen filters the blood. It means even RBC can squeeze out through those pores of discontinuous capillary |
| Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) have tight junction. (Limit diffusion) |
These above illustrate the importance of the presence of discontinuous capillary over those structures.
Difference between capillaries & sinusoid
| Capillaries |
Sinusoids |
| Small lumen |
Larger dilated lumen |
| Regular lumen |
Irregular, tortuous lumen |
| Endothelial lining continuous |
Endothelial lining discontinuous |
| Basal lamina complete |
Basal lamina discontinuous |
| Phagocytic cells absent |
Present (Kupffer cells in liver sinusoid) |
| Present whole over the body |
Present in liver, spleen & bone marrow
|
Veins
Veins are vessels that collect & bring deoxygenated blood from the capillary networks to heart except pulmonary veins.
• Have all three layers but thinner walls with larger lumen compared to corresponding arteries.
• Large lumen & thin walls make veins good storage vessels so-called as capacitance vessels (blood reservoirs) because they contain up to 65% of blood supply.
Classification
• Venules
• Small to medium-sized veins
• Large veins
Histological structure of vein
Tunica adventitia (outer connective tissue coat)
• Thicker than tunica media & form 2/3rd of the thickness of the wall of the vein
Composed of:
• Dense connective tissue
• Collagen fiber but much less elastic fibers with few muscles
Tunica media (middle muscular coat)
• Thinner than tunica adventitia
• Composed of circular arranged smooth muscle cells
Tunica intima (Inner endothelial coat)
Consists of:
• Endothelium with its basement membrane
• Internal elastic lamina is not distinct
Summary:
Tunica media is thin, but tunica adventitia is thicker.
The lumen of the vein is quite bigger & collapsable as compared to their thickness.
But in the artery,
• Tunica media is thicker than tunica adventitia
• The lumen of the artery is small & patent (non-collapsing) as compared to their thickness
Difference between Artery & Vein
| Artery |
Vein |
| Smaller lumen but greater thickness |
Larger lumen but lesser thickness |
| Sub endothelial layer is well defined |
Sub endothelial layer is not well defined |
| Internal elastic lamina distinct |
Internal elastic lamina not distinct |
| External elastic lamina distinct |
External elastic lamina not distinct |
| Thick Tunica media in comparison to tunica adventitia |
Thin tunica media in comparison to tunica adventitia |
| Tunica adventitia thinner, form 1/3rd of thickness.& present less amount of collagen fibers |
Tunica adventitia thicker, forms 2/3rd of the thickness.& present large amount of collagen fiber |
| Valves absent |
Valves present |
| Blood flow away from heart |
Blood flow towards heart |
| The velocity of blood flow is rapid |
The velocity of blood flow is slow |
| Blood pressure is very high. |
Blood pressure is very low |
| Pulse is present. We measure the pulse rate in the artery, not in vein. |
Pulse is not present |
| Usually found in deeper in body structures as they are subject to high blood pressure and any damage to artery could cause excessive blood loss leading to death |
Usually present superficial of body.
All you see from outside are veins |
Carry oxygenated blood except the pulmonary artery.
In the case of a fetus, the umbilical artery also doesn't carry oxygenated blood. |
Carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein & portal veins |
Comments (0)