Ossification
5 years ago 9141
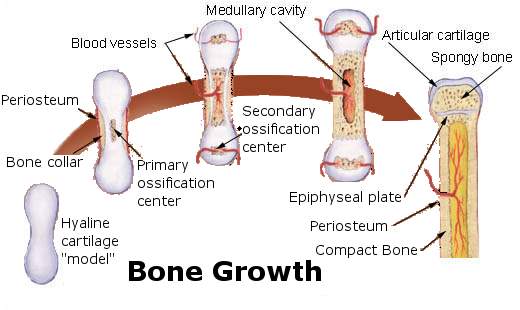
| The primary ossification center is that from where, the bone starts ossified which appears before birth. |
| The primary ossification center is that from which, the main part of the bone is ossified & is appears before birth, usually during the 8th week of intrauterine life, which forms diaphysis (later called as the shaft of a long bone). |
| The secondary ossification center is that from which accessory part of a bone is ossified & is appears mostly after birth, which forms the epiphysis. |
| • Epiphysis develops from the secondary ossification center. |
| • Diaphysis (shaft) develop from the primary ossification center. |
| • The Epiphyseal center which appears first, unit last with the diaphysis & vice-versa. |
| • That means epiphysis that ossify first fuse with diaphysis last & the epiphysis that ossifies last fuses first with diaphysis except fibula. |
| • Secondary ossification center appears first in the lower end, |
| that means epiphysis of lower end of fibula ossify first but also fused with diaphysis first. |
| • As the upper epiphysis of fibula fused last, the upper end of the fibula is the growing end of the fibula as usual. |
| • There is no violation in determining the growing end. It's same for all long bones (opposite to the direction of nutrient foramen) |
| • The epiphysis which is the first to appear, is the last to join, and the epiphysis which is the last to appear is the first to join. • The only exception is the fibula. |
|
In fibula
• The secondary ossification center appears 1st in the lower end and fused first with diaphysis. • The secondary ossification center appears later in the upper end & fused last with diaphysis. |
|
Intramembranous ossification
Mesodermal model (Formed by undifferentiated mesenchyme)
↓
Directly converted into bone.
(By mineralization of matrix.)
|
|
Endochondral Ossification
Undifferentiated mesenchyme ↓ Form Cartilage model ↓ Converted to bone later |
|
Base of skull below the highest nuchal line is formed by Intra cartilaginous ossification.
|
| Intramembranous ossification | Intra cartilaginous ossification |
| By direct mineralization of matrix secreted by osteoblast | By deposition of bone matrix in pre-existing cartilage matrix |
| Primary center of ossification only present | Both primary & secondary center of ossification present |
| From mesenchymal tissue | Modified from hyaline cartilage model |
| Most of the flat bone ie. Ribs, Sternum, Clavicles Bones of the skull that form cranial vault, Mandible, maxilla, hip bone, vertebrae |
Short & long bones ie. Humerus, femur, tibia, fibula, etc. |
|
Intramembranous ossification
• Mandible • Maxilla
• Most of the flat bones of the skull that form the cranial vault • Sternum • Ribs • Vertebrae • Hip bone |
| Intra cartilaginous ossification • Short & long bones of the body • Base of the skull • Humerus • Radius & ulna • Femur • Tibia & fibula • Bones of hands & legs |
Comments (0)