Glands
5 years ago 2467
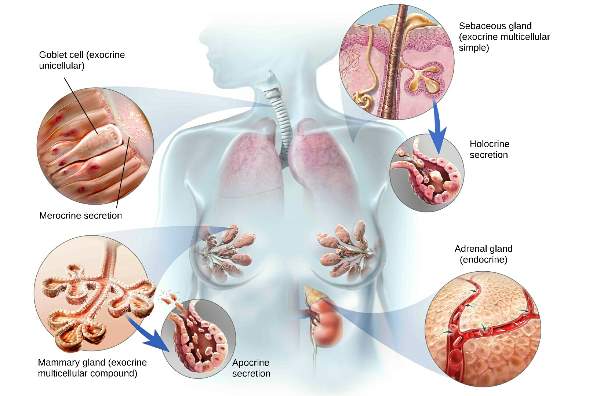
| A) A/c to cellular arrangement 1. Unicellular Goblet cell |
| 2. Multicellular • Exocrine: Sweat, Salivary, Sebaceous, Mammary glands • Endocrine: Thyroid, Pituitary glands |
| B) A/c to the nature of secretion 1. Mucous: Goblet cell 2. Serous: Parotid, Sweat gland, Pancreas 3. Mixed: Sublingual, Submandibular gland |
| C) A/c to the development 1. Ectodermal: Mammary, Lacrimal, Glands of skin 2. Mesodermal: Gonads, Kidney 3. Endodermal: Liver, Thyroid, Parathyroid |
| D) A/c to mode of secretion 1. Apocrine (Apical) Mammary gland 2. Holocrine (whole) Sebaceous gland 3. Merocrine (no loss) Endocrine, Digestive gland |
|
A- Apocrine
Apical portions of cells are lost during secretion. Holo-Whole
Mero-Mine (no loss)
|
| • Parotid gland Purely serous |
|
• Sublingual gland
Mixed; but predominantly mucous |
| • Submandibular gland Mixed; but predominantly serous |
|
• Sweat gland
Watery & salty secretion
|
|
• Sebaceous gland
Present around hair follicle
Oily fatty secretion
|
| 1) Parenchyma Composed of • Glandular epithelium (Secretory in function) • Duct (Lined by epithelium) |
| 2) Stroma • Supports the parenchyma • Composed of connective tissue • Blood vessels, lymphatics & nerves present in connective tissue |
| Exocrine Gland | Endocrine Gland |
| Have ducts | Ductless gland |
| Secrete enzymes, milk, sweat, saliva | Secrete hormones |
| Transport their secretion through ducts | Transport their secretion through bloodstream |
| Only acts where they are locally secreted | Show their action all over the body |
| Example: Digestive glands, Sweat and mammary gland |
Example: Pituitary, Thyroid, islets of Langerhans of Pancreas |
| Mucosa (Mucous Membrane) An epithelial membrane having glandular epithelium which secrete mucus. Goblet cell- secrets thick mucus Lines the cavities exposed or related to the external environment. |
|
Example:
Gastrointestinal tract (GIT) Respiratory Tract
Urogenital Tract |
|
Layers in Mucosa
Surface Epithelium
Basement membrane
Lamina Propria
Muscularis mucosa
|
| The mucosa is covered by the film of thick slippery mucus secreted by epithelial cells. |
|
Serosa
Lines the closed cavities of the body.
|
|
Example:
Pericardium
Pleura
Peritoneal cavity
|
|
Serosa Layer
Epithelium (Mesothelium)- Simple Squamous
Basement Membrane
Lamina Propria
|
|
Serous membrane
• Pleura
• Pericardium
• Peritoneum
|
| Serosa secretes watery secretion called serous fluid for the protection. |
|
Mucosa of Gut wall
• Related to lumen- exposed to the environment through mouth & Anus
|
|
Serosa of Gut
• Exposed to Peritoneal Cavity
|
| Serous | Mucus |
| Thin watery secretion rich with protein & water | Thick slippery secretion |
| Comprise of zymogens, antibodies & inorganic ions | Viscous comprise of mucin |
| Secreted by serous acini (of serous gland) | Secreted by mucous acini (of mucous gland) |
| Solubilized dry food, Initiate starch digestion (amylase) Protect organs (by serous fluid) |
Lubricate oral cavity Gastric Mucus protect from gastric acid Make stool slippery in large intestine |
| Example: By Parotid gland (Serous Saliva) Serous membrane (Serous fluid) |
Example By Sublingual gland, Goblet cell |
| Large intestine has a maximum no. of goblet cells for secretion of mucus. As the maximum water reabsorption occurs in the large intestine, dry stool is formed. So, mucus is needed for its slippery smooth movement. |
| Respiratory Epithelium is lined by Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium with numerous intersperse goblet cells for secretion of mucus that film over the mucosa of the respiratory tract. Cilia is needed for the movement of these thick mucus. |
| The secretion from the nose is one kind of mucus. |
| • The epithelial cells possessing contractile properties like smooth muscle known as myoepithelial cells. |
| • Found in exocrine glands (i.e mammary gland, salivary gland, lacrimal gland, sweat gland) |
| • Cytoplasm contains myosin & a large no. of actin filaments. • The cells are specialized for contraction & helps to propel secretory products into duct. |
|
• Actin & Myosin are the contractile protein found in muscle.
• When Ca++ bind to Troponin-C protein of actin filament, Actin slide over the myosin thick filament).
|
|
• Usually, all postganglionic sympathetic nerves are adrenergic.
But the postganglionic nerves that supply the sweat glands are cholinergic.
This is the peculiarity of the nerve supply of the sweat gland.
|
Comments (0)