Epithelial Tissue
5 years ago 5467
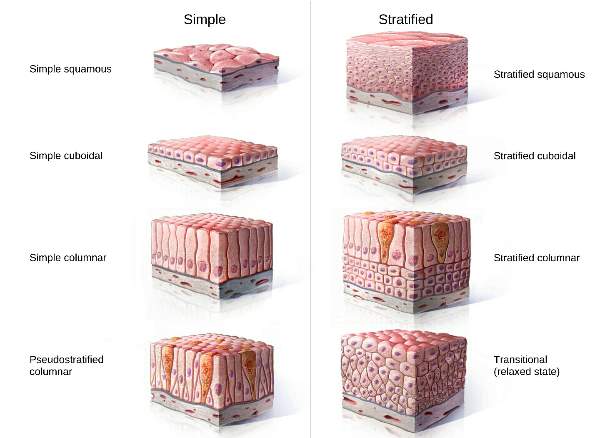
| 1) Epithelial tissue → lined the surface or body cavities, and secretory in function |
| 2) Connective tissue → support & protection |
| 3) Muscular tissue → For movement |
| 4) Nervous tissue → For transmission of nervous impulses |
| • Glands are the modification of epithelial cells. • And its cells (parenchyma) are supported by connective tissues (Stroma). |
| Lining epithelium related to the external outer environment like 1) Epidermis of skin 2) Corneal epithelium & conjunctiva of eye |
| 3) Lining epithelium of lower part of the anal canal 4) Lining epithelium of urethral opening in penis, vagina |
| 5) The epithelial lining of the mouth cavity, nose cavity, paranasal sinuses These all develop from ectoderm. |
|
Lining epithelium of
• Respiratory tract, GIT Tract,
• Glands of the digestive tract (Liver, Pancreas, Gallbladder)
|
| → develop from endoderm |
| Lining epithelium of • Heart (Endocardium-simple squamous), • Blood vessels, Pleura, Pericardium |
| → develop from mesoderm |
| • There is no direct blood supply to the epithelial cells. It gets nutrition from underlying blood vessels (in lamina propria) by diffusion. |
| • Cells are closely packed to each other • Cells rest on basement membrane |
|
• Origin from all 3 germ layers
• Maximum cellular substance and minimum intracellular substance (opposite of connective tissue) |
|
1. Single-layer
• Simple
(Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar)
• Pseudostratified Columnar
|
|
2. Multi-layer
• Stratified
(Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar) • Transitional
|
|
Neuroepithelium
For Receptor
|
|
Olfactory Epithelium
Nasal cavity receptor for smell
|
|
Endothelium
Lining of Blood & Lymphatic vessels
Simple Squamous
|
|
Endocardium
Lining of the inner part of the heart
Simple Squamous
|
|
Mesothelium
Lining of serous cavities
Simple Squamous
|
|
Respiratory Epithelium
Lining of most parts of the Respiratory Tract
Pseudo-stratified Squamous
|
| Nasal Cavity has two epithelium • In upper 1/3 rd of roof
Olfactory Epithelium
• Remaining
Respiratory Epithelium
|
| 1. Covering and lining the surface (By skin) |
| 2. Absorption (From endothelial lining of intestine) |
| 3. Secretion (From gland) |
| 4. Lubrication (From serous cavities i.e Pleural, Peritoneal & Pericardium) |
| 5. Prevent water loss (By skin) |
| 6. Prevent reabsorption (By urinary bladder) |
|
Almost every air-filled cavities/ Air pathway
→ lined by pseudo-stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
|
| Example (Nasal cavity, Trachea, Larynx, Bronchus, Middle ear cavity, Auditory tube) |
|
Exception
• Oropharynx - Both air & food pathway → lined by Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
|
• Respiratory Part of lung (Lung alveoli)
→ lined simple squamous
→ because gases needed to be exchanged between pulmonary blood vessels and lung alveoli.
|
| Area related to the outer external surface, which need extra-large protection |
| like Mouth cavity, Pharynx, Lower part of anal canal and vagina → lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
| Skin → by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
|
• Dry membrane → Keratinized
• Mucous related wet membrane → Non keratinized
|
|
For absorption
→ simple columnar epithelium
|
|
Maximum part of GIT Tract (from the Lower part of esophagus up to the level of the rectum)
→ lined by simple columnar epithelium
|
|
• For Diffusion, Secretory
→ Simple Squamous
|
|
• For Absorption
→ simple columnar
|
|
• Urine related
→ Transitional epithelium
|
|
• Air related
→ Pseudo-stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
|
|
• Protection
→ Keratinized/Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
• Ciliated
→ in the respiratory tract for movement of mucous
→ & in uterine tube for sperm mobility |
|
A/c to the location
Simple squamous epithelium has different names • Endocardium
The lining of the heart (Endocardium) (Innermost layer of the heart) |
|
• Endothelium
The lining of blood vessels & lymph
|
|
• Mesothelium
Lining of serous cavities: Pericardium, pleura, peritoneum
|
|
• Epicardium
Form by Visceral layer of serous pericardium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
|
• Myocardium
By Cardiac Muscle
|
|
• Endocardium
Form by Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
| • In the oral cavity, there is mastication of food so, the oral cavity is lined by non-keratinized squamous epithelium to prevent friction. |
| • Esophagus is lined by this epithelium as the broken food particles pass through the esophagus towards the stomach. |
| • Vocal cord is lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium because the food & particles that accidentally enter the larynx could damage the vocal cord. |
| Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium | Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
| Superficial cells are not living | All cells are living |
| Superficial cells have no nuclei | All cells contain nuclei |
| Surface is dry | Surface is moist |
| Keratin is found | Absent keratin |
| • Upper layer → contains umbrella-shaped cells (dome-shaped) |
| • Middle layer → contains cuboidal a polyhedral cells |
| • Basal cells → are cuboidal/columnar |
|
Opening of both male & female urethra
Lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
As related to the external environment (extra-protection)
|
| Stratified squamous epithelium | Transitional epithelium |
| Numerous superimposed cell layers | Only 4-6 layers of cells |
| Superficial cells are squamous type | Superficial cells are of umbrella (dome-shaped) |
| Don't allow distension & contraction | Allow free distension & contraction |
| Main function is to prevent wear & tear | Main function is to prevent urine absorption |
| Found in moist cavities like oral cavity, tongue, lower pharynx, vagina | Found in urinary tract |
| Stratified (multi-layer): • They are named after the cell type present in the superficial layer (whatever be the cell beneath them) |
Comments (0)