Cell Division
5 years ago 3399
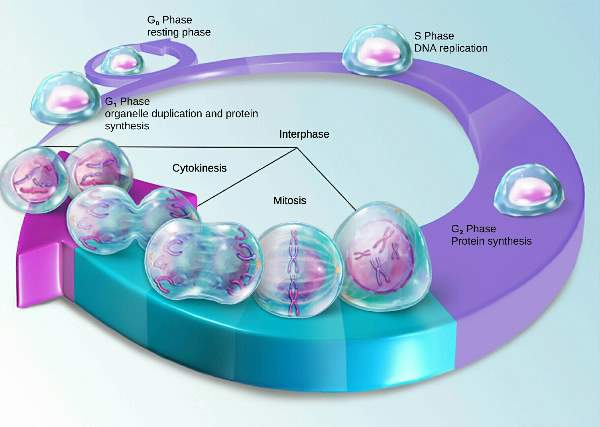
| It is the cyclical sequence of events involving DNA replication and cell division (mitosis) to produce two identical daughter cells. |
| Basically, it is done by duplication of cellular contents (interphase), nuclear division (mitosis) and cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis). |
| - It is the preparatory phase for replication of DNA |
| - Here, transcription (RNA synthesis), translation (protein synthesis). |
| - Act as 1st checkpoint: If any damage has occurred in DNA, then the G1 phase does not go to S-phase for further process. First DNA would repair, then only proceed forward. |
| - Preparatory phase for mitosis with further protein & organelles synthesis occur need for mitosis |
| - Act as 2nd checkpoint: If any error has occurred in replication, then the G2 phase is not proceeding forward to the mitosis phase. |
| - Here nuclear division occurs and cells divide into two daughter cells. |
| - After passing all checkpoints (G1, G2) phase with no error, the mitotic phase occurs. |
| • But it is absent in neurons (Neuron cannot regenerate). |
| Due to the abnormal function of the spindle fibers, one or more chromosomes fail to migrate properly during anaphase. |
| There will be an unequal division of chromosome number in the divided two daughter cells. This abnormality of the chromosome is known as non-dysfunction. |
| In this case, one daughter cell receives extra chromosomes & the other daughter cell has less no. of chromosomes. This leads to monosomy, trisomy. |
Comments (0)