
MRI Scans: Understanding the Differences Between 3T and 1.5T Scanners
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a vital diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the way we understand and treat medical conditions. Among the wide variety of MRI machines available, the 3T (3 Tesla) and 1.5T (1.5 Tesla) MRI scanners are the most commonly used. Their differences, strengths, and limitations play a crucial role in determining which scanner is the right fit for specific medical needs. In this article, we will explore what sets these machines apart, their unique applications, and how they impact patient care.
What is an MRI and Why is it Important?
MRI is a non-invasive imaging technology that uses powerful magnets, radio waves, and a computer to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it safer for repeated use. This makes MRI particularly effective for diagnosing conditions related to the brain, spine, joints, and soft tissues.
The quality and clarity of an MRI scan depend on the strength of the magnetic field, measured in Tesla (T). Higher Tesla ratings indicate stronger magnetic fields, which generally translate to more detailed images. This is where the 1.5T and 3T MRI scanners come into play.
What is a 1.5T MRI Scanner?
A 1.5T MRI scanner operates with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla, which has been the standard for MRI machines for many years. It is widely used in hospitals and diagnostic centers because of its balance between image quality, scan speed, and cost.
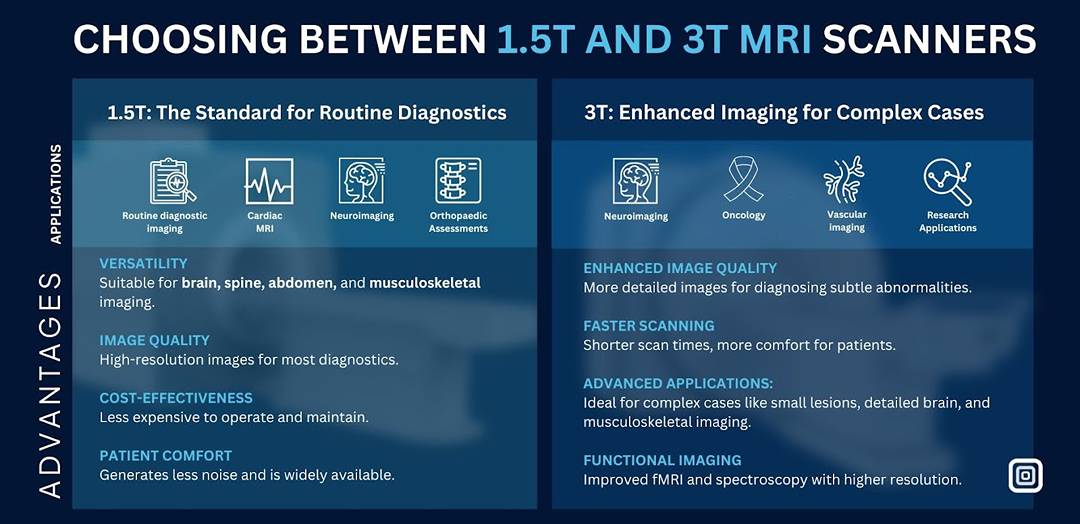
Advantages of 1.5T MRI Scanners
-
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including brain imaging, cardiac scans, and musculoskeletal diagnostics.
-
Accessibility: More affordable and widely available than 3T scanners, making it a practical choice for many healthcare facilities.
-
Reduced Artifacts: Less prone to image distortions caused by metal implants or other artifacts, which is especially important for patients with pacemakers or joint replacements.
-
Comfortable for Patients: Tends to produce less noise and heat, improving the overall patient experience.
Limitations of 1.5T MRI Scanners
- The image resolution may not be as high as that of a 3T scanner, particularly for small or subtle abnormalities.
- Scans may take slightly longer compared to a 3T scanner.
What is a 3T MRI Scanner?
A 3T MRI scanner operates with a magnetic field strength of 3 Tesla, making it twice as powerful as the 1.5T scanner. This higher field strength enhances image resolution and scan speed, making it ideal for more detailed examinations.
Advantages of 3T MRI Scanners
-
Superior Image Quality: Provides higher-resolution images, which are especially valuable for detecting small lesions, brain abnormalities, or subtle changes in soft tissues.
-
Faster Scans: Reduces scan time, which is particularly beneficial for patients who may find it challenging to remain still for extended periods.
-
Advanced Applications: Ideal for specialized imaging, such as functional MRI (fMRI), spectroscopy, and imaging of the inner ear or small blood vessels.
-
Research and Innovation: Frequently used in advanced medical research and clinical trials due to its precision and clarity.
Limitations of 3T MRI Scanners
-
Higher Cost: More expensive to operate and maintain, which can increase the cost of scans for patients.
-
Sensitivity to Artifacts: More prone to artifacts caused by metal implants or patient movement.
- Patient Comfort: The stronger magnetic field can lead to increased noise and heating, which may cause discomfort for some patients.
Comparing 1.5T and 3T MRI ScannersWhen to Choose 1.5T vs. 3T MRI?
The choice between a 1.5T and a 3T MRI scanner largely depends on the specific medical scenario, patient needs, and the resources of the healthcare facility. Here are some scenarios to help guide the decision:
1.5T MRI is Recommended When:
-
General Diagnostics: For routine scans of the brain, spine, joints, and abdomen.
-
Metal Implants: When patients have metal implants, the lower magnetic field reduces the risk of image distortion.
-
Cost Sensitivity: When budget constraints are a concern for the patient or healthcare provider.
3T MRI is Recommended When:
-
Detailed Imaging is Required: For neurological, cardiac, or vascular imaging where higher resolution is critical.
-
Shorter Scan Times: For patients who have difficulty staying still, such as children or individuals with anxiety.
- Research and Complex Cases: For advanced diagnostics and clinical research requiring the highest level of image precision.
Patient Experience: What to Expect During a Scan
Regardless of the scanner used, the process of an MRI scan is generally the same:
-
Preparation: Patients may be asked to remove any metal objects and wear hospital-provided clothing.
-
Positioning: Patients lie on a movable table that slides into the MRI machine.
-
Imaging: The scanner generates images through a series of pulses, which may create loud noises. Earplugs or headphones are often provided.
-
Duration: A typical scan lasts between 15 to 90 minutes, depending on the complexity of the examination.
Patients undergoing a 3T MRI may notice a louder environment and possibly slight warming due to the stronger magnetic field. Technicians are always present to ensure patient comfort and safety.
Future Trends in MRI Technology
MRI technology continues to evolve, with advancements aimed at improving patient comfort, reducing scan times, and enhancing image quality. Innovations like 7T MRI scanners are on the horizon, promising even greater resolution and diagnostic capabilities. However, the balance between cost, accessibility, and practicality will remain crucial in determining widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Both 1.5T and 3T MRI scanners are invaluable tools in modern medicine, each with its own strengths and limitations. The 1.5T scanner remains a reliable and cost-effective choice for general diagnostics, while the 3T scanner excels in providing detailed imaging and faster scans for complex cases. Understanding these differences empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions tailored to individual medical needs.
Whether you are undergoing an MRI for routine diagnostics or advanced imaging, the choice between a 1.5T and 3T MRI is a critical step in ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best option for your specific situation.

Comments (0)