What is Sims Position?
The Sims position, also known as the lateral recumbent position in which the patient lies on one side either the right or left side, lower leg slightly bent or straight, flexion of the hip & knee of the upper leg more toward the chest, and lower arm kept behind the back & upper arm in front with elbow flexion. It is a commonly used position in medical settings for a variety of procedures and examinations. Sims Position is particularly used for rectal examinations, sigmoidoscopy, enemas, and certain surgeries involving the rectum or perineum.
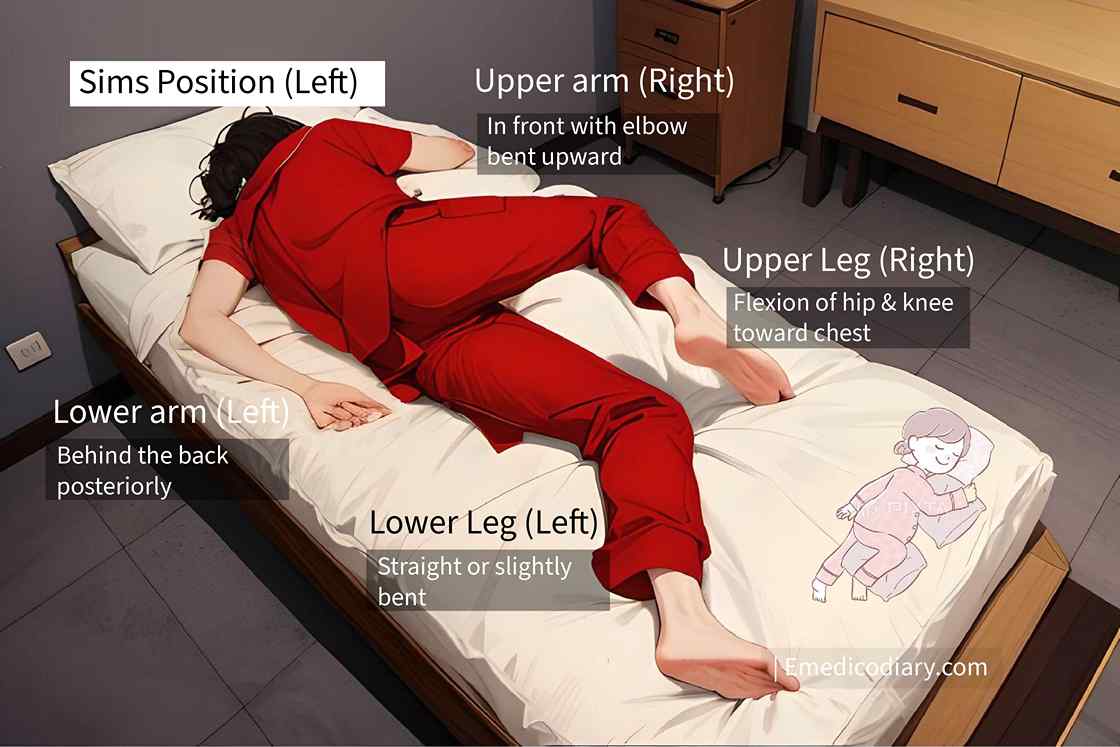
What is the left sims position?
The Left Sims position is the position in which the patient lies on the left side, the left leg slightly bent or straight, flexion of the hip & knee of the right leg more toward the chest, the left arm kept behind the back & right arm in front with elbow flexion.

This is the Sims position diagram (left side) resembling the alphabet H.
How would you place a patient in the sims position?
The procedures of sims position are
- Lie on one side either left or right side.
- Keep the lower arm behind the back posteriorly.
- Keep the upper arm in front with semi flexed elbow.
- Flex the upper leg more toward the chest i.e. semi-flexion of hip & knee joint
- Slightly bend the lower leg.
In the case of the Left Sims position
Procedure of left lateral sims position are:
- Lie the patient on the left side.
- Keep the left arm (lower arm) behind the back posteriorly.
- Keep the right arm (upper arm) in front with semi flexed elbow.
- Flex the right leg (upper leg) more toward the chest i.e. semi flexion of hip & knee joint.
- Slightly bend the left leg (lower leg)

Sims Position Diagram (Left)
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to position a patient in the Sims position:
1. Explain the procedure: Clearly communicate the purpose and process of the procedure to the patient, obtaining informed consent, and addressing any questions or concerns they may have.
2. Prepare the patient: Ask the patient to remove their lower clothing, such as pants or skirts, while maintaining their privacy. Offer a gown or drape for covering and ensure the patient feels comfortable and at ease.
3. Assist the patient: Help the patient lie on side either the left side or right side, facing the edge of the examination table or bed. The patient's body should be straight and aligned with the table, with their knees slightly bent.
4. Position the arms: The patient's uppermost arm should be flexed at the elbow and placed comfortably in front of them. The lower arm should be extended straight below the uppermost arm.
5. Adjust the lower body: Flex the patient's uppermost leg at the hip and knee, placing a pillow or rolled-up towel behind the knee for support. The lowermost leg should remain straight or slightly bent for stability.
6. Align the patient: Ensure the patient's hips and shoulders are squared with the edge of the table or bed, allowing for easier access to the rectal area.
7. Maintain patient comfort: Check with the patient to ensure they are comfortable in the position. Adjust the pillow, towel, or supporting devices as needed to prevent strain or discomfort.
8. Provide privacy and draping: Once the patient is in the desired position, cover them with a sheet or drape, exposing only the area required for the procedure.
Remember, patient comfort, dignity, and privacy should always be prioritized during any medical procedure. Additionally, it is essential to adhere to proper infection control practices, including hand hygiene.
Why is Sims position used?
Sims position is commonly used for Rectal Examination, Sigmoidoscopy, Enema, examination during vaginal wall prolapse. Here are a few examples described in brief.
1. Rectal Examination: The Sims position is commonly used for performing rectal examinations. It allows easy access to the rectal area and facilitates proper visualization and palpation of the rectum and surrounding structures.
2. Sigmoidoscopy: Sigmoidoscopy is a procedure used to examine the lower part of the colon (sigmoid colon) using a flexible tube with a light and camera. The Sims position is often employed to position the patient for sigmoidoscopy, as it allows for easier insertion of the sigmoidoscope and better visualization of the sigmoid colon.
3. Enemas: Enemas involve the introduction of liquid into the rectum and colon through the anus. The Sims position is commonly used to administer enemas, as it facilitates proper positioning of the patient and allows gravity to assist with the flow of the enema solution.
4. Perineal Procedures: The Sims position can be used for various perineal procedures, such as incision and drainage of perianal abscesses or hemorrhoidectomies. It provides optimal exposure and access to the perineal area.
It's important to note that the specific procedures performed in the Sims position may vary depending on the patient's condition, the medical setting, and the healthcare provider's preferences. typically learn about the appropriate positioning for different procedures during their clinical training, and they should always follow the guidance of their instructors and supervising physicians.
What is the Sims position best for?
Sims position is best for administration of enema because it widens the view of perineum & descending colon level is lowered making the fluid easy to flow.
Advantages of Sims position
The Sims position offers several advantages when used for medical procedures. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Accessibility: The Sims position provides optimal access to the rectal area, perineum, and sigmoid colon. It allows for better visualization and palpation of these regions, making it easier to perform procedures such as rectal examinations, sigmoidoscopy, and perineal surgeries.
2. Patient Comfort: The Sims position is generally comfortable for patients, as it allows them to lie on their side with their body aligned and supported. The flexed uppermost leg and the use of pillows or towels provide additional comfort and stability. When patients are comfortable, they are more likely to cooperate during procedures, making the experience smoother for both the patient and the medical person.
3. Safety: Proper positioning of the patient is crucial for ensuring safety during medical procedures. The Sims position helps maintain stability and prevents the patient from rolling or shifting during the procedure. This stability reduces the risk of injury and allows medical students to perform procedures with greater precision and control.
4. Exposure and Visualization: By placing the patient in the Sims position, the relevant anatomical structures are more exposed and visible. This enhanced visibility enables medical person to better identify and assess abnormalities, lesions, or other findings. It also allows for easier insertion of instruments or devices, facilitating procedural success
5. Learning Opportunities: The Sims position provides an ideal learning environment for medical students. It allows them to practice and refine their skills in a controlled setting under the supervision of experienced healthcare professionals. The position also offers a clear view of the procedure, allowing instructors to provide immediate feedback and guidance to help students improve their technique.
6. Versatility: The Sims position is versatile and can be used for various procedures, including rectal examinations, sigmoidoscopy, enemas, and perineal surgeries. One can learn and practice multiple techniques in a single position, enhancing their clinical skills and versatility.
It's important to note that while the Sims position offers advantages for certain procedures, it may not be suitable or necessary for every medical intervention. The choice of patient positioning depends on the specific procedure, patient condition, and healthcare provider's judgment.
Disadvantages of Sims position
While the Sims position has several advantages, there are also a few potential disadvantages associated with its use. These disadvantages include:
1. Limited Exposure: While the Sims position provides good exposure to the rectal area, perineum, and sigmoid colon, it may limit visibility and access to other areas of the body. Some procedures or examinations may require a different position or approach to adequately assess or treat different anatomical structures.
2. Limited Practice Opportunities: Medical students may not always have frequent opportunities to practice procedures in the Sims position due to various factors, such as limited patient availability or specific case requirements. This limited exposure can potentially impact their confidence and proficiency in performing procedures in this position.
3. Patient Discomfort or Embarrassment: Despite efforts to ensure patient comfort, some individuals may find the Sims position uncomfortable or embarrassing. This discomfort or unease can affect their cooperation during the procedure, making it challenging for medical person to perform the necessary steps accurately.
4. Safety Concerns: Improper patient positioning or inadequate support can potentially lead to patient discomfort, strain, or even injury during procedures. It is essential for medical person to receive proper training and supervision to ensure patient safety and minimize the risk of any adverse events.
5. Technical Challenges: Some procedures, such as sigmoidoscopy, may require specific technical skills and coordination to manipulate instruments effectively.
It's important to address these disadvantages by implementing appropriate training, effective communication with patients, and maintaining patient comfort and privacy.
The Sims position, while commonly used in medical practice, has some limitations when it comes to practice for medical students. These limitations include:
• Limited Variability: The Sims position offers a specific set of anatomical landmarks and positioning that may not reflect the diversity encountered in real clinical scenarios. Patients come in various shapes and sizes, and their positioning needs may differ based on their individual anatomy and condition.
• Incomplete Simulation: Simulated patient encounters or practice scenarios using mannequins or standardized patients may not fully replicate the complexity and unpredictability of real patients. While the Sims position can be practiced in a simulated setting, it may not provide the same level of realism as working with actual patients.
• Lack of Communication Skills: The Sims position primarily focuses on the technical aspects of procedures, such as proper positioning and instrument manipulation. However, medical person also need to develop effective communication skills to interact with patients and ensure their comfort, understanding, and cooperation during procedures. These aspects may be limited when practicing in the Sims position alone.
• Limited Exposure to Alternative Positions: While the Sims position is useful for specific procedures, medical students should also be familiar with alternative positions that may be more appropriate for different situations. Being proficient in a range of positions allows for greater adaptability and preparedness in clinical practice.
• Ethical Considerations: In some cases, the use of the Sims position may raise ethical concerns related to patient autonomy, privacy, and informed consent.
A position similar to the Sims position that medical students may learn and practice is the lithotomy position. While there are some differences between the two positions, the lithotomy position also offers advantages for certain procedures. Here's an overview of the lithotomy position:
• Positioning: In the lithotomy position, the patient lies on their back with their buttocks at the edge of the examination table or bed. Their hips are flexed and knees are flexed, with the legs supported in stirrups or leg holders. The feet are positioned above the level of the hips, allowing for better access to the genital and perineal areas.
• Access and Exposure: The lithotomy position provides excellent access and exposure to the genitalia, perineum, and lower reproductive and urinary tracts. This position is often used for procedures such as pelvic examinations, vaginal examinations, gynecological surgeries, and certain urological procedures.
• Patient Comfort and Safety: Patient comfort and safety are important considerations in the lithotomy position. Adequate padding should be provided to support the patient's lower back, buttocks, and legs. Proper positioning and careful attention to patient comfort can enhance cooperation and reduce the risk of discomfort or injury during procedures.
• Visualization and Instrumentation: The lithotomy position allows for improved visualization of the pelvic organs, making it easier for medical students to perform procedures or examinations that require visualization or instrumentation of the vaginal or rectal areas. It facilitates the use of specula, vaginal probes, and other instruments for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
It's important to note that while the lithotomy position has its advantages, it also has limitations and considerations similar to the Sims position.

Comments (0)