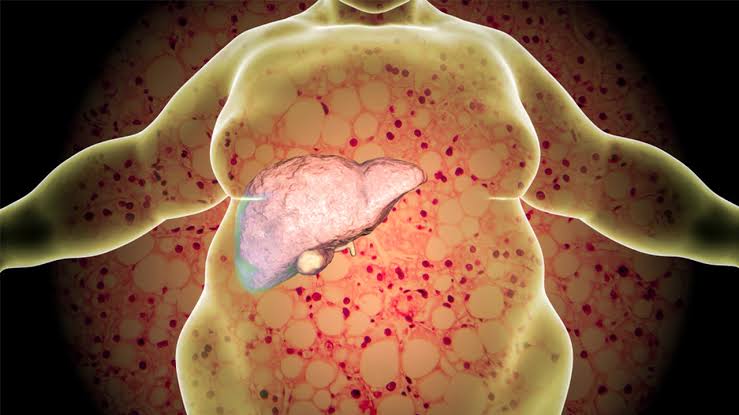
Understanding MASH/MAFLD: Key Causes and Symptoms
MASH/MAFLD (Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can lead to inflammation and scarring of the liver tissue.
This condition is increasing rapidly worldwide and is estimated to affect approximately 25% of the global population. Understanding the key causes and symptoms of MASH/MAFLD is crucial for early detection and management of the condition, as it can progress to more severe forms of liver disease if left untreated. There are various diagnostic processes used to help identify this condition, such as blood tests for fatty liver disease.
Causes of MASH/MAFLD
MASH/MAFLD is caused by a combination of factors, including obesity, metabolic disorders, genetics, medications, toxins, a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and gut microbiota dysbiosis. Understanding the underlying causes of MASH/MAFLD is crucial for its early detection, prevention, and management.
Symptoms of MASH/MAFLD
In the early stages, MASH/MAFLD may not cause any symptoms and is often diagnosed incidentally during routine blood tests or imaging studies.

Copyright: Anna Tarazevich on Pexels | License: CC0 Public Domain
However, as the disease progresses, it can lead to various MASH symptoms, such as
- Fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort
- Enlarged liver
- Jaundice - a yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Mental confusion.
As the condition worsens, it can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, known as ascites. Some patients may also develop liver cirrhosis, which can cause severe complications such as liver failure and liver cancer.
It is essential to be aware of these MASH symptoms, particularly if you have risk factors such as obesity or metabolic disorders, to seek timely medical attention and management.
Diagnosis of MASH/MAFLD
Diagnosing MASH/MAFLD requires a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a liver biopsy.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are an essential part of the diagnostic workup for MASH/MAFLD. Elevated liver enzymes are often seen in individuals with MASH/MAFLD. These enzymes leak into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged or inflamed. In addition to liver enzymes, blood tests can also detect markers of inflammation.

Copyright: Artem Podrez on Pexels | License: CC0 Public Domain
Imaging studies
Imaging studies, such as ultrasound, CT, and MRI, are commonly used to diagnose MASH/MAFLD. They can detect the presence of fat in the liver and assess the extent of liver damage.
Liver Biopsy
Liver biopsy is a diagnostic procedure that involves taking a small sample of liver tissue for examination under a microscope. It is considered the gold standard for confirming the diagnosis of MASH/MAFLD and assessing the extent of liver damage.
A liver biopsy can help differentiate MASH/MAFLD from other liver diseases and can provide information on the severity and progression of the condition. However, liver biopsy has some limitations, including the risk of complications such as bleeding and infection.
Therefore, it is usually reserved for cases where the diagnosis of MASH/MAFLD is uncertain, or the severity of liver disease needs to be assessed. In most cases, a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and imaging studies is sufficient to diagnose and monitor MASH/MAFLD.
Complications of MASH/MAFLD
Complications of MASH/MAFLD can include liver cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer, and other liver-related diseases. As the disease progresses, the liver becomes scarred and loses its ability to function properly. This can lead to serious complications and increase the risk of mortality. Regular monitoring and management of the condition are crucial in preventing or delaying the development of complications.
Management of MASH/MAFLD
The management of MASH/MAFLD involves lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and regular exercise, as well as treatment of underlying conditions, such as diabetes and high cholesterol.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or reduce liver inflammation. The ultimate goal of management is to prevent or slow down the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of complications such as liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Prevention of MASH/MAFLD
Prevention of MASH/MAFLD involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet.

Copyright: Cliff Booth on Pexels | License: CC0 Public Domain
Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption and managing underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and high cholesterol, can also reduce the risk of developing MASH/MAFLD.
Public health strategies, such as education and awareness campaigns and policy changes to promote healthy environments and behaviors, are also important in preventing the development and progression of MASH/MAFLD at the population level.
Key Management and Prevention Strategies for MASH/MAFLD
MASH/MAFLD is a chronic liver disease with fat accumulation. Early management is crucial in preventing progression and complications. Lifestyle modifications, treatment, and monitoring are key. Preventative strategies like healthy habits and public health initiatives are vital to reducing the burden. Consequently, it is necessary to properly understand the causes and symptoms of MASH/MAFLD.

Comments (0)