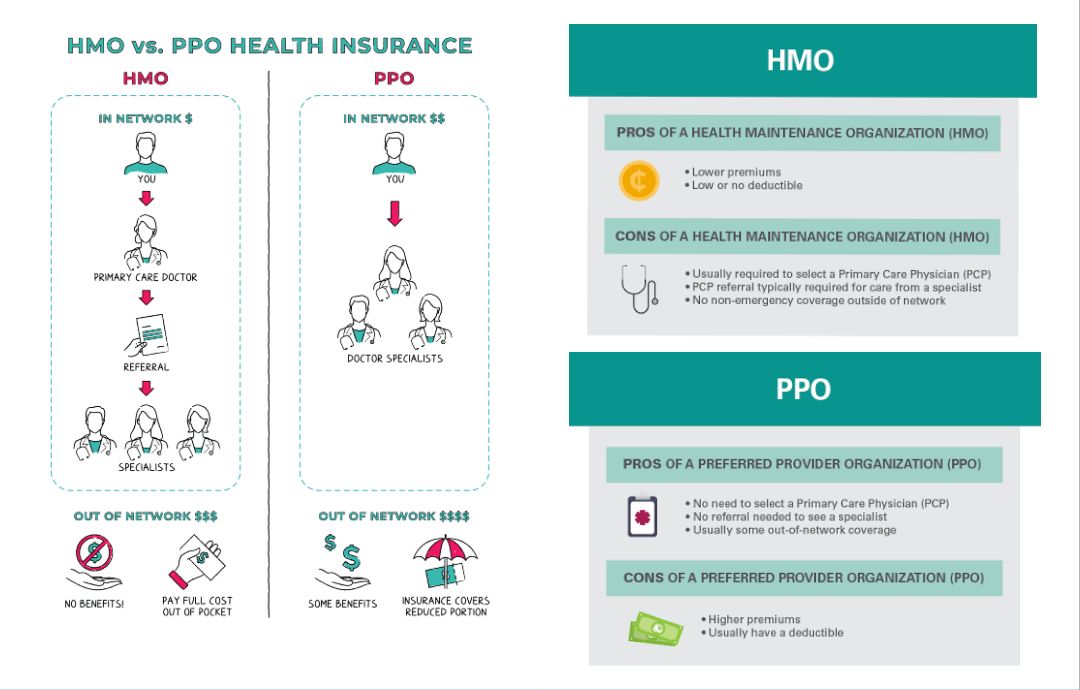
HMO :
HMO stands for Health Maintenance Organization. It is a type of managed healthcare system that provides medical services to members for a fixed fee. HMOs typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as a gatekeeper for all medical services. If specialized care is needed, the PCP refers the patient to specialists within the HMO's network. HMOs often have a network of healthcare providers, such as doctors, hospitals, and clinics, with whom they have negotiated discounted rates for services. Members of an HMO usually pay a monthly premium and may also be required to make co-payments for certain services. The main goal of an HMO is to provide cost-effective healthcare by emphasizing preventive care and reducing unnecessary medical expenses.
PPO :
PPO stands for Preferred Provider Organization. It is a type of managed healthcare system that offers a network of preferred healthcare providers to its members. Unlike HMOs, PPOs provide more flexibility and choice in selecting healthcare providers.
In a PPO, members have the freedom to see any healthcare provider they choose, both within and outside the network. However, there are financial incentives to use in-network providers. When members visit preferred providers within the network, they generally receive higher levels of coverage and pay lower out-of-pocket costs.
PPOs typically do not require members to choose a primary care physician or obtain referrals to see specialists. This allows for more direct access to specialists without needing prior authorization.
Members of a PPO usually pay a monthly premium and may also have an annual deductible and co-payments for certain services. PPOs generally offer a wider range of covered services compared to HMOs, but the premiums may be higher due to the increased flexibility and choice available to members.
HMO vs PPO
HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) and PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) are two different types of managed healthcare systems. Here are some key differences between HMOs and PPOs:
- Provider Network: HMOs have a network of healthcare providers (doctors, hospitals, clinics) that members must choose from for their medical care. Members typically need to select a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates and manages their healthcare. In contrast, PPOs offer a network of preferred providers, but members have the option to see out-of-network providers as well, albeit at higher costs.
- Referrals and Specialists: HMOs generally require members to obtain a referral from their PCP to see a specialist. The PCP acts as a gatekeeper, directing patients to specialists when necessary. PPOs do not typically require referrals, allowing members to directly visit specialists without prior authorization.
- Cost Structure: HMOs usually have lower monthly premiums compared to PPOs. However, HMO members may need to pay co-payments for each visit or service. PPOs often have higher premiums but offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and usually have lower out-of-pocket costs for both in-network and out-of-network services.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: In HMOs, out-of-network services are generally not covered, except in emergency situations or with prior authorization. PPOs, on the other hand, offer partial coverage for out-of-network services, although the member's share of the cost is typically higher than when using in-network providers.
- Coordination of Care: HMOs emphasize coordinated and managed care through the PCP, who oversees the patient's healthcare and referrals to specialists. PPOs offer more autonomy to members in selecting their providers and do not require a PCP to manage their care.
Ultimately, the choice between HMO and PPO depends on individual preferences, such as desired provider flexibility, cost considerations, and the importance of coordination of care. It's important to review the specific details of each plan and consider personal healthcare needs when making a decision.
which one is best hmo vs ppo
Determining the "best" option between HMO and PPO depends on individual circumstances, preferences, and healthcare needs. Here are some factors to consider when evaluating HMOs and PPOs:
- Provider Choice: If having more freedom to choose healthcare providers, including specialists, is important to you, a PPO may be more suitable. PPOs generally have a broader network and allow members to see out-of-network providers, albeit at higher costs. However, if you are comfortable with a more restricted network and prefer a primary care physician managing your care, an HMO may be a good option.
- Cost Considerations: HMOs tend to have lower monthly premiums compared to PPOs. If controlling monthly expenses is a priority, an HMO might be more financially advantageous. However, it's important to consider the potential for higher out-of-pocket costs, such as co-payments for each visit or service, with an HMO. PPOs generally have higher premiums but provide greater flexibility and often have lower cost-sharing for both in-network and out-of-network services.
- Coordination of Care: HMOs emphasize coordinated care through a primary care physician who oversees and manages your healthcare. If you prefer a healthcare system that involves a gatekeeper for specialist referrals and comprehensive care coordination, an HMO may be a good fit. On the other hand, PPOs offer more autonomy in choosing providers and do not require referrals, allowing for direct access to specialists.
- Healthcare Needs: Consider your specific healthcare needs, including the frequency of doctor visits, the need for specialized care, and any existing medical conditions. Evaluate which plan aligns better with those needs. For example, if you require regular specialist visits or anticipate needing out-of-network services, a PPO's flexibility may be more advantageous.
Ultimately, there is no universally "best" option. It's essential to carefully evaluate your healthcare priorities, financial considerations, and desired level of provider choice to determine whether an HMO or PPO is the most suitable fit for your specific circumstances. It can be helpful to review the details of each plan, including the provider networks, cost structures, and covered services, before making a decision.
HMO insurance
HMO insurance, also known as an HMO plan or HMO health insurance refers to a type of managed healthcare plan that operates under the Health Maintenance Organization model. HMOs are structured to provide comprehensive healthcare services to their members within a specific network of healthcare providers.
Here are some key features and characteristics of HMO insurance:
- Provider Network: HMO insurance plans have a network of healthcare providers, including primary care physicians (PCPs), specialists, hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. Members are required to choose a PCP from within the network, who acts as the primary point of contact for their healthcare needs.
- PCP and Referrals: In HMO insurance, members must select a primary care physician (PCP) who manages and coordinates their healthcare. The PCP serves as a gatekeeper for specialist referrals. Generally, members need a referral from their PCP to see a specialist within the HMO network.
- In-Network Coverage: HMO insurance primarily covers services provided by healthcare professionals and facilities within the designated network. Members typically have lower out-of-pocket costs, including co-payments and deductibles, when they use in-network providers.
- Limited Out-of-Network Coverage: HMO insurance plans generally have limited or no coverage for services obtained from healthcare providers outside the network, except in cases of emergency or with prior authorization. Out-of-network services may not be covered, and members may have to pay the full cost.
- Cost Structure: HMO insurance plans often feature lower monthly premiums compared to other types of insurance plans. However, members typically need to pay co-payments for each visit or service, and some plans may also require meeting deductibles before coverage fully applies.
- Emphasis on Preventive Care: HMOs typically place a strong emphasis on preventive care and wellness programs. They often promote routine check-ups, screenings, and preventive services to help members maintain their health and prevent more serious conditions.
It's important to note that the specifics of HMO insurance plans can vary depending on the insurance provider and the region. It's recommended to carefully review the details and terms of the specific HMO insurance plan you are considering to understand its coverage, network, and any limitations or requirements associated with the plan.
PPO insurance meaning
PPO insurance, also known as a Preferred Provider Organization, refers to a type of managed healthcare plan that provides flexibility and choice to its members when selecting healthcare providers. PPO insurance plans allow individuals to receive medical services from both in-network and out-of-network providers, although there are financial incentives to use in-network providers.
Here are some key features and characteristics of PPO insurance:
- Provider Network: PPO insurance plans have a network of preferred providers, including doctors, hospitals, specialists, and other healthcare professionals. Members have the freedom to choose any healthcare provider they prefer, whether they are within the network or outside of it.
- In-Network and Out-of-Network Coverage: PPO insurance offers coverage for both in-network and out-of-network services. In-network providers have negotiated contracts with the insurance company, resulting in discounted rates for services. Out-of-network providers may still be covered, but at a higher cost to the member, often with higher deductibles, co-insurance, or out-of-pocket expenses.
- No Requirement for Referrals: PPO insurance plans typically do not require members to obtain a referral from a primary care physician (PCP) in order to see a specialist. Members can directly seek specialized care without prior authorization.
- Cost Structure: PPO insurance plans generally have higher monthly premiums compared to HMO plans. However, PPO members usually have more flexibility in choosing providers and may have lower cost-sharing when using in-network services compared to out-of-network providers.
- Coordination of Care: PPO insurance plans do not require a PCP to coordinate or manage a member's care. Members have the freedom to visit specialists or receive care directly from any healthcare provider they choose, without needing a gatekeeper for referrals.
- Out-of-Pocket Costs: PPO plans typically have co-payments, deductibles, and co-insurance that members must pay for covered services. The out-of-pocket costs may vary depending on whether the provider is in-network or out-of-network.
It's important to review the specific details of a PPO insurance plan, including the provider network, covered services, and cost-sharing arrangements, to understand its benefits, limitations, and financial implications. This will help you make an informed decision about which plan best suits your healthcare needs and preferences.

Comments (0)