Sleep Cycle
Sleep
It is a physiological process by which bodily functions are periodically rested. There is a loss of critical
reactivity two events in the external environment and subjects can be aroused by sensory stimulation. The study of sleep is known as polysomnography.
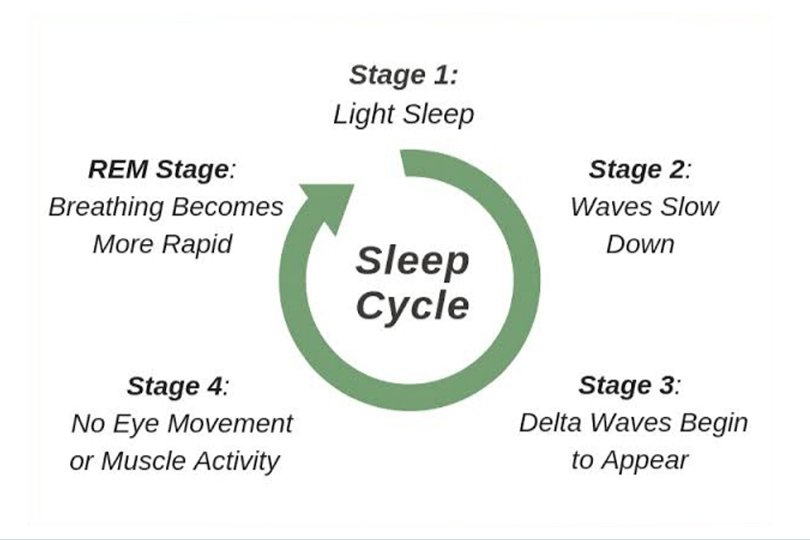
Sleep Cycle
An average sleep Cycle last about 90 minutes ideally. You need four to six cycles of sleep every 24
hours to feel fresh and rested. Each cycle contains four individual stages; Three that form non-rapid eye
movement (NREM) and one rapid eye movement (REM). In general, there are 4 periods of the sleep cycle
where each cycle moves sequentially through every four stages of sleep; wake, light sleep, deep sleep,
REM and repeat. Cycle earlier in the night tends to have more deep sleep while the latter cycle has a higher
proportion of REM. A first sleep cycle is often the shortest ranging from 60 to 90 minutes while the latter cycle
tends to fall between 90 to 120 minutes.
Sleep type
1) Non-Rapid Eye Movement ( NREM):
2) Rapid Eye Movement ( REM)
1) Non-Rapid Eye Movement ( NREM) or Slow Wave sleep :
It takes about 60 to 90 minutes. It is known as slow-wave sleep or somnambulant which is
sleepwalking. It occupies 80% of the sleep cycle. It has four different stages as bellows;
A) Stage 1
In this stage, we have very light sleep which can be easily aroused by moderate
stimulation or lack of awareness. In this stage, alpha waves are reduced in
frequency and amplitude.
B) Stage 2
True sleep – further lack of sensitivity to activation and arousal. Here sleep
spindles may be caused. Sleep spindles mean bursts of regular waves of
frequency 14-15 Hz of a few seconds duration due to reverberation activities
between the thalamus and cerebral cortex.
C) Stage 3
In this stage, sleep deepens. Sleep spindles are now superimposed on a
background of waves of the delta.
D) Stage 4
It has deep sleep. It also has a high threshold of awakening. Activation and
arousal only with vigorous stimulation. When an awakened person doesn’t
report dreaming. High delta waves are produced.
2) Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Or Paradoxical sleep
It occupies about 20 % of the sleep cycle. It is the final stage of the sleep cycle where people
dream. It is also called Paradoxical sleep. Deepest sleep greatest relaxation and difficulty
of arousal therefore can’t easily be aroused by sensory stimulation when awakened
subjects report 80% of the time that they have been dreaming. EEG resembles alter awake
state rapid low voltage, irregular waves called as desynchronized EEG. Hence aca
Paradoxical sleep because the sleeping person is difficult to arouse despite having a
desynchronized EEG that is characteristic of an awake alter state. During this stage, BP and
heart rate increase, and arms and legs are paralyzed so that dreamers can’t come out of
dreams and also increase autonomic activities.
Physiological Changes During Sleep Cycle
I) Heart rate, cardiac output, vasomotor tone, and blood pressure decreases.
II) Tidal volume, respiratory rate, and pulmonary ventilation decrease.
III) Urine volume decreases while specific gravity increases hence more concerned
urine.
IV) Salivary lacrimal secretion decreases but sweat secretion increase
V) Muscle completely relaxed and minimum tone
VI) Deep reflexes are reduced superficial reflexes that remain unchanged.
Event During Sleep Parasomnia
a) NREM sleep Parasomnia
i) Somnambulism – sleepwalking
ii) Sleep talking
iii) Nocturnal enuresis – Bed wetting especially in children
iv) Bruxism – Teeth biting
v) Night terrors
b) REM Sleep Parasomnia
I) Narcolepsy
II) Nightmare
Polysomnography leads a person to know about the following thing
1) Insomnia
Condition of being unable in initiating or maintaining
sleep feeling of the individual in spite of adequate
opportunity for sleep.
2) Narcolepsy
Chronic brain disease which starts with sudden onset
of REM sleep and there is an uncontrolled urge to
sleep during daytime activities with loss of muscle
tone.
3) REM behaviors disorder:
REM sleep is associated with hypertonia therefore a
a person jumps out of bed during sleep and acts out their
dreams.
4) Sleep apnoea
breathing starts and stops while
sleeping.
5) Unusual sleep behaviors –
sleepwalking, moving excessively, rhythmic movement.
6) Periodic limb movement disorder
unconscious extension and flexion of legs.
Some ways to balance the sleep cycle
1) Set a daily same schedule of sleeping and getting
up.
2) Night rituals should be followed like drinking hot
water or milk, taking a bath, using song fragrance,
listening to mild music, going for walks, reading Nobel
and many more.
3) By avoiding drowsiness after meals.
4) Light therapy that is taking a sun bath which
stimulate body hormones and provide good sleep at
night.
5) Daily exercise should not be avoided
6) Free your body from the screen before you sleep.
7) Unhealthy diet causes a problem in our stomach that
disturb the sleep cycle. So eat at least one hour before
bedtime and it should be light and healthy.
8) Use of smoke, alcohol, caffeine, and drugs should be
stopped as it destroy 3rd and 4th sleep cycle.

Comments (0)